- Introduction
CARO 2020 is a new format for the issue of audit reports (attachment to the primary report) in case of statutory audits of eligible companies under the Companies Act, 2013. CARO 2020 has included additional reporting requirements after consultations with the National Financial Reporting Authority (an independent regulatory body for regulating the audit and accounting profession in India) as compared to CARO 2016.
The primary aim of CARO is to enhance the overall quality of reporting and disclosure of overall material matters of the Company by the company auditors.
- Effective date
CARO, 2020 is applicable for the Financial years commencing on or after 1st April 2020.
(earlier it was applicable from 1st April 2019)
- Applicability
There are no changes proposed in the applicability section of CARO, 2020. It applies to all companies (including exceptions) as per the previous CARO, 2016. We have listed down below the category of such companies to have a ready reference.
CARO, 2020 applies to all companies including foreign companies, except:
- Banking company;
- Insurance company;
- Company licensed to operate under Section 8 of Co. Act, 2013;
- Small Company;
- Private Limited Company, not being a subsidiary or holding of public company, having:
- Paid up capital and Reserves & surplus not more than 1 Crore as on balance sheet date;
- Borrowing not exceeding 1 Crore from bank/financial institution at any point of time during financial year;
- Revenue not exceeding 10 Crore during financial year as per the financial statements
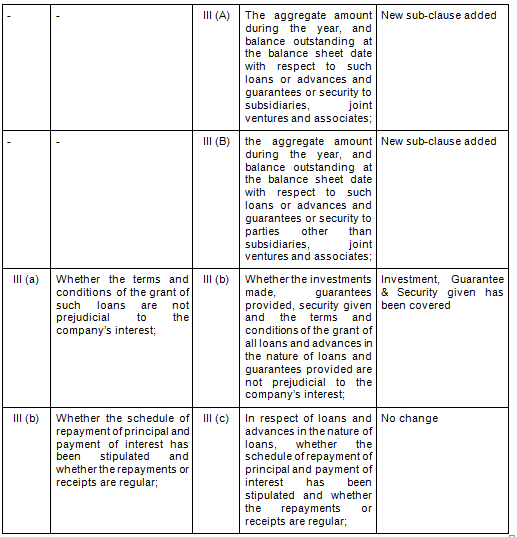
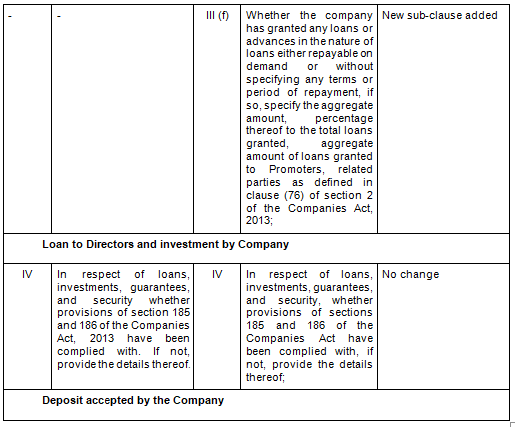
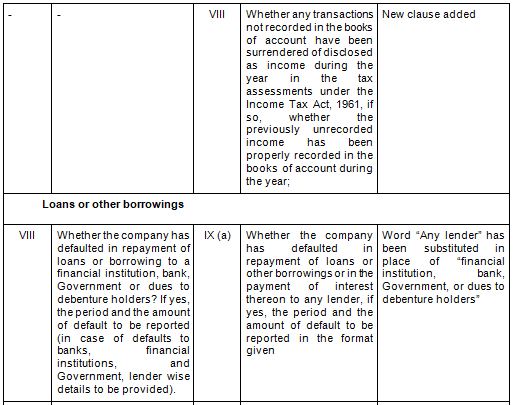
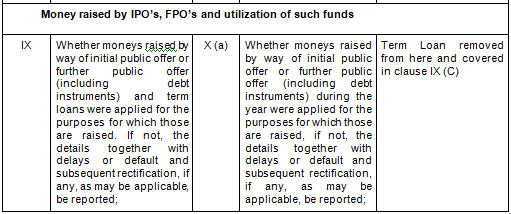
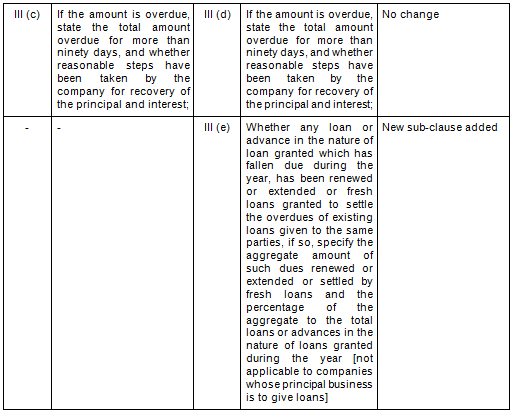
- Comparative Clauses
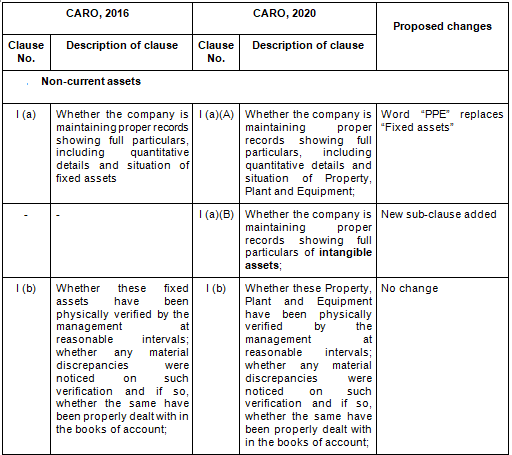
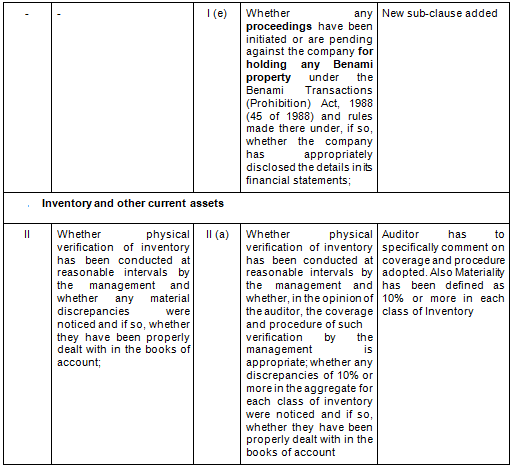
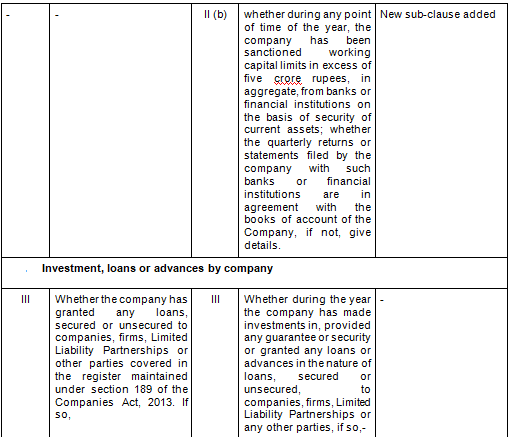
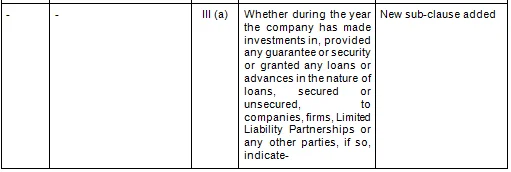
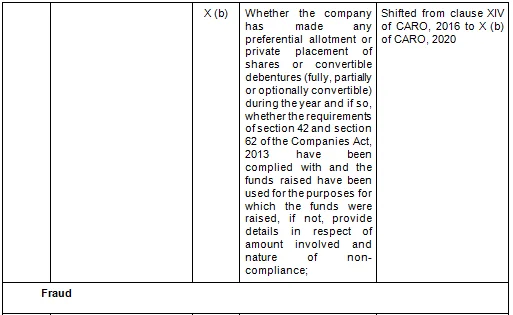
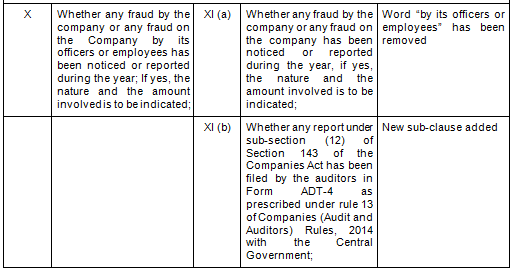
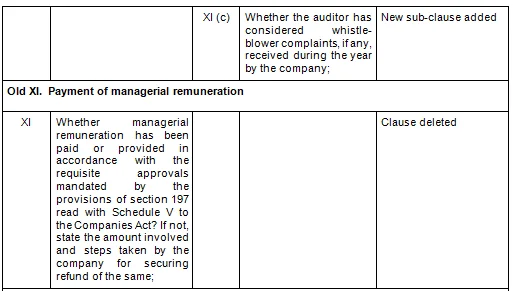
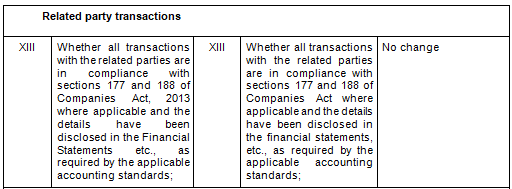
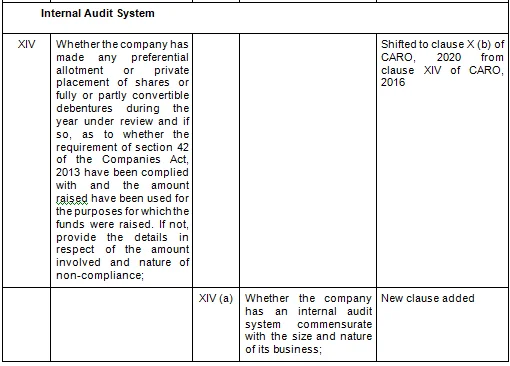
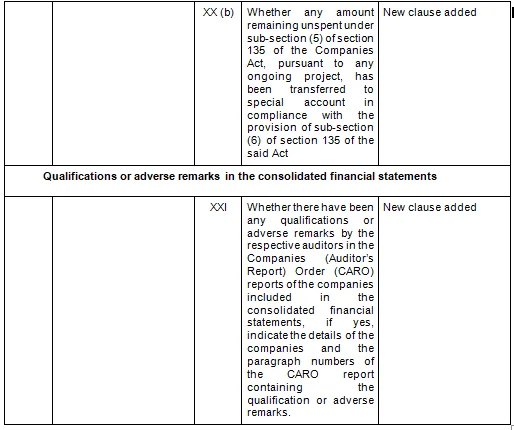
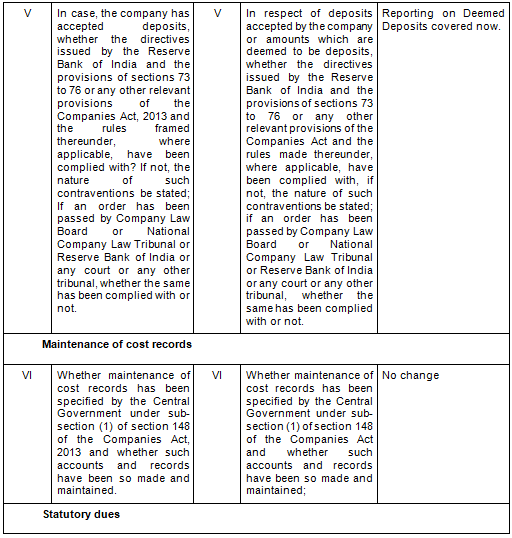
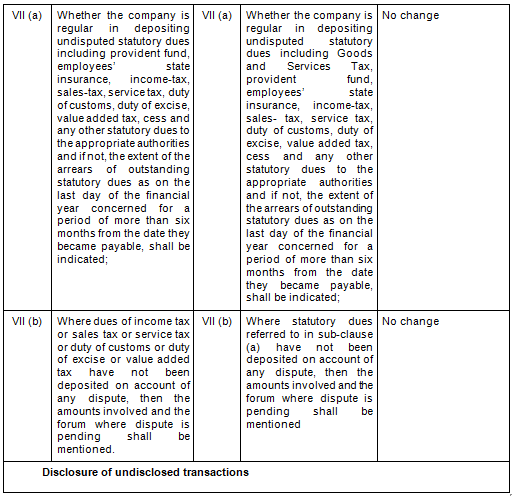
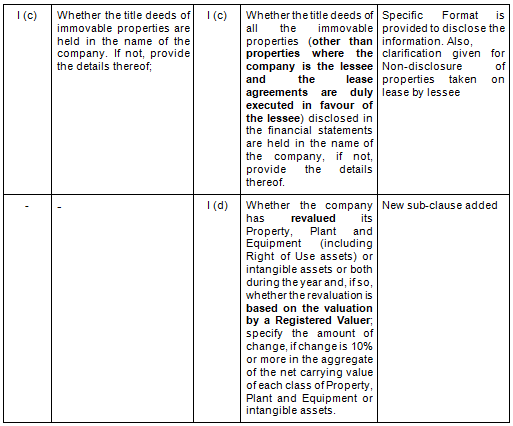
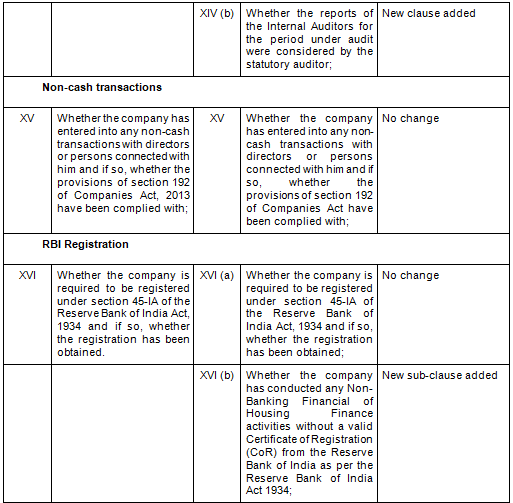
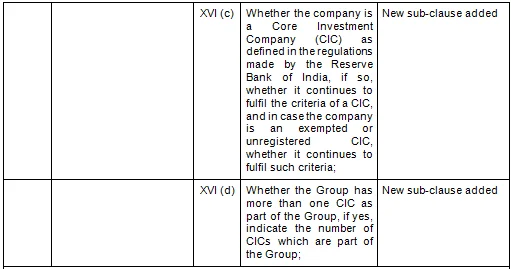
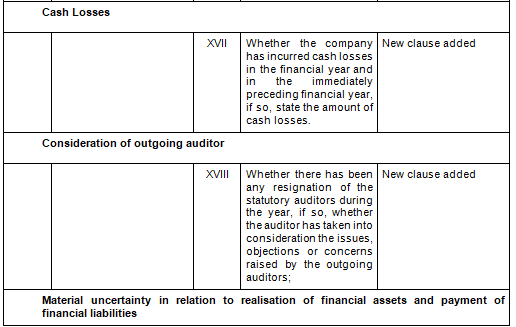
There are in total 21 clauses in CARO 2020 as compared to the existing CARO 2016 that has 16 clauses.
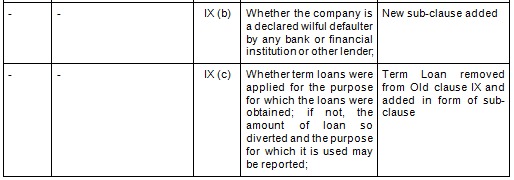
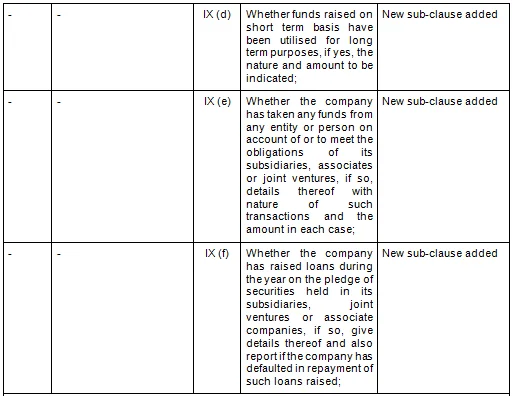
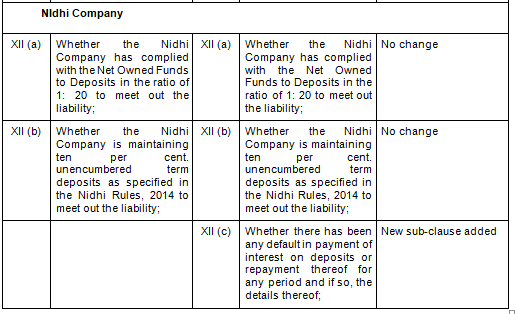
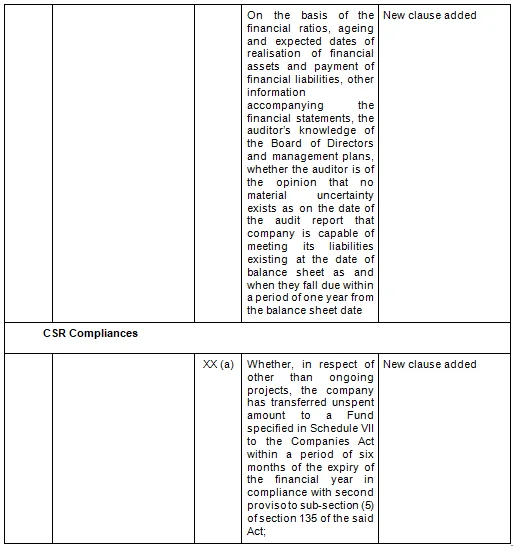
- Key Changes/ Highlights between CARO, 2020 and CARO, 2016
Let’s analyze the proposed changes clause-wise between CARO 2020 and CARO 2016.

























We Are Problem Solvers. And Take Accountability.
Related Posts


Navigating the CERT-IN Directions: Implications and Challenges for Indian Businesses
Blog Content Overview1 Introduction2 Highlights of the CERT-IN Directions2.1 Applicability2.2…
Learn More

Board Observers: Navigating the Influence Without the Vote
Blog Content Overview1 Understanding the Role of Board Observers2 Board…
Learn More

Types of Agreements used in SaaS Industry
Blog Content Overview1 What is SaaS? 2 What are SaaS Agreements? 3…
Learn More









