What is Financial Modeling for Startups?
The process of projecting and predicting revenue, customers, workers, costs, etc. into the future in order to comprehend and evaluate the profitability and feasibility of the firm is known as financial modeling for startups. Since the firm is still in its early stages, this modeling will assist in creating the budget and business plan that they will be able to show to possible investors. Additionally, financial modeling helps startups monitor their performance against the financial plan by identifying areas of underperformance. This allows them to make the necessary adjustments to their strategy to ensure long-term sustainability and success. Finally, financial modeling helps startups set realistic goals for revenue growth and profitability. Therefore, entrepreneurs may ensure a bright and secure future for their organisation by developing a robust financial strategy. It considers revenue estimates, costs, and historical performance. A financial model aids in the informed decision-making of corporate stakeholders. Financial models are used by bankers, credit analysts, accountants, valuation advisers, and research analysts to assess a company’s financial viability.
A financial model is simply a tool that’s built-in Excel to forecast a business’ financial performance into the future. The forecast is typically based on the company’s historical performance, assumptions about the future, and requires preparing an income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Financial modeling is the process of estimating the financial performance of a company or business by taking into account all relevant factors, including growth and risk assumptions, and interpreting their impact. It enables the user to acquire a concise knowledge of the current financial position of the company and its projected growth, and a clear understanding of the financial forecasts.
Advantages of building a financial model for startups
There are multiple advantages given by financial modeling for startups which are as follows:
- Planning and Forecasting of Finances
Making precise financial estimates and projections is the goal of financial modeling for startups. It aids in both comprehending possible financial results and helping to create reasonable goals for the company. It enables startup owners to prepare for various contingencies and make well-informed choices depending on anticipated financial success. - Investing and Communicating with Investors
It’s true that startups frequently need to raise money in order to expand. A thorough understanding of the company’s development potential, financial stability, and predicted profits is offered by a well-built financial model. It primarily serves to increase the startup’s credibility while pitching to possible investors. This indicates a deep comprehension of the monetary components of the nature of business. - Planning for Resources and Capital Allocation
The best possible use of financial resources is made possible via financial modeling. Startups can find areas of high profitability, cost inefficiencies, and cash flow bottlenecks by examining the financial predictions. This facilitates their ability to deploy resources in a strategic manner, make well-informed investment decisions, and efficiently manage cash flow. - Evaluation and Reduction of Risks
Startups may use financial modeling to undertake sensitivity analysis and evaluate how different risks and uncertainties affect the financial success of their company. Through the process of recognising possible risks and their associated financial repercussions, entrepreneurs may create backup plans and lessen the likelihood of unfavourable outcomes. - Evaluation and Outcome Plan
Financial modelling is essential for figuring out a startup’s valuation when it comes to potential exit strategies like acquisitions or initial public offerings (IPOs). Startups can assess their worth and get better terms during investment rounds or exit talks by projecting their future financial performance. - Monitoring and Accountability of Performance
In order to assess the real financial performance of the business, a financial model acts as a benchmark. By regularly updating the model with real financial data, business owners are able to track the company’s development, spot deviations from the plan, and move quickly to address them. It makes proactive decision-making easier and improves responsibility. - Making Strategic Decisions
For startups, financial modeling offers an organized framework for assessing strategic choices. This enables business owners to evaluate the financial effects of different choices, including the introduction of new products, market expansions, price adjustments, infrastructure improvements, and technological investments. Making educated judgments that support the startup’s financial goals is another benefit.
Sample Financial Model for Startups
To ease the effort, Treelife is sharing a sample format of the financial model, which assists the founders/others to work out the outcome at one go. We believe that a financial model example should be clear, self-explanatory, and very pragmatic in its approach.
Download the Financial Model Worksheet by Treelife here.
Why should you use a Financial Model?
The output of a financial model is used for decision making and performing financial analysis, whether inside or outside of the company. Inside a company, executives will use financial models to make decisions about:
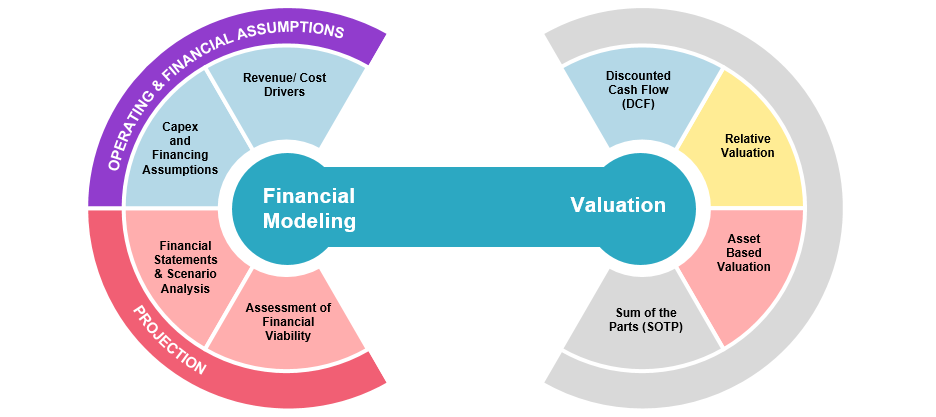
Types of Financial Model
Startups can use a variety of financial modeling techniques, some of which are listed below, to assess various elements of their business:
- Model for Forecasting Revenue
The main goal of this model is to project future startup income streams. To predict sales statistics over a certain time period, it considers variables including growth rates, pricing strategy, market size, and client acquisition. Models for revenue forecasting assist startups in assessing their future revenue and making plans appropriately. - Expense Model
An expenditure model aids in the estimation and monitoring of operational costs for a startup. Together with variable costs like marketing expenditures and cost of goods supplied, it mostly consists of fixed costs like utilities, payroll, rent, and so forth. Expense models assist startups in determining their cost structure, prospects for cost savings, and efficient cash flow management. - Model of Cash Flow
Because it evaluates the availability and timing of capital inflows as well as withdrawals, the cash flow model is crucial for startups. A cash flow model follows every transaction that occurs in the business’s cash flow. This covers elements like financial commitments, outlays, earnings, and other funding sources. It helps new businesses to prepare ahead for any financial constraints, manage their cash flow, and making informed decisions about funding requirements - Valuation Model
The value of a startup is ascertained using valuation models. The process of estimating a business’s worth takes into account a number of variables, including market dynamics, financial performance, growth potential, and similar firm values. Startups may utilize valuation models to better understand their present worth, which is helpful when seeking funding, having M&A talks, or thinking through exit possibilities. - Fundraising and Financing Models
Funding is necessary for startups to sustain their expansion. The selection of funding choices, such as debt financing, equity financing, or government subsidies, is aided by finance and fundraising models. These models are useful for understanding how various funding possibilities affect company characteristics including ownership dilution, capital structure, and financial indicators. - Investment Models and ROI
Investment models and ROI (Return on Investment) assess the prospective profits and financial viability of certain projects or investment possibilities. These models may be used by startups to evaluate the feasibility of introducing new products, making infrastructure investments, or entering new markets. Prioritizing resource allocation and making educated investment decisions are made easier with the use of ROI and investment models.
Methods Used in Financial Modelling
Financial modelling may be done in a variety of ways, depending on the particular demands and specifications of a business. Four popular methods for financial modelling that have been considered are as follows:
- Analyzing Historical Data
This kind of strategy includes looking at previous financial data, which aids in understanding the performance and patterns of the companies in the past. It comprises compiling financial accounts, transaction records, and other pertinent information from earlier time periods. Startups are able to estimate future financial success by using patterns, growth rates, and seasonality that may be found in past data. - Bottom-Up Method
The financial model is constructed using the bottom-up method, taking into account certain operational factors and hypotheses. Startups begin by projecting several aspects of their business, such as average revenue per client, units sold, and the number of customers. Then, cash flow, revenue, and costs are computed using these assumptions. This methodology facilitates a finer-grained examination and an in-depth comprehension of the many influences on the financial statements. - Modelling Based on Scenarios
The creation of several financial models based on several scenarios or hypotheses is facilitated by scenario-based modelling. Startups can analyse the possible financial results under various conditions and create best-case, moderate-case, and worst-case scenarios. With this specific strategy, companies may evaluate their financial stability and make plans for a range of unforeseen events. It also aids in assessing the influence. It also aids in assessing how adjustments to important variables or outside influences affect the company’s financial performance.
Building a Startup Financial Model (Step-by-Step Guide)
- Collect Information and Data
First, gather all pertinent startup-related financial and non-financial data. This contains any other information required to comprehend the company and its activities, such as financial statements, market research, historical transaction records, and industry benchmarks. - Describe the Goal of the Model
Make sure you understand the goals and parameters of the startup finance model. Ascertain the model’s unique queries or scenarios, such as those pertaining to finance needs, revenue forecasts, or value analyses. This will assist in directing the financial model’s emphasis and structure. - Make Decisions Using the Model
Make decisions by using the financial model as a tool. It is for determining the effects of strategic decisions, analysing various situations, and coming to well-informed conclusions regarding the operations, expansion plans, and funding requirements of the business. A startup’s changing demands might be better met by having the model reviewed and updated on a frequent basis. - Project Outlay of Funds
Calculate the startup’s operational costs, which include fixed costs like utilities, rent, payroll, etc., as well as variable costs like cost of goods sold, marketing, etc. Divide spending into appropriate categories, then create formulae or computations to forecast spending in the future based on the determined hypotheses. - Make a statement of profit and loss.
Make a profit and loss (P&L) statement that lists the startup’s costs, earnings, and profitability for a given time period, preferably monthly or annually. Make sure that the P&L statement appropriately reflects all income and expense elements, such as taxes, depreciation, and interest costs. - Construct a Cash Flow Forecast
Create a cash flow prediction that estimates your costs and income. Cash inflows from investments, financing operations, and income must be included in this prediction, as well as cash outflows for capital expenditures, debt repayment, and costs. Take into account the cash flow schedule and budget for any potential gaps in the cash flow. - Create a Balance Sheet
Create a balance sheet that lists the assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity for the startup. Assets and liabilities, including cash, inventory, accounts receivable, debt, and equity, must be included. Over time, take into account further changes in assets and liabilities to make sure the balance sheet stays in balance. - Record Assumptions and Techniques
Provide a detailed account of all the methods, computations, and assumptions that went into the financial model. The ease of updating, transparency, and comprehension of the model by others are all ensured by this documentation. - Verify and Enhance
By comparing the forecasts to actual facts and making necessary adjustments to the assumptions, you can continuously evaluate and improve the financial model. Add real financial data to the model and evaluate how accurate the forecasts are. Update the financial model on a regular basis to account for fresh data or modifications to the startup’s situation. - Perform an analysis of sensitivity.
To find out how changes to important variables and assumptions would affect the financial model, perform sensitivity analysis. Examine various situations and determine how adjustments to income, costs, or other factors impact the startup’s cash flow and financial success. This analysis aids in determining the most important risks and drivers.
Assumptions employed in Financial Modeling
The financial modelling for startups is based on the following assumptions:
- Cost Presumptions
The price at which the startup will sell its goods or services is determined in part by these pricing assumptions. Value-based pricing, cost-plus pricing, competitive analysis, and any other pertinent variables serve as the foundation for this. Pricing hypotheses need to take into account the target market, positioning, and profitability goals of the company. - Growth Rate of Revenue
For the purpose of forecasting future sales, revenue growth rate assumptions are made. This is predicated on past performance, market research, industry trends, or the development plan of the startup. It is crucial to take into account elements like price strategy, client acquisition, market share, and prospective market expansion. - Working Capital Premises
Estimating the startup’s short-term assets and liabilities is made easier with the aid of working capital assumptions. Inventory, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and other operating assets and liabilities are included in this. Working capital predictions are influenced by assumptions regarding supplier relationships, inventory turnover, payment terms, and collection timeframes. - Tax Presumptions
Estimating the relevant tax rates and any tax breaks or incentives that the startup may be eligible for is made easier with the use of tax assumptions. Depending on the jurisdiction and the startup’s eligibility for particular tax incentives, different tax assumptions may apply. - Financial Premises
Monitoring anticipated capital inflows and outflows is made easier with the use of financing assumptions. Assumptions on debt financing, equity financing, and other funding sources may be included in this. In order to evaluate the effects, startups must estimate the terms, time, and quantity of funding operations. - Running Costs
When predicting the startup’s cost structure, operating expense assumptions are crucial. Assumptions regarding wages, rent, utilities, marketing expenditures, administrative fees, and any other operational expenses are included in this. When assessing these costs, startups might take into account anticipated investments, industry benchmarks, or previous data. - Investments in Capital
Assumptions made about capital expenditures are related to investments made in long-term assets including machinery, infrastructure, technology, and buildings. Based on their expansion goals and operational needs, startups must project the time and cost of capital expenditures. The life expectancy and depreciation of assets must be taken into account.
Why Entrepreneurs should prefer a Financial Model?
Entrepreneurs should concentrate on creating a financial model for a number of reasons :
- It Aids in Making Decisions
An analytical framework in the form of a financial model helps entrepreneurs make well-informed company decisions. It enables people to weigh potential outcomes, determine the financial implications of alternative plans of action, and select the best solutions. A financial model directs entrepreneurs towards making decisions that are consistent with their aims and objectives by helping them comprehend the financial effects of their actions. - Allocation of Resources
A financial model aids entrepreneurs in allocating resources as efficiently as possible inside their firm. Entrepreneurs may find inefficiencies, manage cash flow, and deploy resources wisely by predicting revenue, costs, and cash flow. It helps business owners prioritise investments, keep expenditures under control, and make the most use of their existing resources by offering insights into the financial consequences of various options. - Investing and Raising Money
A strong financial model is necessary when looking for outside investment or funding. Financial predictions are usually required by lenders and investors to evaluate the viability and possible return on investment. A strong financial model shows that the entrepreneur is aware of the financial dynamics, potential for growth, and capacity for profit-making of the company. It boosts investor confidence and raises the likelihood of obtaining capital or investment. - Hazard Assessment
A financial model aids in the efficient risk management of enterprises. Through the use of sensitivity analysis and scenario planning, entrepreneurs may get insight into the financial ramifications of several risks, including shifts in market dynamics, pricing strategies, or operational elements. With the use of a financial model, business owners may recognize possible hazards, create backup plans, and decide on the best course of action to reduce them. - Monitoring Performance
When comparing the actual financial performance of a startup to its expectations, a financial model acts as a benchmark. Entrepreneurs are able to track their progress, spot deviations from the plan, and take necessary corrective action by periodically updating the model with real-world data. It helps with performance monitoring, improves accountability, and makes it possible for business owners to quickly resolve any financial problems. - Extended-Term Scheduling
Entrepreneurs may set realistic goals for their firm and prepare for the long run with the help of a financial model. Through the process of financial performance projection, entrepreneurs are able to appraise the viability of their company ideas, analyse methods for expansion, and determine the necessary funds to reach their goals. A financial model helps entrepreneurs create a precise and workable strategy by acting as a roadmap for the startup’s financial future. - Monitoring Performance
When comparing the actual financial performance of a startup to its expectations, a financial model acts as a benchmark. Entrepreneurs are able to track their progress, spot deviations from the plan, and take necessary corrective action by periodically updating the model with real-world data. It helps with performance monitoring, improves accountability, and makes it possible for business owners to quickly resolve any financial problems. - Extended-Term Scheduling
Entrepreneurs may set realistic goals for their firm and prepare for the long run with the help of a financial model. Through the process of financial performance projection, entrepreneurs are able to appraise the viability of their company ideas, analyse methods for expansion, and determine the necessary funds to reach their goals. A financial model helps entrepreneurs create a precise and workable strategy by acting as a roadmap for the startup’s financial future. - Strategies for Valuation and Exit
When seeking funding, forming alliances, or thinking about exit strategies, entrepreneurs frequently need to estimate the startup’s worth. By anticipating future financial performance, cash flow, and profitability, a financial model is essential to determining the startup’s worth. By giving them knowledge of the financial factors that influence valuation, it enables business owners to make well-informed choices regarding expansion, funding, and possible exits.
Conclusion
The financial model in India is utilized in a number of stages in the operations of the entities. It combines finance, accounting, and business metrics to create a mathematical representation of the growth prospects of the entity. Financial modeling is a highly valued tool and benefits the entity in numerous ways


