Quick Summary
Convertible debentures are attractive to investors because they offer a balanced blend of fixed income and potential equity appreciation. Investors receive regular interest payments, providing a steady income stream. Additionally, the option to convert these debentures into equity allows participation in the company’s growth, offering potential capital gains if the company’s stock performs well. This combination of fixed returns and equity upside makes convertible debentures a compelling choice for those seeking both income and growth opportunities in their investment portfolios.
Blog Content Overview
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Types of Convertible Debentures
- 3 Features of fully and partly convertible debentures
- 4 Legal Background
- 5 Why Investors Prefer Convertible Debentures
- 6 Benefits of issuing convertible debentures
- 7 Tax Considerations around Convertible Debentures
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 Frequently Asked Questions on Convertible Debentured
Introduction
A convertible debenture is a debt instrument issued by a company that can be converted into equity shares of the issuing company after a specified period or upon the fulfillment of certain conditions. These instruments combine the features of debt (fixed interest payments) and equity (conversion option), making them attractive to both companies and investors. A convertible note or debenture is usually an unsecured bond or a loan as in there is no primary collateral interlinked to the debt.
A convertible debenture can be transformed into equity shares after a specific period. The option of converting debentures into equity shares lies with the holder. A convertible debenture will provide regular interest income via coupon payments and repayment of the principal amount at maturity.
Types of Convertible Debentures
Convertible debentures can be used by companies to raise capital from both domestic and foreign investors and can adopt a variety of forms based on the terms and conditions attached to the issue of such instruments. This can take the form of debentures that fully or partially convert into debt, whether compulsorily or at the debenture holder’s option.
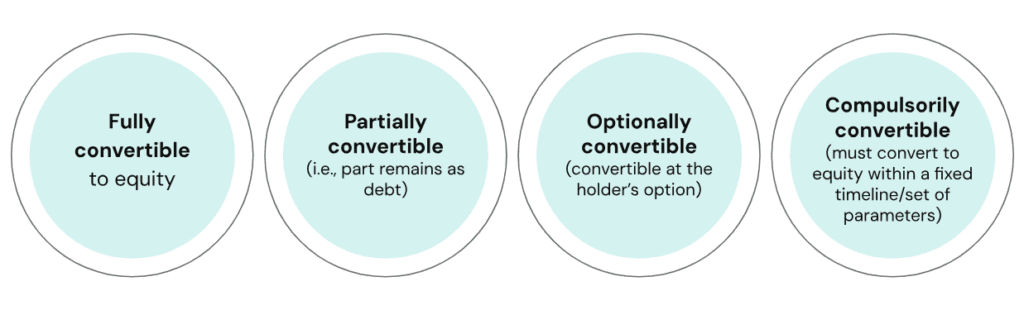
- Fully Convertible Debentures (FCDs): These can be entirely converted into equity shares after a specified period, with no remaining debt after conversion.
- Partially Convertible Debentures (PCDs): A portion of the principal is converted into equity shares, while the remaining debt continues to be paid with interest.
- Optionally Convertible Debentures (OCDs): These give the holder the option to convert the debentures into equity shares at their discretion, within a predetermined period.
- Compulsorily Convertible Debentures (CCDs): These must be converted into equity shares after a specified period, regardless of the holder’s preference.

Features of fully and partly convertible debentures
| Parameters | Fully Convertible Debentures | Partly Convertible Debentures |
| Definition | The value can be changed into the company’s equity shares. | Only some portion of the debentures would convert to company’s equity shares. |
| Flexibility in terms of financing | They have a highly favourable debt-equity ratio. | They have a favourable debt-equity ratio. |
| Classification for calculation | They are classified as equity. | The convertible portion is classified as equity, whereas, the non-convertible part is classified as debt. |
| Suitability | Fully convertible debentures are suitable for companies which do not have an established track record. | Partly convertible debentures are suitable for those companies that have an established track record. |
| Popularity | They are highly popular among investors. | They are not very popular among investors. |
Legal Background
Governed primarily by the Companies Act, 2013, the issue of convertible debentures is permitted under Indian law, subject to compliance with a robust framework (including mandatory filings with the competent Registrar of Companies and maintenance of the appropriate records by the company). Issue of debentures by public listed companies is also permitted, subject to conditions set out in the regulations issued by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) from time to time. Indian law also permits foreign investors to invest in Indian entities against the issue and allotment of compulsorily convertible debentures, however the same is subject to regulatory processes set out in the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA) and the regulations issued from time to time by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Companies Act, 2013
Section 2(30) defines a ‘debenture’ to “include debenture stock, bonds or any other instrument of a company evidencing a debt, whether constituting a charge on the assets of the company or not.” In other words, any debenture is a debt instrument for a company.
Section 71 lays down the conditions attached to the issue of debentures by a company and permits the issue to be made with an “option to convert such debentures into shares, either wholly or partly at the time of redemption.” However, where any debenture is to be converted into equity, the company is required to first obtain approval of its shareholders on the terms of issue and conversion, which necessitates the holding of a general meeting and form filing with the Registrar of Companies having competent jurisdiction.
Debentures can be issued through private placement under Section 42 but are strictly subject to the corporate procedures set out in the provision (read with the relevant rules). It is pertinent to note that as per the Companies (Acceptance of Deposits) Rules, 2014 it is compulsory for the compulsorily convertible debenture into an equity share capital within a period of 10 years otherwise it will be viewed as a “deposit” under the Companies Act, 2013 and the provision of “deposit” will be taken into consideration in assessing the company’s compliance status with applicable laws.
SEBI Regulations
The SEBI Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements Regulations mandate disclosure of conversion terms, pricing mechanism and timelines for conversion when convertible debentures are issued by any public listed company.
Such issues are further governed by: (i) the SEBI Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements Regulations, which mandates continuous reporting and compliance obligations; and (ii) SEBI Pricing Guidelines which set out pricing norms to ensure fairness and transparency in the issue process.
FEMA and RBI Regulations
Under the Foreign Direct Investment Policy, foreign investment can be made in shares, mandatorily and fully convertible preference shares, and mandatorily and fully convertible debentures. In other words, a foreign investor cannot subscribe to optionally convertible or partly convertible debentures under the FDI Policy and remain in compliance with the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 and the regulations prescribed by RBI from time to time. Where the issue of any fully and mandatorily convertible debenture is made to a foreign investor and/or non-residents, such issue must comply with the pricing and conversion guidelines set out in FEMA. Further, such issues must be made in accordance with the norms contained in the FDI Policy published by the government of India from time to time1, and any convertible instruments with fixed returns may qualify as External Commercial Borrowings, requiring RBI approval.
Why Investors Prefer Convertible Debentures
Investors typically prefer convertible debentures on the basis of the following factors:
- Balance of Risk and Reward: Investors receive fixed interest payments during the holding period, providing a steady income stream and mitigating downside risk. The option to convert into equity allows investors to participate in the company’s growth and benefit from potential capital appreciation.
- Priority Over Equity: Until conversion, convertible debentures are treated as debt, giving investors priority over equity shareholders in case of liquidation.
- Customizable Features: Convertible debentures can be structured to align with investors’ preferences, such as favorable conversion ratios, timelines, and pricing terms.
- Alignment with Growth Companies: For companies in high-growth sectors, convertible debentures provide a pathway for investors to capture long-term value while minimizing initial exposure.
- Mitigation of Dilution Concerns: Investors retain their debt status until conversion, avoiding immediate equity dilution and allowing time to evaluate the company’s performance.
- Flexibility for Strategic Decisions: The ability to decide on conversion provides investors with the flexibility to align their decisions with market conditions and company milestones.
Benefits of issuing convertible debentures
For an investor the benefits from asking for convertible debentures are as follows –
The most popular benefits of convertible debentures for investors are as follows –
- Investors receive a fixed-rate of interest on a continued basis and also have the option to partake in stock price appraisal.
- In case the company’s share price declines, investors are entitled to hold onto the bonds until maturity.
- Convertible debenture holders are paid before other shareholders in the event of liquidation of the company.
- Being a hybrid investment instrument, investors are entitled to fixed interest payouts and also have the option of converting their loan to equity when the company is performing well or when its stock prices are rising.
- As per the Companies (Acceptance of Deposits) Rules, 2014 which does not include clause xi of Rule 2 (1) (c) can raise the amount of issuance of debentures as referred in Schedule III of the Act which also not include the insubstantial assets of the debentures compulsorily convertible into a equity share capital of the company within a period of 10 years. So it is compulsory for the compulsorily convertible debenture into an equity share capital within a period of 10 years otherwise it will be viewed as deposit under the Companies Act, 2013 and the provision of ‘deposit’ will be taken into consideration. With the amendment made in the year 2016, the time period has increased from 5 years to 10 years.
Tax Considerations around Convertible Debentures
- Tax deductible on interest payments: Interest on convertible debentures is allowable as a tax deduction to the Indian Company thereby resulting in an effective tax saving of 30% (subject to the availability of sufficient profits).
- Tax on conversion of convertible debentures: Conversion of compulsorily convertible debentures into equity shares is not liable to tax in India.
- Conversion ratio: Under the existing regulations, the ratio of conversion of convertible debentures into equity shares/price of conversion, has to be specified upfront at the time of issue of any such debentures.
Challenges Involved
- Complex Structuring: Requires careful alignment with regulatory norms and investor expectations.
- Reporting and Compliance: Stringent disclosure obligations under applicable laws.
- Market Risks: Potential for lower returns if the company underperforms before conversion.
Conclusion
Convertible debentures offer a compelling option for both investors and issuers, balancing risk mitigation with growth potential. From an investor’s perspective, they provide steady returns during the debt phase and the opportunity to participate in equity value creation. In India’s regulatory landscape, convertible debentures are governed by robust frameworks ensuring transparency and investor protection. For companies, especially startups and high-growth ventures, these instruments present an effective way to secure funding while managing equity dilution and fostering long-term partnerships with strategic investors. As ESG considerations gain prominence, convertible debentures also align well with sustainable and responsible investment strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions on Convertible Debentured
1. What is a Convertible Debenture?
A convertible debenture is a type of debt instrument issued by a company that can be converted into equity shares at a later date, usually at the discretion of the investor. It offers the benefits of both debt (interest payments) and equity (conversion to shares).
2. What are the key benefits of Convertible Debentures for investors?
- Fixed Income: Investors receive regular interest payments, offering a predictable return.
- Upside Potential: The option to convert into equity gives investors the potential to benefit from the company’s future growth.
- Downside Protection: In case of liquidation, debenture holders are prioritized over equity shareholders for repayment.
3. What are the risks associated with Convertible Debentures?
- Conversion Risk: If the company’s stock price underperforms, the conversion option may be less valuable.
- Interest Rate Risk: Like other debt instruments, convertible debentures are subject to interest rate fluctuations.
- Liquidity Risk: Since these are long-term investments, they may not be as liquid as other types of securities.
4. What are the types of convertible debentures?
- Fully Convertible: Entirely converts to equity.
- Partially Convertible: Part equity, part debt.
- Optionally Convertible: Conversion at holder’s choice.
- Compulsorily Convertible: Must convert within a timeline.
5. What regulations govern convertible debentures in India?
Companies Act, 2013 (for private and public listed companies), SEBI regulations (for listed companies), and FEMA and RBI (for foreign investors).
6. Why do investors prefer them?
They offer fixed returns, equity upside, priority in liquidation, customizable terms, and mitigate immediate equity dilution.
7. What are the tax benefits?
Interest is tax-deductible for issuers, and conversion to equity is not taxable. Capital gains tax applies on sale of equity shares.
8. When can investors convert their debentures into equity?
Investors typically have the option to convert their debentures into equity after a predefined period or during specific events (e.g., funding rounds, IPO). The exact timing is determined by the terms outlined in the agreement.
9. How do Convertible Debentures benefit companies?
Convertible debentures allow companies to raise capital without immediately diluting equity ownership. They also provide investors with a potential equity upside, making them an attractive option for startup funding.
10. Are Convertible Debentures tax-efficient?
Convertible debentures may offer tax advantages in certain jurisdictions, as interest payments are typically tax-deductible for the company. However, tax treatment can vary depending on local laws.
References
We Are Problem Solvers. And Take Accountability.
Related Posts


Steps for Importing Under Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
A Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is a formal arrangement between two or more countries designed to facilitate trade by reducing...
Learn More

How to Import Goods from India – Step-by-Step Guide
India has emerged as a major player in the global trade ecosystem, exporting goods and services to over 200 countries....
Learn More

Licenses and Permits Required for Exporting from India
India has emerged as a major player in global trade, exporting to over 200 countries across sectors like pharmaceuticals, textiles,...
Learn More













