Blog Content Overview
- 1 Accounts Receivable in India : Meaning and Importance for Indian Businesses
- 2 How Does Accounts Receivable Work? (Process Explanation)
- 3 Accounts Receivable Examples: Real-Life Applications in Indian Businesses
- 4 Importance of Accounts Receivable Management for Indian Businesses
- 5 Key Metrics to Monitor in Accounts Receivable Management
- 6 How to Improve Accounts Receivable Management in India
- 7 Accounts Receivable Financing Options in India
Accounts Receivable in India : Meaning and Importance for Indian Businesses
What is Accounts Receivable?
Definition
Accounts receivable refers to the outstanding payments a business is owed by its customers for goods or services delivered on credit. Simply put, when a company sells products or services without immediate payment, the amount due from the customer is recorded as accounts receivable (AR). This amount is classified as a current asset on the company’s balance sheet because it represents cash expected to be received within the normal operating cycle usually within 30 to 90 days.
In accounting terms, accounts receivable means:
- Money owed by customers to the business
- Unpaid invoices or bills issued on credit sales
- A vital component of working capital management
Why Understanding Accounts Receivable is Crucial for Indian Businesses
For businesses operating in India whether startups, SMEs, or large enterprises grasping the concept of accounts receivable is essential due to the following reasons:
1. Cash Flow Management and Liquidity
Accounts receivable directly impact a business’s cash flow. Efficient collection of receivables ensures that companies have enough liquidity to meet operational expenses, pay suppliers, and invest in growth. Poor AR management can lead to cash crunches, slowing down business operations.
2. Working Capital Optimization
Since AR forms a significant part of working capital, delays in receivables can disrupt the balance between current assets and liabilities. For Indian businesses, optimizing AR means better control over working capital, which is critical in sectors with tight margins and competitive markets.
3. Credit Risk and Bad Debts Prevention
Understanding AR helps companies assess credit risk evaluating which customers are likely to delay or default on payments. Proper management mitigates the risk of bad debts, protecting the company’s profitability and financial health.
4. Improved Customer Relationships
Clear policies and timely invoicing improve transparency and customer trust. Indian businesses often face challenges with delayed payments due to informal credit terms. Strong AR systems encourage prompt payment while maintaining good customer relations.
5. Compliance and Financial Reporting
For compliance with Indian accounting standards (Ind AS) and taxation (GST implications on invoices and payments), maintaining accurate AR records is mandatory. Proper accounts receivable management ensures financial statements reflect the true financial position and comply with statutory audits.
Difference Between Accounts Receivable and Other Receivables
| Type of Receivable | Definition | Typical Examples in India | Classification |
| Accounts Receivable | Amounts owed by customers for credit sales | Outstanding invoices from clients | Current Asset |
| Notes Receivable | Formal, written promises to pay, often with interest | Promissory notes, IOUs | Current or Non-current |
| Other Receivables | Non-trade receivables such as advances or refunds | Employee loans, advances to vendors | Current or Non-current |
Note: Accounts receivable specifically relates to trade-related debts, while other receivables cover miscellaneous claims.
Key Terms Related to Accounts Receivable
- Invoice: A document issued by a seller to a buyer detailing the sale, price, and payment terms; it triggers the creation of accounts receivable.
- Credit Sales: Sales where payment is deferred, allowing the customer to pay at a later date as agreed.
- Payment Terms: Conditions agreed upon regarding when and how payments should be made, including due dates and any discounts or penalties.
How Does Accounts Receivable Work? (Process Explanation)
Understanding the accounts receivable process is crucial for Indian businesses to manage cash flow efficiently and maintain healthy customer relationships. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how accounts receivable operates from the point of sale to payment collection.
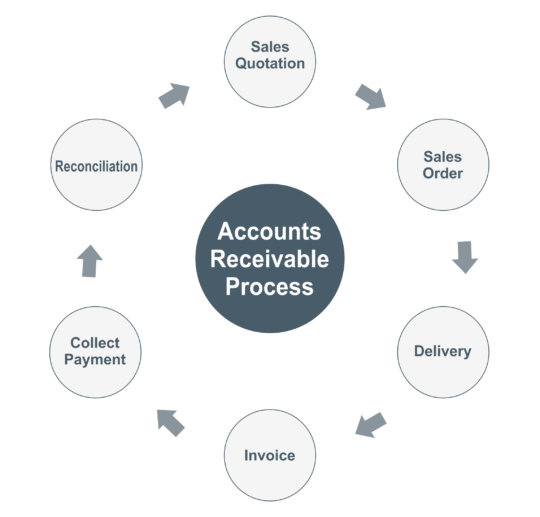
Stepwise Accounts Receivable Process from Sale to Payment
| Step No. | AR Process Step | Description |
| 1 | Sale on Credit | The business sells goods or services to the customer on credit, allowing deferred payment instead of immediate cash receipt. |
| 2 | Issuing Invoice | An invoice is generated detailing the products or services, amount due, and payment terms. This acts as the formal request for payment. |
| 3 | Payment Terms & Due Date | The invoice specifies payment terms such as net 30, net 60 days, or any customized timeline agreed upon with the customer. |
| 4 | Payment Collection | The customer makes the payment within the stipulated time frame via cheque, electronic transfer, or other accepted modes. |
| 5 | Recording & Reconciliation | The payment is recorded in the accounting system and matched against the corresponding invoice to update accounts receivable balances. |
Accounts Receivable Examples: Real-Life Applications in Indian Businesses
Understanding accounts receivable examples helps Indian businesses visualize how credit sales translate into financial transactions and impact cash flow. Below are practical examples tailored for various industries in India.
Simple Accounts Receivable Example in an Indian Business Context
Example:
A Mumbai-based IT services company completes a software development project for a client and issues an invoice of ₹5,00,000 with payment terms of 45 days. The client is expected to pay the amount within 45 days. Until the payment is received, ₹5,00,000 is recorded as accounts receivable on the IT company’s balance sheet.
- Transaction: Credit sale of software services
- Invoice amount: ₹5,00,000
- Payment terms: 45 days
- AR status: Outstanding until payment collection
This example illustrates how AR represents money owed by customers and forms part of the company’s current assets.
Accounts Receivable Across Different Indian Industries
| Industry | Accounts Receivable Scenario | Typical Payment Terms | AR Management Focus |
| Manufacturing | Goods sold to distributors with 30-60 days credit period | 30 to 60 days | Managing large volume invoices, credit risk assessments |
| Services | Consultancy firms invoicing clients post-project completion | 30 to 90 days | Timely invoicing, follow-up on overdue payments |
| Retail | Wholesale goods supplied on credit to retailers | 15 to 45 days | Frequent reconciliation, managing multiple small invoices |
| Construction | Billing based on project milestones, with extended payment terms | 60 to 120 days | Monitoring long receivable cycles, dispute resolution |
| Healthcare | Medical equipment suppliers providing devices on credit | 30 to 60 days | Strict documentation and invoice verification |
Each sector’s AR process varies based on industry norms and customer relationships, impacting cash flow differently.
Importance of Accounts Receivable Management for Indian Businesses
Effective management of accounts receivable (AR) is vital for maintaining the financial health and sustainability of businesses in India. Proper AR management ensures timely cash inflows, reduces risks, and strengthens overall business operations.
Why Effective Accounts Receivable Management Matters
- Ensures Consistent Cash Flow: AR represents expected cash inflows; managing it well guarantees that the business has the funds needed to cover expenses and invest in growth.
- Optimizes Working Capital: Efficient collection of receivables shortens the cash conversion cycle, freeing up capital for day-to-day operations.
- Supports Business Sustainability: Reliable cash flow and minimized credit risk enable businesses to withstand market fluctuations and economic uncertainties common in India.
Impact of AR Management on Key Financial Areas
| Financial Aspect | Impact of Accounts Receivable Management |
| Cash Flow | Faster collections improve liquidity, reducing the need for external borrowing. |
| Working Capital | Efficient AR reduces cash tied up in receivables, enhancing operational efficiency. |
| Business Sustainability | Stable inflows ensure ongoing operational capability and resilience against payment delays. |
Key Challenges in Managing Accounts Receivable in India
- Late Payments: Common in sectors like manufacturing and construction, causing cash flow disruptions.
- Credit Risk: Risk of customer defaults due to economic slowdown or poor credit evaluation.
- Disputes Over Invoices: Differences in invoice amounts, delivery terms, or GST details often delay payments.
- Regulatory Complexities: Compliance with GST and invoicing norms requires meticulous documentation.
Benefits of Good Accounts Receivable Management
- Faster Cash Collections: Streamlined invoicing and proactive follow-ups reduce payment delays.
- Reduced Bad Debts: Effective credit assessment and monitoring minimize defaults.
- Improved Customer Relationships: Transparent communication builds trust and repeat business.
- Better Financial Planning: Accurate receivable data aids in budgeting, forecasting, and strategic decisions.
Key Metrics to Monitor in Accounts Receivable Management
Efficient management of accounts receivable (AR) relies heavily on tracking essential financial metrics. These key indicators help Indian businesses optimize cash flow, reduce risks, and improve working capital management.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
Definition: This ratio measures how many times a company collects its average accounts receivable during a financial period, indicating the efficiency of credit and collection policies.
Formula:
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales / Average Accounts Receivable
- Higher ratio = faster collections and better cash flow
- Typical benchmark in Indian SMEs varies by sector, with 6-12 times annually considered healthy
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO)
Definition: DSO indicates the average number of days it takes for a company to collect payment after a sale.
Formula:
DSO = (Accounts Receivable / Total Credit Sales) × Number of Days
- In India, typical DSO ranges between 30-60 days depending on the industry
- Lower DSO means quicker cash inflows, critical for cash-strapped MSMEs
Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC)
Overview: CCC measures the total time (in days) it takes for a company to convert its investments in inventory and other resources into cash flows from sales, combining inventory turnover, receivables, and payables cycles.
Formula:
Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC) = Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) + Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) – Days Payables Outstanding (DPO)
- A shorter CCC improves liquidity and operational efficiency.
- Indian businesses face challenges with long CCC due to extended payment cycles in sectors like manufacturing and construction.
Summary Table of Key AR Metrics
| Metric | Formula | What It Indicates | Ideal Scenario for Indian Businesses |
| Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio | Net Credit Sales ÷ Average AR | Efficiency of collections | Higher is better (faster collections) |
| Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) | (Average AR ÷ Total Credit Sales) × Days | Average collection period | Lower is better (quicker payments) |
| Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC) | DSO + Days Inventory – Days Payables | Overall cash flow cycle | Shorter cycle preferred |
How to Improve Accounts Receivable Management in India
Effective AR management can be enhanced by adopting the following best practices tailored to the Indian business environment:
- Implement Technology & Software: Use ERP systems and cloud-based AR software (e.g., Tally, Zoho Books) for automated invoicing, payment reminders, and real-time tracking.
- Establish Clear Credit Policies: Define credit limits, payment terms, and customer evaluation criteria to minimize defaults.
- Regular Reconciliation and Reporting: Frequently reconcile AR accounts to detect discrepancies and overdue invoices promptly.
- Proactive Follow-ups: Maintain consistent communication with customers through emails, calls, and reminders to encourage timely payments.
- Legal Framework Awareness: Utilize India’s legal provisions for debt recovery, such as the Limitation Act, Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRT), and Negotiable Instruments Act for bounced cheques, when necessary.
Accounts Receivable Financing Options in India
What is Accounts Receivable Financing and Factoring?
- Accounts Receivable Financing involves borrowing funds against outstanding invoices to improve immediate cash flow.
- Factoring is a form of AR financing where a business sells its invoices to a third-party factor at a discount, receiving upfront payment while the factor assumes collection responsibility.
How Indian Businesses Can Leverage AR Financing
- Access quick working capital without waiting for customer payments.
- Particularly useful for MSMEs facing cash flow constraints due to delayed payments.
- Enables business continuity and growth by funding operational expenses and new projects.
Pros and Cons of Accounts Receivable Financing
| Pros | Cons |
| Immediate cash flow improvement | Costs include discount fees or interest charges |
| Reduces pressure of chasing overdue payments | May affect customer relationships if factor is aggressive |
| Improves working capital and liquidity | Dependency can increase financial costs over time |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Accounts Receivable
-
What is the meaning of accounts receivable in simple terms?
Accounts receivable refers to the money a business is owed by its customers after selling goods or services on credit. It represents unpaid invoices and is considered money the business expects to receive soon.
-
How does accounts receivable affect a company’s cash flow?
Accounts receivable impacts cash flow by representing expected incoming payments. Efficient collection of receivables ensures steady cash inflows, which helps a company pay its expenses and invest in growth. Delays in collections can cause cash shortages.
-
What are common challenges in accounts receivable management in India?
Common challenges include late payments from customers, high credit risk due to insufficient credit checks, disputes over invoice details, and compliance complexities with GST invoicing and tax regulations.
-
How can businesses reduce the days sales outstanding (DSO)?
Businesses can reduce DSO by:
- Setting clear payment terms
- Sending timely invoices and payment reminders
- Offering early payment discounts
- Using automated AR software for tracking
- Conducting credit assessments before extending credit
-
Is accounts receivable considered an asset or liability?
Accounts receivable is considered a current asset because it represents amounts expected to be converted into cash within the company’s normal operating cycle.
-
Can accounts receivable be sold or financed? How does that work in India?
Yes, accounts receivable can be sold or financed through methods like factoring or AR financing. In India, businesses sell outstanding invoices to third-party factors who pay upfront (minus fees) and collect payments from customers, improving liquidity and cash flow.
We Are Problem Solvers. And Take Accountability.
Related Posts

The Reverse Flip Playbook – For Indian Founders
DOWNLOAD PDF The landscape for Indian startups has fundamentally shifted. A growing number of founders are making a deliberate choice...
Learn More

Angel Tax Exemption – Eligibility, Declaration, How to Apply
The angel tax, introduced by Section 56(2)(viib) of the Income Tax Act, 1961, applies to unlisted companies (startups whose shares...
Learn More

ESG Compliance in India – BRSR, SEBI Regulations & What Founders Need to Know
ESG used to be something listed enterprises stuck into their annual reports. In 2026, that's no longer true. ESG compliance...
Learn More











