Page Contents
With the increasing awareness and hype surrounding Cryptocurrency, NFTs, and other Digital Currencies, understanding the concept of Blockchain Technology has become crucial. Blockchain technology is a distributed digital ledger that records data, documents, and transactions securely and transparently.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology:
- Decentralized: Blockchain allows for a decentralized network composed of multiple nodes or participants. This ensures the network is secure and minimizes the risk of malicious interference while providing financial sovereignty and democratic control to participants.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P): Blockchain technology leverages the power of P2P networks to provide a shared and reliable ledger of transactions. All nodes carry out the same tasks equitably without the presence of a central administrator.
- Transparency: Blockchain makes transaction history more transparent, as all nodes on the network share a copy of the document, enabling all users to see updated records.
- Security: Blockchain is superior to any other recording system, as it ensures all documents of transactions are updated or altered by consensus by the nodes in the network. This decentralized storage of information ensures that no individual holds the right to update records.
- Efficiency: Blockchain streamlines transactional processes through traditional paperwork, minimizes the risk of error, eliminates the involvement of third-party beneficiaries, and makes transactions efficient and faster.
How Blockchain Technology Works:
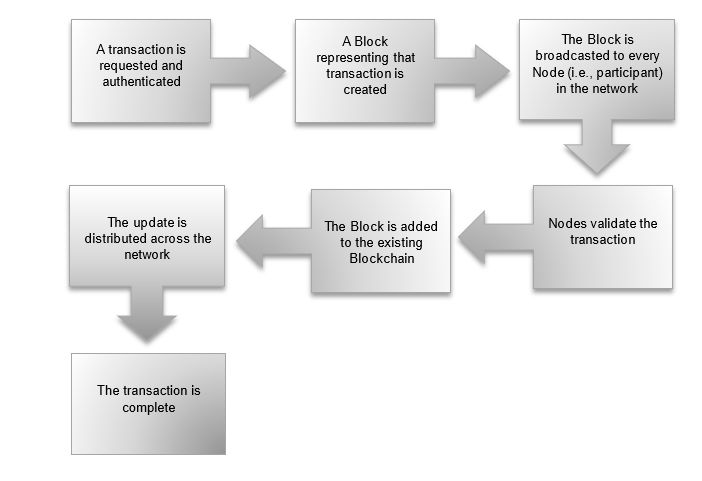
Blockchain technology is the concept of digitally storing data in the most transparent, secure, and efficient way. The data is recorded on blocks and chained together cryptographically to create an unalterable digital ledger. Each participant on the Blockchain network has access to the entire database and its history, ensuring transparency, security, and efficiency. Let us now try to understand the working of the Blockchain technology from the flowchart below:
Types of Blockchains:
- Public Blockchain: Also known as Permissionless Blockchains, Public blockchains are open networks that allow anyone to participate in the network. The data on a public blockchain is secure as it is not possible to modify the data or interfere with the same once it is validated on the blockchain.
- Private Blockchain: Private blockchains, also known as authorized blockchains, are managed by the network administrator and only a single organization has authority over the network.
Potential Use Cases:
- Cryptocurrency: The most well-known use of Blockchain Technology is for cryptocurrency exchanges. When people exchange or spend cryptocurrency, the transactions are recorded on a blockchain, with each block representing a separate transaction that is validated by the participants in the network.
- Financial Exchanges: Blockchains can also be used for traditional exchanges to allow for faster and less expensive transactions. Decentralized exchanges provide better management and security because investors do not have to deposit their assets with a central authority.
- Banking: Blockchain may be used to process transactions in fiat currency such as dollars and euros to make such transfers secure, quick, and more economical, especially for processing cross-border transactions.
- Insurance: Using smart contracts on the blockchain can increase the transparency of customers and insurers. Recording all claims on the blockchain would prevent duplicate claims for the same event and speed up the process for applicants to receive payments.
- Lending: Smart contracts built on the blockchain allow for secure lending, triggering the payment of services, margin calls, full repayment of loans, the release of collateral, etc. on the happening of certain events.
- Real Estate: By recording real estate transactions using blockchain technology, a safer and more accessible way to identify and transfer real estate can be provided, speeding up transactions, reducing paperwork, and saving costs.
- Healthcare: Blockchain can be used to protect medical records, health records, and other related electronic records, ensuring that medical professionals have accurate and up-to-date information about their patients and improve treatment.
Drawbacks of Blockchain Technology:
- Power Consumption: The power consumption in the blockchain is high due to mining activities, maintaining a real-time ledger, and communicating with other nodes.
- Scalability: The size of the block equals the data it stores, which poses serious difficulties for practical use, as each participant node needs to verify and approve a transaction.
- Storage: Blockchain databases are stored indefinitely on all network nodes, causing storage space issues.
- Privacy and Security: The public blockchain is not entirely secure as anyone on the network can legally access data, leading to privacy concerns.
- Regulations: Regulatory regimes in the financial arena are a challenge for blockchain implementation, as blockchain applications need to establish a process to identify the culprit in the event of a scam.
In conclusion, Blockchain Technology is a powerful tool with numerous potential use cases and benefits, especially in the rapidly growing field of Cryptocurrency, NFTs, and digital currencies. However, there are also drawbacks to be considered, such as power consumption, scalability, storage, privacy and security, and regulatory challenges. Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of blockchain technology make it an important development to watch as it continues to evolve and adapt to new regulatory regimes. As the world becomes more technologically advanced, it is essential to stay informed about the latest developments in blockchain technology, as it has the potential to revolutionize how we store and exchange data in the future.
FAQs about Blockchain Technology
- What are the main benefits of using blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology offers several benefits, including decentralization, transparency, security, and efficiency. By providing a decentralized network, blockchain ensures that the network is secure and minimizes the risk of malicious interference while giving participants control and financial sovereignty. Additionally, blockchain offers transparency by making transaction history more visible to all participants, and it provides security by ensuring that documents of transactions are updated or altered by consensus by the nodes in the network.
- How is blockchain technology different from traditional database technology?
Blockchain technology differs from traditional database technology in several ways. First, blockchain is a distributed ledger that is shared among participants in a decentralized network, while traditional databases are often centralized, controlled by a single party or authority. Additionally, blockchain is more secure due to its decentralized nature, while traditional databases are more vulnerable to malicious interference. Lastly, while traditional databases require specific permissions to access and modify data, blockchain enables participants to access records while maintaining security and transparency.
- How does blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies work together?
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies work together as blockchain is the underlying technology that allows cryptocurrencies to operate securely, transparently, and efficiently. Each cryptocurrency uses a specific blockchain to record transactions, where each transaction is verified and then added to a new block in the chain.
- Can blockchain technology be used in industries beyond finance?
Yes, blockchain technology has a wide range of potential applications beyond finance, including industries like healthcare, insurance, supply chain management, and more. For example, blockchain technology can be used to protect medical records, ensuring that medical professionals have accurate and up-to-date information about their patients.
- How do you ensure the security of blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is inherently secure due to its decentralized nature, making it incredibly difficult for malicious actors to interfere with the network. Additionally, several other security measures can be taken to make sure blockchain technology is secure, such as encrypting data, using multi-factor authentication, and implementing measures to prevent unauthorized access to the network.
Disclaimer:
The content of this article is for information purpose only and does not constitute advice or a legal opinion and are personal views of the author. It is based upon relevant law and/or facts available at that point of time and prepared with due accuracy & reliability. Readers are requested to check and refer to relevant provisions of statute, latest judicial pronouncements, circulars, clarifications etc before acting on the basis of the above write up. The possibility of other views on the subject matter cannot be ruled out. By the use of the said information, you agree that the Author / Treelife is not responsible or liable in any manner for the authenticity, accuracy, completeness, errors or any kind of omissions in this piece of information for any action taken thereof.