Blog Content Overview
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What Is ESG Compliance? (And What It Isn’t)
- 3 Who Does ESG Compliance Apply to in India?
- 4 The ESG Regulatory Framework in India (2026 Update)
- 5 BRSR vs. Voluntary ESG Reporting
- 6 How ESG Affects Fundraising, Due Diligence & Exit Readiness
- 7 ESG Compliance Checklist for Founders
- 8 Common ESG Mistakes Companies Make
- 9 ESG Implementation Roadmap for Founders
- 10 Why ESG Compliance Is Strategic, Not Just Regulatory
AI Summary
ESG compliance in India has evolved drastically, becoming essential for all large listed companies, startups, and foreign enterprises by 2026, driven by SEBI's BRSR framework. This guide outlines the nuances of ESG—Environmental, Social, and Governance—and distinguishes it from CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility). Founders must recognize that even if they aren't legally bound to report, investors increasingly weigh ESG factors in investment decisions. BRSR mandates comprehensive reporting, while BRSR Core requires independent assurance on key performance indicators. Companies are urged to integrate ESG principles early to avoid regulatory hurdles in funding and exits. Ensuring ESG readiness is not just about compliance; it enhances investor confidence, operational efficiency, and market access, ultimately benefiting valuation and long-term business sustainability.
Introduction
ESG used to be something listed enterprises stuck into their annual reports. In 2026, that’s no longer true. ESG compliance in India is now relevant across the board for large listed companies navigating SEBI’s BRSR Core requirements, for growth-stage startups managing their first institutional round, and for foreign companies entering the Indian market. If you’re a founder, understanding the ESG landscape isn’t optional it directly shapes how investors assess your business.
This guide covers what the law actually requires, who it applies to, where voluntary disclosure ends and mandatory reporting begins, and most practically what you should do now to build ESG readiness into your company’s foundation.
What Is ESG Compliance? (And What It Isn’t)
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) is a framework for measuring a company’s impact and conduct. Environmental covers carbon emissions, energy, water, and climate risk. Social covers employee welfare, supply chain ethics, and diversity. Governance covers board composition, transparency, anti-corruption practices, and decision-making quality.
ESG compliance in India, strictly defined, means adhering to regulations set by SEBI, MCA, and related authorities that govern how companies must measure, report, and demonstrate ESG performance. This is distinct from voluntary sustainability reporting, ESG ratings, and CSR spending which are related but separate concepts.
| Founder’s Distinction to Know: CSR ≠ ESG. CSR (under Companies Act Section 135) is a spending mandate eligible companies must allocate 2% of average net profits. ESG is a reporting and governance discipline it requires measuring, disclosing, and improving performance across environmental, social, and governance metrics. You can spend generously on CSR and still fail ESG diligence. |
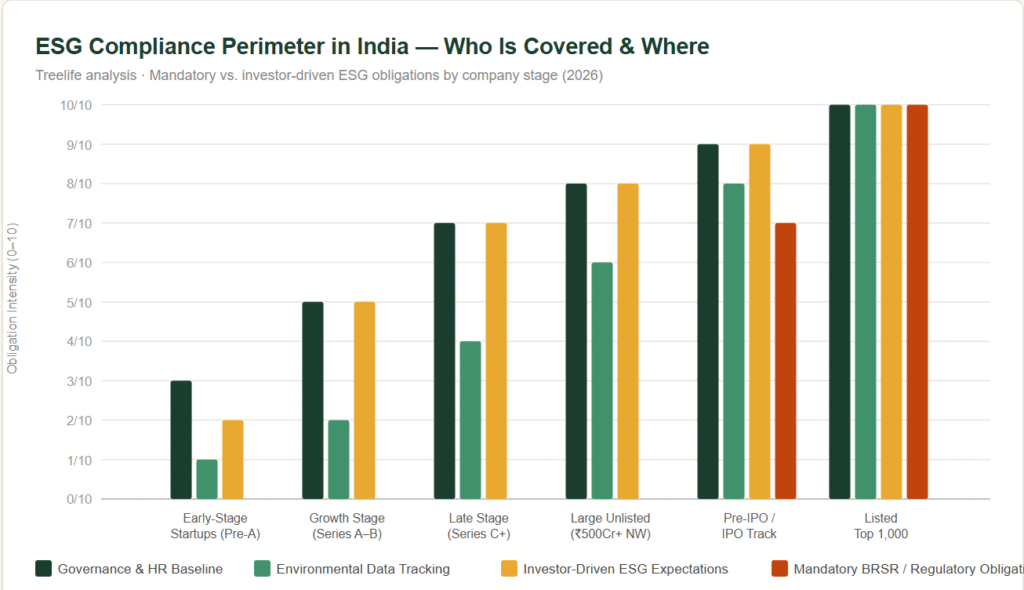
Who Does ESG Compliance Apply to in India?
There are mandatory obligations primarily driven by SEBI and investor-driven expectations that function as soft requirements even where the law doesn’t mandate disclosure.
| Entity Type | Mandatory BRSR? | CSR Mandate? | ESG in Practice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top 1,000 listed companies (by market cap) | Yes — since FY 2022-23 | If eligible | Full BRSR + BRSR Core assurance |
| Listed companies beyond top 1,000 | Voluntary (expanding) | If eligible | Phased mandatory expansion expected |
| Large unlisted (₹500Cr+ net worth) | No (yet) | Yes | PE/investor ESG diligence is common |
| Growth-stage startups (Series A-C) | No | Usually no | Investor-driven ESG expectations apply |
| Foreign entities entering India | Depends on structure | If subsidiary qualifies | Global ESG commitments cascade down |
| Companies on IPO track | Yes from listing | If eligible | ESG readiness is part of pre-IPO checklist |
The important nuance for founders: even if you are not legally required to file a BRSR today, your Series B or Series C investors especially those backed by global LPs almost certainly have internal ESG policies that affect how they evaluate and structure deals. ESG readiness is becoming a fundraising requirement before it becomes a regulatory one.
The ESG Regulatory Framework in India (2026 Update)
SEBI and the BRSR Framework
The most significant ESG regulatory development in India remains SEBI’s Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) framework, introduced in 2021 and made mandatory for the top 1,000 listed companies from FY 2022-23 onward. BRSR replaced the earlier Business Responsibility Report (BRR) with far more granular reporting requirements.
BRSR requires companies to report across three sections: Section A covers general company disclosures; Section B covers management and process disclosures across the nine National Guidelines on Responsible Business Conduct (NGRBCs); Section C covers principle-wise performance indicators split between essential (mandatory) and leadership (aspirational) disclosures.
BRSR Core: The 2023 Addition That Matters
In 2023, SEBI introduced BRSR Core a distilled set of KPIs across nine ESG attributes that require independent third-party assurance. Companies can no longer simply self-declare their ESG performance on these parameters. The nine BRSR Core attributes are:
| # | BRSR Core Attribute | Category |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions — Scope 1, 2, and 3 | Environmental |
| 2 | Water Consumption & Intensity | Environmental |
| 3 | Energy Consumption & Intensity | Environmental |
| 4 | Waste Generated & Management | Environmental |
| 5 | Employee Health & Safety Metrics | Social |
| 6 | Gender & Social Diversity in Pay & Workforce | Social |
| 7 | Job Creation in Smaller Districts & Towns | Social |
| 8 | Openness of Business (Anti-Corruption) | Governance |
| 9 | Supplier & Customer Engagement (Fair Practices) | Governance |
BRSR Core assurance was phased in from FY 2023-24 for the top 150 listed companies, expanding to the top 250 from FY 2024-25, with further expansion expected. SEBI has also indicated it may introduce value chain reporting obliging large companies to collect ESG data from key suppliers which would significantly expand the compliance perimeter.
| 2026 Development to Watch: SEBI is reviewing whether to extend BRSR mandatory requirements beyond the top 1,000 listed entities, and is separately consulting on ESG Rating Providers (ERPs) regulation. If you are on an IPO track or being acquired by a listed entity, ESG disclosure will apply to you sooner than you may expect. |
Companies Act, 2013 – CSR as the Governance Floor
Section 135 mandates CSR spending for companies with a net worth of ₹500 crore or more, a turnover of ₹1,000 crore or more, or a net profit of ₹5 crore or more in any preceding financial year requiring 2% of average net profit to be spent on Schedule VII activities. MCA has been tightening CSR compliance; unspent amounts must be transferred to specific government funds, and companies must file CSR-2 forms disclosing activities in detail.
Other Applicable Regulations
The Environmental Protection Act, 1986, and rules under it form the hard environmental compliance floor for businesses with direct environmental footprints. POSH, the Factories Act, and the Code on Wages are the social compliance floor. POSH compliance in particular is increasingly reviewed in investor due diligence.
BRSR vs. Voluntary ESG Reporting
Many companies adopt voluntary ESG frameworks before mandatory BRSR obligations kick in or alongside them for richer disclosures.
| Framework | Type | Who Uses It | India Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| BRSR | Mandatory (top 1,000) | Listed companies | Primary regulatory standard |
| GRI | Voluntary | MNCs, large Indian cos | Globally recognized; maps to BRSR |
| TCFD | Voluntary | Finance-sector heavy | Relevant for companies with global investors |
| SASB | Voluntary | US-investor-backed cos | Used in cross-border due diligence |
| CDP | Voluntary | Climate-focused | Growing with net-zero commitments |
For most Indian startups and growth-stage companies, voluntary reporting even a simple internal ESG data tracker is the right starting point. Mapping it to BRSR or GRI categories from the outset means you won’t need to rebuild your data infrastructure when mandatory obligations arrive.
How ESG Affects Fundraising, Due Diligence & Exit Readiness
This is where ESG gets directly relevant for founders not yet thinking about regulatory compliance. ESG is now a deal-shaping variable in Indian venture and private equity markets particularly for funds with global LPs subject to European or US sustainability disclosure rules.
What Investors Are Actually Looking For in ESG Diligence
- Governance foundations: Clean cap table, board composition, independent oversight, documented related-party transactions, compliant ESOP plans.
- Employee practices: POSH policy and ICC in place, standardized employment contracts, PF/ESIC/gratuity current, diversity metrics tracked.
- Environmental footprint: For most software companies this is light. For manufacturing, consumer goods, or logistics emissions, waste, and compliance history are material.
- Data governance: PDPB-aligned data privacy policies. Increasingly treated as a governance metric.
- Supply chain: For B2B companies with manufacturing or outsourcing exposure responsible sourcing policies and fair supplier contracts.
| ESG in Exit Transactions: In M&A and secondary transactions, ESG gaps discovered late in due diligence often result in price adjustments, escrow holdbacks, R&W requirements, or deal failure. Companies that have clean ESG documentation command smoother exits and better terms. |
ESG Compliance Checklist for Founders
Governance
- Board composition documented independent directors where applicable
- Related-party transactions logged and board-approved
- Cap table maintained and share certificates issued correctly
- ESOP plan established, compliant, and documented
- Annual board and shareholder meetings held and minutes maintained
- Anti-bribery and anti-corruption policy in writing
- Whistleblower mechanism in place
- Data protection / privacy policy aligned with PDPB requirements
Social / HR
- POSH policy in place and Internal Complaints Committee (ICC) formed
- Standardized, legally reviewed employment contracts
- PF, ESIC, and gratuity contributions current
- Leave, maternity/paternity policies documented
- Pay equity data tracked internally
- Diversity metrics (gender, differently-abled) tracked
- Employee health and safety policy in place
- Contractor/third-party workforce covered by compliant agreements
Environmental
- Energy consumption tracked (office/operations)
- Waste generation and disposal documented
- Carbon footprint estimate available (Scope 1 and Scope 2 at minimum)
- Environmental clearances current (for manufacturing/physical operations)
- Supplier environmental due diligence (for supply-chain heavy companies)
Regulatory Filings
- MCA annual filings current (AOC-4, MGT-7)
- GST filings current
- CSR-2 filed if CSR obligations are triggered
- FEMA / RBI filings current if foreign investment received
- BRSR filed (if in top 1,000 listed companies)
- BRSR Core assurance obtained (if in top 150-250 companies)
Common ESG Mistakes Companies Make
1. Treating ESG as a marketing function, not a governance function
ESG reports drafted by the marketing team without underlying data infrastructure or board oversight create legal liability in due diligence not just reputational risk. ESG has to be owned at the CFO and board level.
2. Confusing CSR spend with ESG compliance
A company can donate generously and file its CSR-2 on time while having a board with zero independent directors, POSH non-compliance, and no environmental data. CSR activity does not substitute for governance, environmental, and HR compliance disciplines.
3. Starting data collection too late
BRSR Core requires historical baseline data going back at least two years. Companies that start tracking only when a compliance deadline looms are forced into estimation, which raises assurance red flags. Data collection should start at the pre-Series B stage.
4. Ignoring value chain obligations
As SEBI moves toward value chain disclosures, companies that haven’t started engaging suppliers on ESG metrics will face last-minute scrambles. For complex supply chains, this is a 12-18 month program, not a form-filling exercise.
5. Treating POSH as a checkbox
POSH non-compliance no ICC, no policy, no training records is one of the most common investor diligence findings in Indian startups. Beyond legal exposure, it signals deeper cultural and governance weaknesses. It is also easily preventable.
6. Assuming ESG doesn’t apply until listing
Investor ESG expectations precede listing by several years. Growth-stage companies being evaluated by institutional investors particularly those with global LP bases face ESG diligence questions well before any IPO consideration.
ESG Implementation Roadmap for Founders
| Stage | Focus Area | Key Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Series A | Governance Foundations | Clean cap table, ESOP plan, POSH policy & ICC, employment contracts, board minutes, related-party documentation. |
| Series A–B | Data Baseline | Start tracking energy, headcount diversity, safety incidents. Establish Scope 1 & 2 GHG baseline. Begin responding to investor ESG questionnaires. |
| Series B–C | Framework Alignment | Map internal tracking to BRSR or GRI categories. Draft first internal ESG report. Engage Virtual CFO to own the process. |
| Pre-IPO / Large Unlisted | BRSR Readiness | Begin BRSR-format disclosure prep. Close BRSR Core data gaps. Engage assurance provider early. Brief board on ESG obligations. |
| Listed Entity | Full Compliance | File mandatory BRSR. Obtain BRSR Core assurance. Publish standalone sustainability report. Engage ESG rating agencies proactively. |
Why ESG Compliance Is Strategic, Not Just Regulatory
- Investor Confidence: ESG-ready companies close institutional rounds faster with fewer surprises in diligence.
- Access to Capital: Green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, and DFI funding are available only to companies with credible ESG track records.
- Operational Efficiency: Energy tracking and waste reduction initiatives consistently surface cost savings founders didn’t know existed.
- Talent & Culture: Top-tier talent increasingly evaluates employers on ESG dimensions. Strong governance is a recruitment advantage.
- Market Access: EU buyers now apply ESG requirements to Indian suppliers. BRSR readiness facilitates international B2B relationships.
- Valuation Premium: ESG-aligned companies in comparable M&A and IPO transactions consistently command measurable premiums.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on ESG Compliance in India
-
What is ESG compliance and why is it important for businesses in India?
ESG compliance refers to a company’s adherence to Environmental, Social, and Governance standards, ensuring it operates sustainably, ethically, and transparently. In India, ESG compliance is becoming increasingly important as investors, consumers, and regulators demand businesses to prioritize sustainability and responsible corporate practices. By aligning with ESG principles, businesses can improve their reputation, attract investment, and ensure long-term success.
-
What are the key ESG regulations in India?
In India, key ESG regulations include the Companies Act, 2013, which mandates Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) for certain companies, and SEBI’s BRSR framework, which requires listed companies to disclose their ESG performance. Additionally, the Environmental Protection Act, 1986 lays down rules for environmental compliance. These regulations aim to ensure businesses meet sustainability goals and contribute positively to society.
-
How does the BRSR framework affect ESG reporting in India?
The BRSR framework, introduced by SEBI, mandates that the top 1000 listed companies disclose detailed information on their ESG performance. It enhances transparency and helps businesses align with global sustainability standards. The framework ensures companies report on key aspects like carbon emissions, water usage, and employee welfare, driving accountability and improving investor confidence.
-
What are the benefits of ESG compliance for Indian businesses?
ESG compliance offers several benefits for Indian businesses, including:
- Enhanced reputation: Companies that adopt sustainable practices improve their brand image and build customer trust.
- Investor attraction: Strong ESG performance appeals to investors focusing on sustainability, opening doors to capital and favorable financing terms.
- Operational efficiency: Implementing ESG initiatives helps businesses reduce costs through improved resource management and waste reduction.
-
How can ESG compliance impact access to capital for businesses?
ESG compliance can significantly improve access to capital. As investors increasingly prioritize sustainability, companies with strong ESG performance are more likely to attract funding from ESG-focused investment funds. This opens up opportunities for green financing and sustainable investment, ensuring businesses have the financial resources to grow while maintaining ethical and sustainable practices.
-
How is ESG integrated into business strategy in India?
Indian companies are increasingly integrating ESG principles into their core business strategies. This includes adopting sustainable business models, improving corporate governance, and aligning operations with social responsibility goals. By embedding ESG factors into their strategy, companies can improve their long-term viability, meet regulatory requirements, and attract ethical investors.
-
What is the future of ESG compliance in India?
The future of ESG compliance in India is set to evolve with stronger regulations and an increasing focus on sustainability. Regulatory bodies like SEBI are expected to introduce more comprehensive ESG disclosure requirements, while businesses will integrate sustainability and social responsibility more deeply into their strategies. Companies that proactively adopt these changes will be better positioned to succeed in a market that values transparency and ethical business practices.
-
How does ESG impact the reputation of companies in India?
Adopting ESG principles enhances a company’s reputation by demonstrating its commitment to sustainability and ethical governance. As consumers become more conscious of environmental and social issues, companies with strong ESG practices gain a competitive edge. A positive brand image and consumer trust are key benefits of integrating ESG strategies into business operations.
-
What is the BRSR, and which companies must file it?
The Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR) is SEBI’s mandatory ESG disclosure framework. The top 1,000 listed companies by market capitalization must file a BRSR as part of their Annual Report from FY 2022-23. It requires detailed disclosures on environmental impact, social practices, and governance. SEBI has been progressively expanding BRSR scope.
-
Does ESG compliance apply to startups in India?
Not in the mandatory regulatory sense BRSR is currently mandatory only for the top 1,000 listed companies, and CSR obligations only kick in at defined thresholds. However, institutional investors especially those backed by global LPs routinely assess ESG readiness during due diligence from Series A onwards. Startups that build ESG foundations early face fewer issues at fundraise and exit stages.
-
What is BRSR Core, and how is it different from BRSR?
BRSR Core is a subset of BRSR consisting of nine key ESG performance indicators that require independent third-party assurance companies cannot self-declare these. It was mandated for the top 150 listed companies from FY 2023-24, expanding to the top 250 from FY 2024-25, with further expansion expected.
-
What is the difference between CSR and ESG in India?
CSR under Section 135 of the Companies Act is a spending mandate eligible companies must allocate 2% of average net profits to social/environmental causes. ESG is a measurement, reporting, and governance discipline it requires tracking, disclosing, and improving performance across defined parameters. You can fulfil your CSR obligation and still have poor ESG performance.
-
How do investors assess ESG during due diligence in India?
Investors assess governance (board structure, related-party transactions, ESOP compliance, cap table hygiene), social/HR compliance (POSH, employment contracts, PF/ESIC, diversity), environmental data (energy, waste, emissions), and regulatory compliance history. ESG gaps discovered late in the process often result in price reductions, R&W requirements, or deal conditions.
-
What are the penalties for non-compliance with BRSR?
Listed companies that fail to file a BRSR face penalties under SEBI (LODR) Regulations, including fines and potential suspension of trading in securities. For CSR non-compliance, MCA can levy penalties under the Companies Act. Beyond regulatory penalties, the larger risk is reputational damage and investor confidence erosion.
We Are Problem Solvers. And Take Accountability.
Related Posts

The Reverse Flip Playbook – For Indian Founders
DOWNLOAD PDF The landscape for Indian startups has fundamentally shifted. A growing number of founders are making a deliberate choice...
Learn More

Angel Tax Exemption – Eligibility, Declaration, How to Apply
The angel tax, introduced by Section 56(2)(viib) of the Income Tax Act, 1961, applies to unlisted companies (startups whose shares...
Learn More

ESOP Taxation in India – A Complete Guide for Founders (2026)
Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOPs) have become an essential tool for businesses, especially startups and growth-stage companies, to attract, retain,...
Learn More











