Obtaining an FSSAI registration is essential for food business operators (FBOs) in India to ensure compliance with food safety and standards regulations. The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) mandates that all FBOs, including manufacturers, processors, storage facilities, distributors, and sellers, acquire the appropriate registration or license based on their business size and turnover. For small-scale businesses with an annual turnover of up to ₹12 lakh, a basic FSSAI registration is required. Larger enterprises must obtain either a State or Central FSSAI license, depending on their scale of operations. The registration process involves submitting Form A or Form B through the FoSCoS portal, along with necessary documents such as identity proof, address proof, and details of the food products handled. Compliance with FSSAI regulations not only ensures legal adherence but also enhances consumer trust by affirming the safety and quality of food products.
FSSAI Registration: Mandatory for All Food Businesses in India
Getting an FSSAI registration is a crucial step for anyone starting a food business in India. This includes individuals planning to open restaurants, bakeries, hotels, cloud kitchens, or even food stalls. The requirement applies to all Food Business Operators (FBOs). This broad term encompasses any entity or person involved in the food industry, including those who manufacture, prepare, sell, transport, distribute, or store food products.
FSSAI stands for the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India. This autonomous organization, established under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, is responsible for monitoring and regulating the entire food sector in India. The FSSAI was created under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 (FSS Act). This act consolidates all regulations related to food safety in India. By ensuring food products undergo quality checks, FSSAI helps reduce food adulteration and the sale of substandard products. In addition to registering and licensing FBOs, FSSAI also lays down the rules and regulations that govern the operation of food businesses throughout India.
What is FSSAI Registration?
In India, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) plays a critical role in safeguarding public health by regulating the food industry. To achieve this, FSSAI mandates FSSAI Registration or Licensing for every entity (individual or company) involved in the food business lifecycle, encompassing manufacturing, processing, storage, distribution, and sale of food products.
FSSAI Registration is a 14-digit registration or a license number obtained from FSSAI and printed on food packages. The 14-digit registration number provides details about the assembling state of the product and producer’s permit. Furthermore, the requirement to display the FSSAI registration number on food packaging serves as a nudge for Food Business Operators (FBOs) to prioritize food safety and quality. The Food Safety & Standards (Licensing and Registration of Food Business) Regulations, 2011 form the bedrock for FSSAI’s registration and licensing procedures. These regulations establish clear guidelines regarding the eligibility criteria, application process, and documentation required for FBOs to obtain the necessary authorization.
FSSAI Registration vs. FSSAI License?
The type of FSSAI authorization an entity requires depends on the size and nature of its business operations. FSSAI Registration caters to small-scale food businesses with an annual turnover of up to INR 12 lakh. This includes petty retailers, hawkers, small manufacturers, and temporary stall owners. FSSAI Licenses, on the other hand, are applicable to larger businesses with higher turnovers or specific food business activities.
Difference between FSSAI Registration and FSSAI License –
| Feature | FSSAI Registration | FSSAI License |
| Purpose | Basic compliance for small food businesses | Mandatory for medium and large food businesses |
| Turnover Limit | Up to ₹ 12 lakh per year | Above ₹ 12 lakh per year |
| Type of Businesses | Small manufacturers, retailers, petty vendors, temporary stalls | Food processing & manufacturing units, large retailers, exporters, importers |
| Validity | 5 years | 1 to 5 years (depending on license type) |
| Process | Simpler online application | More complex process with inspections |
| Fee | Lower fees | Higher fees |
| Information Displayed | Registration number displayed at office premises | License number displayed on product packaging |
Food Business Operators (FBO) Who Need FSSAI Registration in India
FSSAI registration is a requirement for a broad spectrum of food businesses, encompassing various sizes and activities. Here’s a breakdown of the FBOs that need to register:
- Retailers and Shops: This includes permanent establishments like grocery stores, snack shops, bakeries, confectionery shops, and more.
- Street Food Vendors: Temporary or fixed stalls selling prepared or packaged food items, such as Gol Gappa stalls, chaat stalls, fruit and vegetable vendors, tea stalls, juice shops, etc., all require registration. Hawkers selling food while moving from one location to another also fall under this category.
- Dairy Units: Milk chilling units, petty milkmen, and milk vendors must register with FSSAI.
- Food Processing Units:
- Vegetable oil processing units
- Meat processing and fish processing units
- All food manufacturing units, including those involved in repacking food
- Facilities processing proprietary or novel food items
- Storage and Transportation:
- Cold storage facilities that refrigerate or freeze food products
- Businesses involved in transporting food products, especially those using specialized vehicles like refrigerated vans, milk tankers, and food trucks
- Distribution and Marketing: Wholesalers, suppliers, distributors, and marketers of food products need to be registered.
- Food Service Establishments:
- Hotels, restaurants, and bars
- Canteens and cafeterias, including mid-day meal canteens
- Food vending agencies, caterers, and dabhas
- PGs providing food service, banquet halls with catering arrangements
- Home-based canteens and food stalls operating in fairs or religious institutions
- Import and Export: Businesses involved in importing or exporting food items, including food ingredients, require FSSAI registration. This extends to e-commerce food suppliers and cloud kitchens.
Determining Your FSSAI License/Registration Type:
The type of FSSAI license or registration an FBO needs depends on specific eligibility criteria. These criteria consider factors like the business’s annual turnover, production capacity, and the nature of food products handled. The FSSAI website provides detailed information on the eligibility criteria for each type of license and registration.
Types of FSSAI Registration in India
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) regulates and ensures food safety across the country. To operate legally within this framework, food businesses (FBOs) need to obtain an FSSAI registration or license. The type of FSSAI registration an FBO requires depends on its size, turnover, and production capacity. Here’s a breakdown of the three main categories:
- FSSAI Basic Registration:
- Eligibility: This is the most basic form of FSSAI registration and is mandatory for small businesses with an annual turnover of up to Rs. 12 lakh.
- Process: Registration is done online through Form A. It’s a relatively simple process requiring basic details about the FBO and its operations.
- Suitable for: Small manufacturers, retailers, marketers, or suppliers dealing in:
- Homemade food products like jams, pickles, candies, etc.
- Small restaurants and cafes
- Food stalls and mobile canteens
- Small-scale storage units
- FSSAI State License:
- Eligibility: This license is required for medium-sized businesses with an annual turnover of more than Rs. 12 lakh but less than Rs. 20 crore.
- Process: Obtaining a state license involves a more detailed application process through Form B. It may require inspections of the FBO’s premises and adherence to stricter hygiene and safety regulations.
- Suitable for: Mid-sized manufacturers, processors, and exporters of food products, such as:
- Bakeries and confectionery units
- Oil processing units
- Packaging and bottling units
- Restaurants with a larger seating capacity
- FSSAI Central License:
- Eligibility: This is the most comprehensive license category, mandatory for large businesses with an annual turnover of more than Rs. 20 crore.
- Process: The central license application process through Form B is the most rigorous, involving in-depth inspections, documentation, and compliance with stringent quality standards.
- Suitable for: Large-scale food manufacturing units, processing plants, and importers, including:
- Multi-state or national food chains
- Large slaughterhouses and meat processing units
- Importers of food products
Step By Step Process of Getting FSSAI Registration Online
Obtaining an FSSAI registration online is a convenient and efficient way for food businesses (FBOs) to comply with food safety regulations in India. This section will guide you through the entire online registration process on the Food Safety Compliance System (FoSCoS) portal.
Step 1: Gather the Required Documents
Before applying online, ensure you have all the necessary documents scanned and saved in a digital format. The specific documents required will vary depending on the type of FSSAI registration you are applying for (Basic, State, or Central). Generally, you will need:
- Basic KYC Documents: Proof of identity (PAN card, Aadhaar card, Voter ID, etc.), proof of address (electricity bill, property tax receipt, etc.)
- Business Details: Business name, nature of business, address of operation, contact details
- Food Category Details: Description of food products manufactured, processed, or traded
- Authorization Letters (if applicable): For manufacturers, a No Objection Certificate (NOC) from the local authority might be required
Step 2: Access the FoSCoS Portal
Visit the official FoSCoS portal (https://foscos.fssai.gov.in/) and navigate to the “Apply for New License/Registration” section.

Step 3: Register or Login
- New Users: Click on “New User Registration” and create an account by providing a valid email address and password.
- Existing Users: If you have already registered, simply log in using your credentials.
Step 4: Choose the Registration Type
On the dashboard, select the appropriate registration type based on your business turnover:
- FSSAI Basic Registration (Form A): For businesses with a turnover of up to Rs. 12 lakh per annum.
- FSSAI State License (Form B): For businesses with a turnover between Rs. 12 lakh and Rs. 20 crore per annum.
- FSSAI Central License (Form B): For businesses with a turnover exceeding Rs. 20 crore per annum.
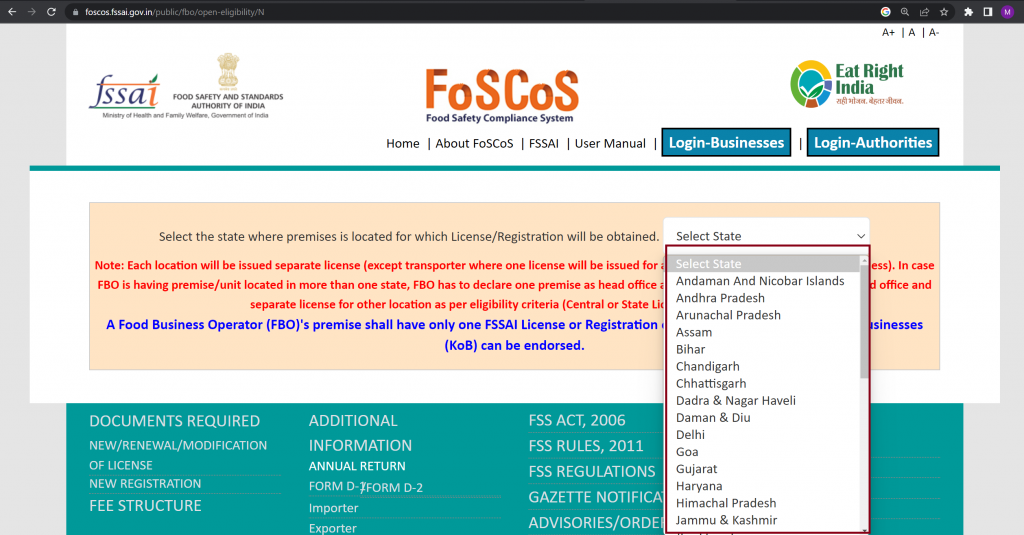
Step 5: Complete the Online Application Form
Carefully fill out the application form with accurate details about your business, including:
- Business name and address
- Nature of business activity (manufacturing, processing, storage, distribution, etc.)
- Food product category details
- Details of food manufacturing or processing premises (if applicable)
- Source of raw materials (if applicable)
Step 6: Upload Required Documents
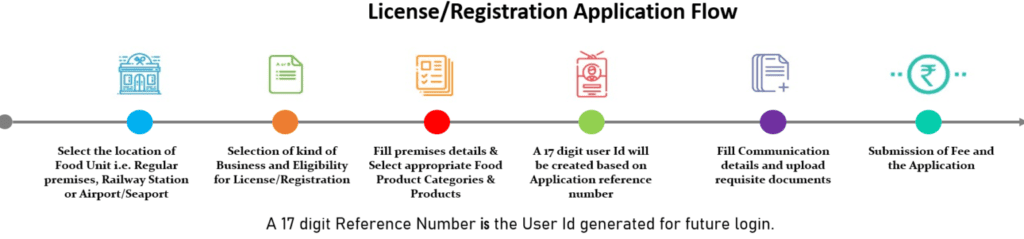
Step 7: Fee Payment
Pay the applicable registration fee online using a debit card, credit card, or net banking facility. The fee varies depending on the type of registration you are applying for.
Step 8: Submit the Application and Track Status
Once you have reviewed all the information and ensured its accuracy, submit the online application form. You will receive a confirmation email with a tracking number. Use this number to track the status of your application on the FoSCoS portal.
Step 9: Department Scrutiny and Inspection (if applicable)
The FSSAI department will scrutinize your application and documents. For State or Central licenses, an inspection of your food premises might be conducted to verify compliance with FSSAI regulations.
Step 10: Granting of FSSAI Registration Certificate
If your application is approved, the FSSAI will issue a registration certificate with a unique registration number. You can download the certificate by logging into your FoSCoS account. If your application is not approved, you will be informed by the Department within 7 days from the date of receipt of an application either physically or online through the FoSCoS portal.
Step 11: Display the FSSAI Certificate Prominently
As per regulations, you are required to prominently display the FSSAI registration certificate at your place of business during operating hours. This signifies your compliance with food safety standards and builds trust with your customers.
By following these steps and keeping the necessary documents prepared, you can efficiently obtain your FSSAI registration online and operate your food business legally within India.
Eligibility for FSSAI Registration
FSSAI registration applies to Food Business Operators (FBOs) involved in various small-scale food business activities. Here’s a breakdown of the eligibility criteria:
- Turnover: Any FBO with an annual turnover of not more than Rs. 12 lakh needs to register.
- Business Type:
- Petty retailers dealing in food products (e.g., local grocery stores).
- Individuals who manufacture or sell any food article themselves (e.g., homemade bakery owners).
- Temporary stall holders selling food (e.g., street food vendors).
- Individuals distributing food in religious or social gatherings (except caterers).
- Small-scale or cottage industries involved in food production.
Food Production Capacity Limits:
For businesses involved in specific food production activities, registration applies if their daily capacity falls under the following limits:
- Food Production (excluding milk and meat): Up to 100 kg/liter per day.
- Procurement, Handling, and Collection of Milk: Up to 500 liters per day.
- Slaughtering: Up to 2 large animals or 10 small animals or 50 poultry birds per day.
- Transportation: Businesses operating a single vehicle for food transportation.
- Vending Machines: Up to 12 vending machines operating within a single state/union territory.
Important Note:
While FSSAI registration caters to small-scale businesses, FSSAI licenses are available for larger businesses with higher turnovers or exceeding the mentioned production capacities.
Eligibility for FSSAI License
While FSSAI registration caters to small-scale operations, FSSAI licenses are mandatory for medium and large businesses. Let’s delve into the eligibility criteria for these licenses.
FSSAI License Categories:
FSSAI licenses are categorized into two depending on the business size:
- State FSSAI License: Applicable to medium-scale businesses.
- Central FSSAI License: Mandatory for large-scale businesses.
State FSSAI License Eligibility:
This license is targeted towards medium-sized manufacturers, transporters, distributors, and wholesalers. Here’s a breakdown of the key requirements:
- Turnover: FBOs with an annual turnover between Rs. 12 lakh and Rs. 20 crore (Rs. 30 crore for transportation and wholesale businesses).
- Business Activities:
- All grain, cereal, and pulse milling units (irrespective of production capacity).
- Food business operations limited to a single state.
- Food Production Capacity Limits: (Daily Capacity)
- Food Production (excluding milk and meat): 1 MT to 2 MT.
- Milk Procurement, Handling, and Collection: 501 liters to 50,000 liters.
- Slaughtering: 3-50 large animals, 11-150 small animals, or 51-1,000 poultry birds.
- Storage capacity: Up to 10,000 MT.
- Transportation fleet: Up to 100 vehicles.
- Hospitality Establishments: Hotels with one to four-star ratings.
- Vending Machines: Up to 100 machines operating within a single state/union territory.
Central FSSAI License Eligibility:
This license caters to large-scale food manufacturers, importers, and exporters. Here are the eligibility criteria:
- Turnover: FBOs with an annual turnover exceeding Rs. 20 crore (Rs. 30 crore for transportation and wholesale businesses).
- Business Activities:
- Food businesses operating in multiple states.
- Importers and exporters of food products.
- Manufacturers of proprietary foods, non-specified foods, food or health supplements, and nutraceuticals.
- Businesses involved in radiation processing of food.
- Food business activities at Central Government Agency premises.
- Caterers, restaurants, canteens, hawkers, or petty retailers operating at railway stations.
- E-commerce food businesses.
- Food Production Capacity Limits: (Daily Capacity)
- Food Production (excluding milk and meat): More than 2 MT.
- Milk Procurement, Handling, and Collection: More than 50,000 liters.
- Slaughtering: More than 50 large animals, more than 150 small animals, or more than 1,000 poultry birds.
- Storage capacity: More than 10,000 MT.
- Transportation fleet: More than 100 vehicles.
- Hospitality Establishments: Hotels with five-star ratings and above.
- Vending Machines: More than 100 machines located in two or more states/UTs.
License Tenure:
Both State and Central FSSAI licenses are issued for a minimum of one year and a maximum of five years.
Documents Required for FSSAI Registration and License
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the documents needed for FSSAI registration/license:
General Documents (Required for All Categories):
- Form A: This is the application form for FSSAI registration/license. You can download it from the FSSAI website https://www.fssai.gov.in/.
- Photo ID Proof: A valid government-issued photo ID (PAN Card, Aadhaar Card, Voter ID, etc.) of the food business operator(s).
- Business Constitution Certificate:
- Proprietorship Declaration (for sole proprietors)
- Partnership Deed (for businesses with partners)
- Certificate of Incorporation (for companies)
- Shop & Establishment License or other relevant business registration certificate.
- Proof of Possession of Business Premises: This could be a rental agreement, No Objection Certificate (NOC) from the owner, utility bills (electricity, water), etc.
- Food Safety Management System Plan (FSMS Plan): A documented plan outlining your food safety procedures for ensuring hygiene and quality control.
- List of Food Products: A detailed list of all food items you manufacture, process, or trade.
- Bank Account Information: Details of the bank account associated with your food business.
Additional Documents (Required for Specific Licenses):
- FSSAI State License (Turnover between ₹12 Lakhs and ₹20 Crore):
- Form B: Duly filled and signed application form.
- Processing Unit Plan: A blueprint showcasing the processing unit layout with dimensions and designated areas for each operation (applicable to manufacturers only).
- Directors’/Partners’/Proprietor Details: List with complete contact information and photo IDs.
- Machinery and Equipment List: Details including names, quantities, and installed capacity.
- Authority Letter: A document from the machinery manufacturer nominating a responsible person for the equipment.
- Water Analysis Report: A report confirming the potability of the water used in the process.
- Cooperative Society Certificate (if applicable): A copy of the certificate obtained under the Coop Act 1861 or Multi-State Coop Act 2002 (for cooperative societies).
- FSSAI Central License (Turnover Above ₹20 Crore or Importers/Exporters):
- All documents required for the State License (mentioned above).
- Ministry of Commerce Certificate (for 100% Export Oriented Units – EOU): A certificate issued by the Ministry of Commerce for EOUs.
- NOC/PA from FSSAI: A No Objection Certificate (NOC) or Prior Approval (PA) document issued by FSSAI (depending on the scenario).
- Import/Export (IE) Code: A document issued by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) for import/export activities.
- Form IX: A specific form required for central license applications.
- Ministry of Tourism Certificate (for hotels): A certificate issued by the Ministry of Tourism (applicable to hotels seeking a central license).
- Turnover and Transportation Proof: Supporting documents that demonstrate your business turnover and transportation details.
- Declaration Form: A signed declaration form as per FSSAI requirements.
FSSAI License Costs
The cost of acquiring a FSSAI license varies depending on your business size and operations.
FSSAI Registration Fee:
This is the most basic tier of FSSAI compliance. It’s ideal for small, home-based businesses or those with a turnover of less than Rs. 12 lakh annually. The FSSAI Basic Registration fee is a minimal Rs. 100 per year.
FSSAI State License Fee:
As your business scales up, you’ll likely need a State License. This applies to businesses with a turnover between Rs. 12 lakh and Rs. 20 crore annually. The FSSAI State License fee ranges from Rs. 2,000 to Rs. 5,000 per year, depending on the specific category of your food business.
FSSAI Central License Fee:
This license is required for large food businesses with a turnover exceeding Rs. 20 crore annually, or those involved in inter-state operations, or exports. The FSSAI Central License has a fixed fee of Rs. 7,500 per year.
Additional Points to Consider:
- The fees mentioned above are for a one-year license period. Renewal fees are typically the same as the initial application fee. Businesses must apply online for renewal, 30 days before the expiry of the current license.
- In case you require a duplicate license/certificate due to loss or damage, you’ll need to pay 10% of the applicable license fee.
Navigate FSSAI Registration with ease Let’s Talk
Tracking Your FSSAI Registration Status
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) keeps applicants informed throughout the registration process. Checking the FSSAI registration status is easy via the portal.
Monitoring Your Application Status
The FSSAI provides multiple ways to check your application status:
- SMS/Email Alerts: The FSSAI will send alerts via SMS or email at crucial stages of your application’s processing. These alerts keep you informed and ensure you don’t miss any critical updates.
- FoSCoS Website: You can actively track your application status on the Food Safety Central System (FoSCoS) website, the official FSSAI online portal. To do this, follow these steps:
- Visit the FoSCoS website (https://foscos.fssai.gov.in/).
- Go to the “Track Applications” tab.
- Enter your 17-digit application reference number, which you received upon submitting your application.
- Click “Search” to view the current status of your application.
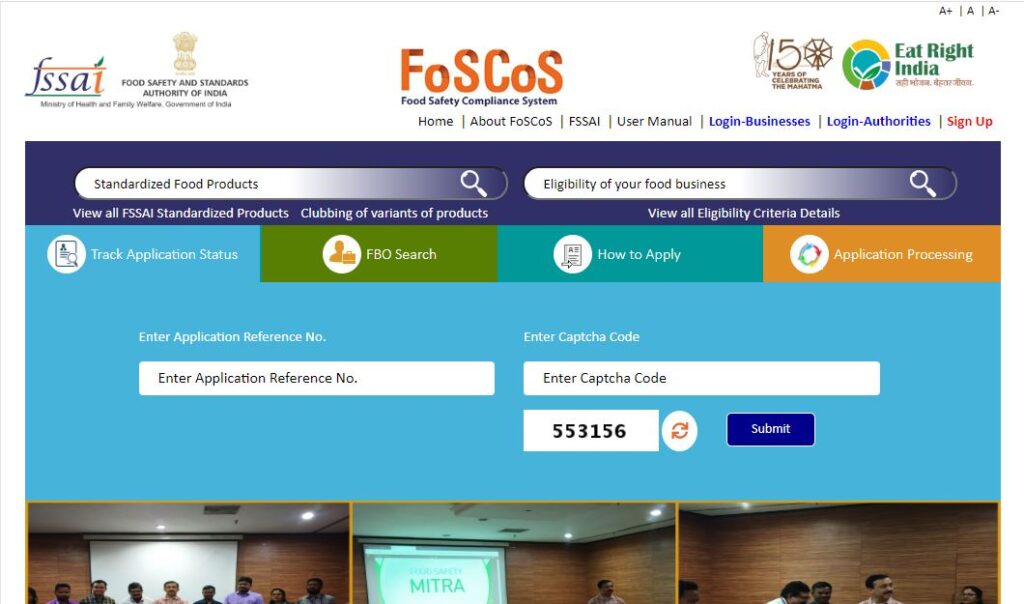
Understanding the FSSAI Registration Statuses
The FoSCoS portal displays your application status using various terms. Let’s explore what each status signifies:
- Submitted: This indicates that the FSSAI has received your application and is initiating the processing procedures.
- Under Scrutiny: The FSSAI is reviewing your application to ensure it meets all the necessary requirements.
- Information Required: The FSSAI requires additional information or clarification regarding your application. You’ll receive details about the required information through an SMS/email alert or within the application status itself on the FoSCoS portal. Respond promptly to avoid delays.
- Application Reverted: This status signifies that the FSSAI has identified some inconsistencies or missing information in your application. They have reverted the application for necessary modifications or clarifications. You’ll be given 30 days from the reverted date to address these concerns and resubmit your application. Failure to respond within the timeframe can lead to application rejection.
- Approved: Congratulations! Your application has been approved by the FSSAI.
- Registration Certificate Issued: This is the final stage, indicating that the FSSAI has issued your FSSAI registration certificate. You can download the certificate by logging into your FoSCoS account.
Benefits of Getting a FSSAI Food License
The license, issued by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), unlocks a multitude of benefits that can propel your business towards success.
- Legal Compliance and Peace of Mind: Operating without an FSSAI license is a punishable offense. The license ensures you adhere to all the regulations set forth by the FSSAI, safeguarding you from hefty fines and penalties.
- Building Trust and Brand Reputation: The FSSAI license signifies your commitment to food safety and hygiene. Displaying the FSSAI logo on your products and the registration number at your premises acts as a badge of honor for your customers.
- Enhanced Market Access and Growth Potential: An FSSAI license opens doors to new business opportunities. It becomes easier to secure licenses for operating in larger markets, participate in trade fairs, and collaborate with bigger retailers.
- Investor Confidence and Funding Opportunities: Investors are more likely to consider funding a business that demonstrates a commitment to quality and legal compliance.
- Improved Supply Chain Management: The FSSAI regulations guide not only food production but also storage, distribution, and import/export. By adhering to these guidelines, you establish a more robust and efficient supply chain.
- Promoting Food Safety and Consumer Awareness: The FSSAI’s core mission is to ensure food safety for all consumers in India. By obtaining a license, you become part of this vital initiative.
To wrap things up, acquiring an FSSAI food license is an investment in the future of your food business. It’s a mark of quality, a symbol of trust, and a key that opens up a world of possibilities for growth and success.
Non-Compliance for FSSAI Registration
Any business operator involved in the food industry, from manufacturing and processing to storage, distribution, and sale, must comply with the regulations set forth under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 (FSS Act). Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in significant consequences.
Inspections and Compliance Levels:
FSSAI designates Food Safety Officers (FSOs) to conduct regular inspections of food business operator (FBO) facilities. During these inspections, the FSO utilizes a checklist to assess the FBO’s adherence to regulations. Based on the findings, the inspection report reflects one of the following compliance levels:
- Compliance (C): The FBO adheres to all applicable regulations.
- Non-compliance (NC): The FBO fails to meet specific regulations.
- Partial Compliance (PC): The FBO meets some, but not all, of the regulations.
- Not Applicable/Not Observed (NA): Certain regulations are not applicable to the FBO’s specific operation, or the FSO could not observe adherence due to limitations during the inspection.
Improvement Notices and License Cancellation:
If the inspection reveals non-compliance (NC) or partial compliance (PC), the FSO may issue an improvement notice under Section 32 of the FSS Act. This notice specifies the areas where the FBO must improve and outlines a timeframe for achieving compliance.
Non-compliance with the improvement notice can lead to serious consequences. The FSO, after providing the FBO with an opportunity to explain their position, may cancel the FBO’s license to operate. This effectively shuts down the business.
Appeal Process:
FBOs who disagree with an improvement notice have the right to appeal. The appeal process involves submitting a petition to the State Commissioner of Food Safety. If the FBO remains unsatisfied with the Commissioner’s decision, they can further escalate the appeal to the Food Safety Appellate Tribunal or even the High Court.
Fines and Imprisonment:
Beyond license cancellation, non-compliance with FSSAI regulations can also result in hefty fines. The penalty amount varies depending on the nature and severity of the violation. In some cases, particularly those involving the sale of unsafe food that causes harm to consumers, the FBO may face imprisonment alongside a fine.
Maintaining Compliance:
Understanding the potential consequences of non-compliance serves as a strong motivator for FBOs to prioritize adherence to FSSAI regulations. By following best practices for food safety, sanitation, labeling, and licensing, FBOs can ensure the safety of consumers and avoid the significant disruptions caused by non-compliance issues.
Fines and Penalties for FSSAI Non- Compliance
| Sl. No. | Particulars | Fine Amount |
| 1 | Food quality not in compliance with the Act | Up to ₹ 2 Lakh |
| 2 | Sub-standard food | Up to ₹ 5 Lakh |
| 3 | Misbranded Food | Up to ₹ 3 Lakh |
| 4 | Misleading advertisement or false description | Up to ₹ 10 Lakh |
| 5 | Extraneous matter in food | Up to ₹ 1 Lakh |
| 6 | Failure to comply with Food Safety Officer direction | Up to ₹ 2 Lakh |
| 7 | Unhygienic processing or manufacture | Up to ₹ 1 Lakh |
| 8 | Operating without a valid FSSAI License | Up to ₹ 5,00,000 |
| 9 | Sale of Adulterated Food | Up to ₹ 5,00,000 |
| 10 | Offenses Leading to Public Harm (e.g., food poisoning outbreak) | Variable (may include imprisonment alongside fines) |
Sample FSSAI Registration Certificate

Frequently Asked Questions on FSSAI Registration
Q: How can I download my FSSAI registration certificate?
A: Once your FSSAI registration is issued, navigate to the Issued tab on your FoSCoS portal dashboard to download your certificate.
Q: What information does the FSSAI registration certificate contain?
A: The certificate provides key details about your business, including your business name and address, food business location, business type, and the validity period of your registration.
Q: How long is an FSSAI license valid for?
A: The validity of your FSSAI license can range from 1 to 5 years, depending on the specific license type you hold and the food products your business deals with.
Q: How do I renew my FSSAI registration/license?
A: To avoid needing a whole new application, ensure you renew your FSSAI registration/license well before the expiry date. Renew your certificate at https://foscos.fssai.gov.in/
Q: What are the FSSAI renewal fees?
A: The FSSAI renewal fees depend on the type of license you hold:
- Basic FSSAI License (Registration): Rs 100 to Rs 500 (varies depending on the number of renewal years chosen).
- Central FSSAI License: Rs 7500 per year.
Q: Are there any additional fees associated with FSSAI renewal?
A: There is a Rs 100 application fee for all FSSAI renewals.
Q: Can I convert a manually issued license to online during renewal?
A: Yes, you can! Contact the designated officer to create a user ID and facilitate the conversion of your license to the online system.
Q: What are the different FSSAI license categories?
A: The FSSAI offers a tiered licensing system based on your business’s turnover and production capacity. There are three categories:
- Basic FSSAI Registration: For businesses with an annual turnover below Rs. 12 lakh.
- State FSSAI License: For businesses with a turnover between Rs. 12 lakh and Rs. 20 crore.
- Central FSSAI License: For large businesses with a turnover exceeding Rs. 20 crore per year.
Q: Do medical stores selling dietary products need an FSSAI license?
A: Yes. All food businesses selling food products, including dietary foods and nutraceuticals, require a valid FSSAI license regardless of their category.
Q: Can I modify my FSSAI license information?
A: Yes, you can apply for modifications to your license information, such as a change of address. However, processing fees might be applicable.
Q: What is an improvement notice, and who issues it?
A: A Designated Officer from FSSAI issues an improvement notice if your business is found to be non-compliant with food safety regulations. This notice specifies the areas requiring improvement.
Q: When can my license be suspended?
A: The FSSAI Designated Officer has the authority to suspend your license if you fail to address the issues highlighted in an improvement notice within the given timeframe.
Q: Can I appeal an improvement notice, suspension, or cancellation?
A: Yes. You have the right to appeal against an improvement notice, suspension, or even cancellation of your license. Appeals can be filed with the State Commissioner of Food Safety or higher authorities within the prescribed time frame.

