Blog Content Overview
- 1 India’s Space Technology Sector: An Industry Overview
- 2 Government Initiatives and Investment Landscape
- 3 Key Participants and Activities
- 4 Regulatory Framework
- 5 Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Policy
- 6 Tax Incentives and Government Schemes
- 7 GIFT City IFSC: A Gateway to Global Markets
- 8 Anticipated Developments
- 9 Conclusion
India’s Space Technology Sector: An Industry Overview
The Indian space sector is currently undergoing a significant transformation, driven by increased private sector participation and substantial government support. With over 523 private companies and research institutions now actively contributing, India’s space economy is projected to reach $44 billion by 2033, capturing nearly 10% of the global market. This manual aims to provide comprehensive insights into the industry overview, investment landscape, legal considerations, tax incentives, and intellectual property rights essential for stakeholders in the space tech ecosystem.
Government Initiatives and Investment Landscape
The government has allocated nearly $1.6 billion for the Department of Space (DoS), which oversees the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and other space-related activities. Since 2014, there has been a notable increase in private investments, particularly in satellite manufacturing and launch services, amounting to $233 million across more than 30 deals by July 2023.
Key Participants and Activities
The Indian spacetech ecosystem comprises a mix of public and private entities working collaboratively to advance the country’s space capabilities. Key activities include:
- Satellite manufacturing
- Launch services
- Space research
- Space-based applications
- Space exploration
- Space debris management
- Commercial spaceflight
- Development of space law and policy
Regulatory Framework
India’s space sector operates under a comprehensive legal and regulatory framework designed to promote innovation and facilitate private sector participation.
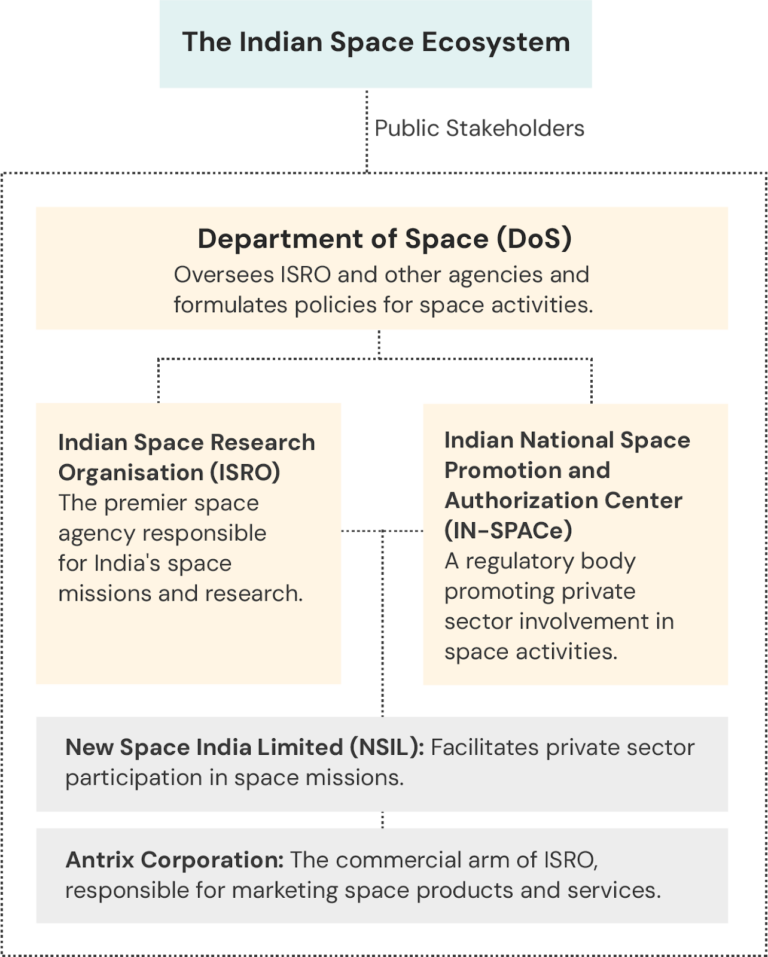
Key regulatory bodies and agencies include:
- Department of Space (DoS)
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe)
- NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)
- Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL)
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Policy
The existing FDI policy allows up to 100% foreign investment in satellite establishment and operation through the government route. Proposed amendments aim to further liberalize the sector, but gaps and ambiguities remain, particularly regarding compliance with sectoral guidelines and definitions of key terms.
Tax Incentives and Government Schemes
To encourage private participation, several tax measures have been implemented, including GST exemptions for satellite launch services and income tax exemptions for R&D expenditures. Key government schemes supporting the sector include:
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme
- Technology Development Fund under DRDO
- iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence)
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM)
GIFT City IFSC: A Gateway to Global Markets
GIFT City (Gujarat International Finance Tec-City) provides a favorable regulatory environment, cutting-edge infrastructure, and a robust ecosystem for space tech companies. It facilitates funding, international collaboration, and regulatory support, making it an ideal gateway for scaling operations and innovation.
Anticipated Developments
The Indian space tech sector is poised for significant growth, driven by increased FDI, public-private partnerships, advanced technologies, and upcoming incentives. The development of reusable launch vehicles and the Gaganyaan mission, slated for 2025, are set to showcase India’s capabilities and bolster its position in the global space community.
Conclusion
India’s space technology sector is at a pivotal moment, characterized by unprecedented growth, innovation, and collaboration. This report serves as a comprehensive guide for industry players, investors, policymakers, and legal professionals navigating the landscape of India’s space tech ecosystem. The combined efforts of public and private entities are driving the sector’s ascent, positioning India as a major player in the global space economy.
We Are Problem Solvers. And Take Accountability.
Related Posts

Compliance Calendar – December 2025 (Checklist & Deadlines)
Sync with Google Calendar Sync with Apple Calendar Staying compliant is not optional it is a legal and financial necessity....
Learn More

New Labour Law in India 2025 – Complete Guide to New Labour Codes
DOWNLOAD PDF India has introduced a historic regulatory change with the new labour law in India 2025. For the first...
Learn More














