Introduction to Convertible Debentures
What Are Convertible Debentures?
Convertible debentures are financial instruments issued by companies that start as debt but offer the unique option to convert into equity shares after a specified period or under certain conditions. Essentially, they are hybrid securities combining the features of both debt and equity. The holder receives fixed interest payments like traditional debentures, but also gains the potential benefit of owning shares in the company by converting the debentures into equity.
This dual nature provides investors with a safety net of fixed returns while also offering the upside of participating in the company’s growth through equity conversion. The conversion terms, including the price and ratio, are predefined at issuance, ensuring transparency and clarity for investors.
Convertible Debentures Meaning and Their Role in Corporate Finance
In corporate finance, convertible debentures serve as a strategic tool for companies looking to raise capital without immediate dilution of ownership. They allow firms to secure debt financing with the promise of future equity conversion, providing flexibility in managing capital structure and balancing debt-equity ratios.
For investors, convertible debentures present a compelling option to earn steady interest income coupled with the possibility of capital appreciation. They are particularly attractive in scenarios where investors seek lower risk than direct equity investment but want exposure to potential upside.
By issuing convertible debentures, companies can often access funding at lower interest rates compared to non-convertible debt, reflecting the added value of the conversion option. This feature makes convertible debentures an important instrument for growth-oriented businesses and startups aiming to optimize their financing costs while preserving long-term equity capital.
Understanding the Basics: Convertible Debentures Explained
How Convertible Debentures Work
Convertible debentures are essentially debt instruments that give the holder an option to convert their debentures into equity shares of the issuing company, usually after a predetermined period. When an investor purchases a convertible debenture, they lend money to the company and receive regular fixed interest payments, similar to traditional debentures. However, unlike regular debentures, convertible debentures come with a built-in option allowing investors to convert their debt into equity shares at a specified conversion price and ratio.
This conversion feature provides flexibility. If the company’s equity performs well, investors can convert their debentures into shares and benefit from capital appreciation. Conversely, if the share price does not perform favorably, investors may choose to hold onto the debentures, earning fixed interest until maturity.
Difference Between Debentures and Shares
The key difference between debentures and shares lies in their nature and rights:
- Debentures represent a loan made by investors to the company. Debenture holders are creditors and have a fixed income through interest payments. They do not have voting rights or ownership in the company unless they convert their debentures into shares.
- Shares, on the other hand, represent ownership in the company. Shareholders have voting rights and can participate in the company’s profits through dividends and capital gains. However, shares come with higher risk, as returns depend on the company’s performance.
Convertible debentures blend these characteristics by starting as debt and potentially transforming into equity, giving investors the best of both worlds.
Fixed Interest vs Potential Equity Upside
A defining feature of convertible debentures is their combination of fixed income and equity participation potential:
- Fixed Interest: Until conversion, debenture holders receive fixed periodic interest payments, providing a steady income stream regardless of company performance.
- Potential Equity Upside: Upon conversion, investors gain equity shares, enabling them to benefit from the company’s growth and share price appreciation.
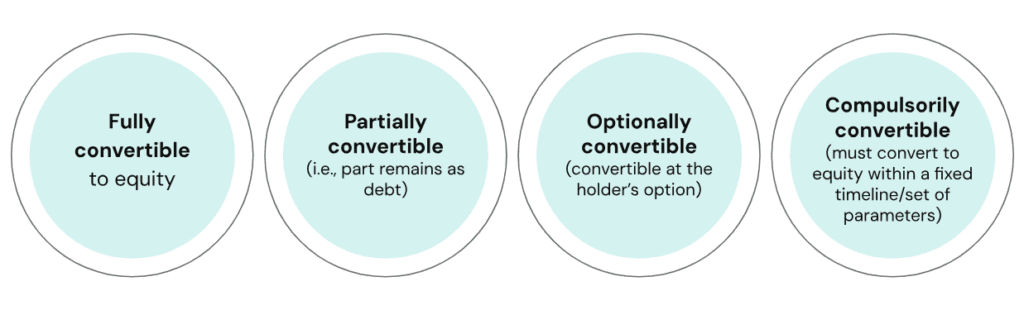
Types of Convertible Debentures in India
Fully Convertible Debentures (FCDs)
Definition:
Fully Convertible Debentures (FCDs) are debt instruments that can be entirely converted into equity shares of the issuing company after a specified period or upon meeting certain conditions. Unlike partly convertible debentures, the entire principal amount converts into shares, eliminating the debt component post-conversion.
Conversion Mechanics:
At the time of issuance, the conversion ratio and conversion price are fixed. Upon maturity or at the investor’s option (based on the terms), FCD holders convert their debentures fully into equity shares. This process increases the company’s share capital as the debt portion is completely converted.
Impact on Company Equity:
Issuing FCDs leads to dilution of existing shareholders’ equity since new shares are issued upon conversion. However, it improves the company’s debt-equity ratio by replacing debt with equity, enhancing the company’s financial stability and creditworthiness.
Legal Reference:
The issuance and conversion of FCDs are governed by the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013, particularly those related to the issuance of debentures and allotment of shares. Compliance with SEBI (Issue and Listing of Debt Securities) Regulations is also essential for listed companies or public offerings of FCDs.
Partly Convertible Debentures (PCDs)
Definition:
Partly Convertible Debentures (PCDs) are hybrid instruments where only a portion of the debenture amount is convertible into equity shares, while the remaining portion continues as a debt instrument until maturity.
Portion Convertible vs Non-Convertible:
For example, a PCD might be structured so that 60% of the amount is convertible into shares, and 40% remains as a non-convertible debenture that pays fixed interest and is redeemed in cash at maturity.
Benefits for Issuers and Investors:
PCDs allow companies to raise capital while controlling equity dilution. For investors, PCDs provide a balance of fixed income (from the non-convertible portion) and the opportunity for capital gains via conversion of the convertible portion.
Legal Reference:
PCDs are subject to the regulations under the Companies Act, 2013, applicable to debentures. The convertible portion is further governed by regulations pertaining to the allotment of shares, and if listed, SEBI regulations related to debt securities apply to the non-convertible portion.
Compulsory Convertible Debentures (CCDs)
Meaning and Mandatory Conversion:
Compulsory Convertible Debentures (CCDs) are debentures that must be converted into equity shares after a predetermined period. Unlike optionally convertible debentures, the conversion is not at the investor’s discretion but mandated by the terms of issuance.
Regulatory Context in India:
In India, CCDs are popular in startup funding and venture capital deals because they comply with regulatory requirements related to foreign direct investment (FDI) and pricing norms. SEBI and RBI guidelines regulate their issuance, ensuring that conversion pricing and timelines adhere to legal frameworks. CCDs help maintain compliance with equity investment norms while providing structured financing.
Legal Reference:
CCDs are significantly influenced by regulations related to foreign direct investment (FDI) in India, governed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulations, including the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999, and related circulars on pricing and reporting requirements. The Companies Act, 2013, also governs the conversion of debentures into shares. SEBI regulations may apply if the CCDs are listed or publicly offered.
Optionally Convertible Debentures (OCDs)
Conversion at Investor’s Discretion:
Optionally Convertible Debentures (OCDs) give the investor the choice to convert the debentures into equity shares within a specified period or continue to hold them as debt.
Key Considerations:
The flexibility benefits investors by allowing them to time conversion based on market conditions or company performance. However, this optionality can pose uncertainty for the company’s capital structure and future equity dilution.
Legal Reference:
The issuance and potential conversion of OCDs are governed by the Companies Act, 2013. SEBI regulations related to debt securities and equity issuances become applicable if the OCDs are listed or offered to the public. The optional nature of conversion adds a layer of complexity in terms of compliance with share allotment regulations.
Non-Convertible Debentures (NCDs)
Definition and Characteristics:
Non-Convertible Debentures (NCDs) are debt instruments that do not carry any option for conversion into equity shares. Investors receive fixed interest payments and the principal amount is repaid on maturity.
Contrast with Convertible Debentures:
Unlike convertible debentures, NCDs provide no opportunity for equity participation or capital appreciation through conversion. They generally offer higher coupon rates to compensate for the lack of conversion benefits.
Summary Table: Types of Debentures and Key Features
| Type of Debenture | Conversion Feature | Equity Dilution Impact | Interest Rate | Conversion Timing | Investor Option |
| Fully Convertible Debentures (FCDs) | 100% convertible | High | Generally lower | At maturity or option | Conversion mandatory/optional per terms |
| Partly Convertible Debentures (PCDs) | Partially convertible | Moderate | Moderate | At maturity or option | Partial conversion |
| Compulsory Convertible Debentures (CCDs) | Mandatory conversion | High | Generally lower | At predetermined date | No option; conversion mandatory |
| Optionally Convertible Debentures (OCDs) | Conversion at investor’s discretion | Variable | Typically moderate | Within conversion window | Investor discretion |
| Non-Convertible Debentures (NCDs) | No conversion | None | Higher than convertible | N/A | No option |
Key Features of Convertible Debentures
Unsecured Nature of Convertible Debentures
Convertible debentures are generally unsecured instruments, meaning they are not backed by specific company assets as collateral. Investors rely on the company’s creditworthiness and future prospects rather than tangible security. This contrasts with secured debentures, which offer asset-backed protection.
Coupon (Interest) Rate Differences Compared to NCDs
Because of the added benefit of conversion into equity, convertible debentures typically offer a lower coupon (interest) rate than Non-Convertible Debentures (NCDs). The potential for capital appreciation via conversion compensates investors for accepting a lower fixed return.
Conversion Price and Ratio Explained
The conversion price is the predetermined price at which a convertible debenture can be exchanged for equity shares. The conversion ratio determines how many shares an investor receives per debenture. These terms are fixed at issuance to provide clarity and predictability for both the company and investors.
Maturity and Conversion Period
Convertible debentures have a maturity period—often ranging from 1 to 5 years—after which the holder can convert the debentures into shares or receive repayment if conversion is not exercised. The conversion window specifies the time frame during which conversion can occur.
Priority in Company Liquidation
Convertible debenture holders generally have a higher claim on company assets than equity shareholders in liquidation, but this is subject to the specific terms of the debenture issuance and applicable insolvency laws.
Benefits of Investing in Convertible Debentures
Regular Fixed Income Through Interest Payments
One of the primary benefits of convertible debentures is the provision of regular, fixed interest payments until conversion or maturity. This steady income stream appeals to investors seeking predictable returns alongside growth opportunities.
Potential for Capital Appreciation via Conversion to Equity
Convertible debentures offer investors the option to convert their debt holdings into equity shares, enabling participation in the company’s upside potential. This feature provides a chance for capital appreciation, especially if the company’s stock price rises significantly.
Lower Risk Compared to Direct Equity Investment
Compared to investing directly in equity shares, convertible debentures carry lower risk. Investors receive fixed interest payments and have priority over equity shareholders during liquidation, providing downside protection while retaining upside exposure through conversion.
Priority Over Shareholders in Liquidation
In the event of liquidation, convertible debenture holders have a higher claim on company assets than equity shareholders, enhancing investment security. This priority reduces the risk of total capital loss compared to pure equity investments.
Tax Implications Overview
Interest earned on convertible debentures is typically taxed as income, while gains from conversion may be subject to capital gains tax, depending on holding periods and specific tax laws. Investors should consider these tax implications when evaluating returns from convertible debentures.
How Convertible Debentures Are Used by Companies in India
Raising Capital with Flexible Financing Options
Companies in India widely use convertible debentures as a versatile tool to raise capital. They provide an attractive alternative to traditional equity or debt by combining fixed returns with the option of future equity conversion. This flexibility helps companies access funds for expansion, working capital, or strategic investments while delaying immediate equity dilution.
Managing Dilution of Ownership
By issuing convertible debentures, companies can control the timing and extent of equity dilution. Since conversion happens at a later date, founders and existing shareholders can maintain control during critical growth phases. This phased approach to equity issuance aids in managing ownership stakes effectively.
Regulatory Compliance Overview (SEBI, RBI)
The issuance of convertible debentures in India is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Companies must adhere to prescribed guidelines on pricing, disclosure, and investor protection. Compliance ensures transparency and legal validity, particularly for listed companies and those raising funds from the public or foreign investors.
Role of Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR)
Indian companies issuing convertible debentures are required to create a Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR) as mandated by the Companies Act, 2013. The DRR ensures that sufficient funds are earmarked to repay debenture holders at maturity or upon conversion, safeguarding investor interests and enhancing corporate creditworthiness.
Important Considerations and Risks of Convertible Debentures
Impact of Share Price Fluctuations on Conversion Value
The conversion value of convertible debentures depends heavily on the company’s share price at the time of conversion. Significant fluctuations can affect the attractiveness of conversion. If the share price falls below the conversion price, investors may forgo conversion, limiting potential gains.
Dilution Risk for Existing Shareholders
When convertible debentures convert into equity shares, it leads to dilution of ownership for existing shareholders. This dilution can impact voting power and earnings per share, which may concern founders and current investors.
Lower Coupon Rates Compared to NCDs
Convertible debentures generally offer lower coupon rates than non-convertible debentures (NCDs) because of the added benefit of potential equity conversion. Investors need to balance fixed income with conversion upside.
Company Credit Risk
Since convertible debentures are often unsecured, investors bear the company’s credit risk. If the company faces financial distress, interest payments and principal repayment may be jeopardized.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Framework
Issuance and conversion of convertible debentures are subject to regulations by SEBI, RBI, and the Companies Act. Non-compliance can lead to legal complications, impacting investor rights and company operations.