Blog Content Overview
Meaning
A fast-track merger is a streamlined process for combining two or more companies. It is typically designed to expedite the merger process, reduce administrative burdens, and facilitate efficient integration of the merging entities. It involves simplifying certain procedural steps and regulatory approvals, allowing the merger to be completed quickly.
Eligibility Criteria
A scheme of merger or amalgamation under section 233 of the Companies Act, 2013 may be entered into between any of the following classes of companies, namely:-
- A holding company and its wholly-owned subsidiary company or such other class or classes of companies;
- Two or more start-up companies; or
- One or more start-up companies with one or more small companies*.
*Small Company means a company whose paid up capital is maximum Rs 4 crore and turnover is maximum Rs 40 crore
Highlights of Recent Amendment
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (“MCA”) made amendments to Rule 25 of the Companies (Compromises, Arrangements and Amalgamations) Rules, 2016, on 15th May, 2023 which states that the Central Government (CG) now has a specific timeframe to approve merger and amalgamation schemes, addressing the previous absence of a defined time frame for approval from the Registrar of Companies (“ROC”) or Official Liquidator (“OL”).
The purpose of these amendments is to streamline and expedite the merger and amalgamation process specifically for start-up companies and small companies under section 233 of the Companies Act, 2013.
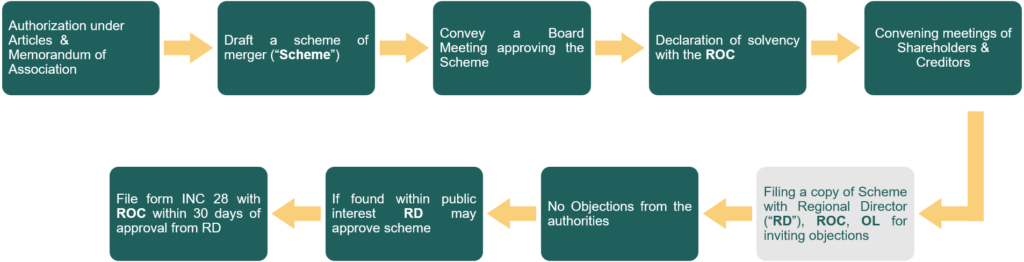
Step Plan for a Fast-track Merger
- Step 1: Authorization under Articles & Memorandum of Association
- Step 2: Draft a scheme of merger (“Scheme”)
- Step 3: Convene a Board Meeting approving the Scheme
- Step 4: Declaration of solvency with the ROC
- Step 5: Convening meetings of Shareholders & Creditors
- Step 6: Filing a copy of Scheme with Regional Director (“RD”), ROC, OL for inviting objections
- Step 7: No Objections from the authorities
- Step 8: If found within public interest RD may approve the scheme
- Step 9: File form INC 28 with ROC within 30 days of approval from RD
Amendments are as follows
Note: The Scheme in each of the aforementioned situations shall be approved or deemed to be approved only if the same is in the public interest or in the interest of the creditors
| IF | THEN |
|---|---|
| No objection/ suggestion received by the CG from ROC/OL within 30 days of the receipt of copy of scheme. | CG shall confirm and approve the scheme within 15 days after the expiry of 30 days. |
| No confirmation from CG within 60 days from the receipt of the scheme. | The scheme shall be deemed to be approved. |
| On receipt of objections/ suggestions from ROC/ OL where such objection/ suggestion are not sustainable. | CG shall approve the scheme and issue confirmation order within 30 days after the expiry of 30 days.If no confirmation order is issued within the aforementioned period, it shall be deemed that it has no objection to the scheme and a confirmation order shall be issued accordingly. |
| On receipt of objections/ suggestions from ROC/ OL where CG is of opinion that the scheme is not in the public interest or in the interest of creditors. | CG shall file an application with the tribunal within 60 days of receipt of the scheme, requesting the tribunal to consider the scheme in the regular manner. If CG does not file the application within the aforesaid period, it shall be deemed that it has no objection to the scheme and a confirmation order shall be issued accordingly. |
We Are Problem Solvers. And Take Accountability.
Related Posts

Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Rules, 2025 – A Deep Dive
On November 14, 2025, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) notified the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Rules,...
Learn More

GST Amendments Effective from 1st April 2026
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework in India is undergoing sweeping changes in 2026. Key highlights include: GST 2.0:...
Learn More

RSU vs ESOP – The Complete India Guide for Founders, HR Leaders & Employees (2026)
India's startup ecosystem has entered a golden era and equity compensation sits at the heart of it. Whether you are...
Learn More











