Blog Content Overview
- 1 Treelife Resources
- 1.1 Explore our resources to fuel your success and propel your business forward.
- 1.2 Latest Posts
- 1.2.0.1 IIT-M start-up Planys Technologies raises ₹43 crore in round led by investor Ashish Kacholia
- 1.2.0.2 VitusCare Raises $2.7M in Series A Funding
- 1.2.0.3 Doctrine of Work for Hire
- 1.2.0.4 Demystifying Legal Metrology Rules in India: Ensuring Fairness in Everyday Transactions
- 1.2.0.5 𝐁𝐨𝐨𝐤-𝐤𝐞𝐞𝐩𝐢𝐧𝐠, 𝐀𝐜𝐜𝐨𝐮𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠, 𝐓𝐚𝐱𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧, 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐅𝐢𝐧𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐢𝐚𝐥 𝐂𝐫𝐢𝐦𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐢𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐞 𝐒𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐢𝐜𝐞𝐬 (𝐁𝐀𝐓𝐅) 𝐑𝐞𝐠𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬
- 1.2.0.6 Significance of Governing Law and Jurisdiction in International Commercial Contracts
- 1.2.0.7 Unconscionable Contracts and Related Principles
- 1.2.0.8 Vitality of Disclaimer of Warranty Clause in SaaS Agreements
- 1.3 Thought Leadership
- 1.4 Introduction
- 1.5 What is a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)?
- 1.6 Types of Non-Disclosure Agreements in India
- 1.7 Essential Clauses in an NDA
- 1.8 Non Disclosure Agreements Format
- 1.9 Legal Validity of NDAs in India
- 1.10 Breach of NDAs: Consequences & Remedies
- 1.11 Importance of Customized NDAs for Businesses
- 1.12 FAQs on Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) in India
- 1.12.0.1 1. What is an NDA, and why is it important in business?
- 1.12.0.2 2. What are the types of NDAs commonly used in India?
- 1.12.0.3 3. What happens if someone breaches an NDA in India?
- 1.12.0.4 4. How can businesses draft an effective NDA?
- 1.12.0.5 5. Are NDAs legally enforceable in India?
- 1.12.0.6 7. Why is it essential to customize an NDA instead of using a generic one?
- 1.12.0.7 8. How long does an NDA remain valid?
- 1.12.1 Related posts:
- 1.13 Why SaaS is the Future of Technology
- 1.14 Inside the SaaS Blueprint – Key Highlights
- 1.15 Key Takeaways for Stakeholders
- 1.16 Introduction
- 1.17 What are Mergers and Acquisitions?
- 1.18 Key Differences Between Mergers and Acquisitions
- 1.19 Types of Mergers and Acquisitions
- 1.20 Merger and Acquisition Process
- 1.21 Benefits and Challenges of Mergers and Acquisitions
- 1.22 Recent and Latest Mergers and Acquisitions in India
- 1.23 Legal and Regulatory Framework Governing M&A in India
- 1.24 Examples of Successful M&A Deals in India
- 1.25 Reasons for Mergers and Acquisitions
- 1.26 Future of Mergers and Acquisitions in India
- 1.27 Conclusion
- 1.28 FAQs on Mergers & Acquisitions in India
- 1.28.0.1 1. What is the meaning of mergers and acquisitions in India?
- 1.28.0.2 2. What is the difference between a merger and an acquisition?
- 1.28.0.3 3. What are the main types of mergers and acquisitions?
- 1.28.0.4 4. Why do companies pursue mergers and acquisitions in India?
- 1.28.0.5 6. What are the challenges in the M&A process in India?
- 1.28.0.6 7. How do synergies work in mergers and acquisitions?
- 1.28.1 Related posts:
- 1.29 Introduction
- 1.30 What is LLP in India?
- 1.31 What are Compliances for LLP in India?
- 1.32 Importance of LLP Compliance
- 1.33 One-Time Mandatory Compliance for LLPs
- 1.34 Mandatory Compliances for LLPs in India
- 1.35 Compliances for Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) in India (Checklist)
- 1.36 Benefits of LLP Compliance
- 1.37 Steps to Ensure LLP Compliance
- 1.38 How to File LLP Compliances in India
- 1.39 FAQs on Compliances for Limited Liability Partnership in India
- 1.40 Introduction to Trademark Registration in India
- 1.41 What is Trademark Registration?
- 1.42 Types of Trademarks in India
- 1.43 Procedure for Online Trademark Registration in India
- 1.43.1 Step 1: Choose a Unique Trademark and Conduct a Trademark Registration Search
- 1.43.2 Step 2: Prepare and Submit the Application (Online/Offline)
- 1.43.3 Step 3: Verification of Application and Documents
- 1.43.4 Step 4: Trademark Journal Publication and Opposition
- 1.43.5 Step 5: Approval and Issuance of Trademark Registration Certificate
- 1.43.6 Additional Points to Note
- 1.44 Documents Required for Trademark Registration in India
- 1.44.1 1. Business Registration Proof
- 1.44.2 2. Identity and Address Proof
- 1.44.3 3. Trademark Representation
- 1.44.4 4. Power of Attorney (Form TM-48)
- 1.44.5 5. Proof of Prior Usage (If Applicable)
- 1.44.6 6. Udyog Aadhaar or MSME Certificate
- 1.44.7 7. Class-Specific Details
- 1.44.8 8. Address Proof of Business
- 1.45 Costs and Fees for Trademark Registration in India
- 1.46 How to Check Trademark Registration Status
- 1.47 Common Grounds for Refusal of Trademark Registration in India
- 1.48 Renewing a Trademark in India
- 1.49 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Trademark Registration in India
- 1.50 Introduction
- 1.51 What is a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)?
- 1.52 Types of Non-Disclosure Agreements in India
- 1.53 Essential Clauses in an NDA
- 1.54 Non Disclosure Agreements Format
- 1.55 Legal Validity of NDAs in India
- 1.56 Breach of NDAs: Consequences & Remedies
- 1.57 Importance of Customized NDAs for Businesses
- 1.58 FAQs on Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) in India
- 1.58.0.1 1. What is an NDA, and why is it important in business?
- 1.58.0.2 2. What are the types of NDAs commonly used in India?
- 1.58.0.3 3. What happens if someone breaches an NDA in India?
- 1.58.0.4 4. How can businesses draft an effective NDA?
- 1.58.0.5 5. Are NDAs legally enforceable in India?
- 1.58.0.6 7. Why is it essential to customize an NDA instead of using a generic one?
- 1.58.0.7 8. How long does an NDA remain valid?
- 1.58.1 Related posts:
- 1.59 Introduction
- 1.60 What are Mergers and Acquisitions?
- 1.61 Key Differences Between Mergers and Acquisitions
- 1.62 Types of Mergers and Acquisitions
- 1.63 Merger and Acquisition Process
- 1.64 Benefits and Challenges of Mergers and Acquisitions
- 1.65 Recent and Latest Mergers and Acquisitions in India
- 1.66 Legal and Regulatory Framework Governing M&A in India
- 1.67 Examples of Successful M&A Deals in India
- 1.68 Reasons for Mergers and Acquisitions
- 1.69 Future of Mergers and Acquisitions in India
- 1.70 Conclusion
- 1.71 FAQs on Mergers & Acquisitions in India
- 1.71.0.1 1. What is the meaning of mergers and acquisitions in India?
- 1.71.0.2 2. What is the difference between a merger and an acquisition?
- 1.71.0.3 3. What are the main types of mergers and acquisitions?
- 1.71.0.4 4. Why do companies pursue mergers and acquisitions in India?
- 1.71.0.5 6. What are the challenges in the M&A process in India?
- 1.71.0.6 7. How do synergies work in mergers and acquisitions?
- 1.71.1 Related posts:
- 1.72 Introduction to Trademark Registration in India
- 1.73 What is Trademark Registration?
- 1.74 Types of Trademarks in India
- 1.75 Procedure for Online Trademark Registration in India
- 1.75.1 Step 1: Choose a Unique Trademark and Conduct a Trademark Registration Search
- 1.75.2 Step 2: Prepare and Submit the Application (Online/Offline)
- 1.75.3 Step 3: Verification of Application and Documents
- 1.75.4 Step 4: Trademark Journal Publication and Opposition
- 1.75.5 Step 5: Approval and Issuance of Trademark Registration Certificate
- 1.75.6 Additional Points to Note
- 1.76 Documents Required for Trademark Registration in India
- 1.76.1 1. Business Registration Proof
- 1.76.2 2. Identity and Address Proof
- 1.76.3 3. Trademark Representation
- 1.76.4 4. Power of Attorney (Form TM-48)
- 1.76.5 5. Proof of Prior Usage (If Applicable)
- 1.76.6 6. Udyog Aadhaar or MSME Certificate
- 1.76.7 7. Class-Specific Details
- 1.76.8 8. Address Proof of Business
- 1.77 Costs and Fees for Trademark Registration in India
- 1.78 How to Check Trademark Registration Status
- 1.79 Common Grounds for Refusal of Trademark Registration in India
- 1.80 Renewing a Trademark in India
- 1.81 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Trademark Registration in India
- 1.82 What is a Trademark?
- 1.83 Why is Trademark Registration Important in India?
- 1.84 Key Industries Benefiting from Trademark Registration
- 1.85 Conclusion
- 1.86 Introduction to Trademarks
- 1.87 Background of Trademarks in India
- 1.88 What is a Trademark Class?
- 1.89 Importance of Trademark Classification
- 1.90 Trademark Classification List
- 1.91 List of Trademark Classes of Goods in India (1-34 Classes)
- 1.92 List of Trademark Classes of Services in India (35-45 Classes)
- 1.93 Online Tools available for Classifying Trademarks
- 1.94 Conclusion
- 1.95 FAQs on Trademark Classification in India
- 1.95.0.1 2. How are goods and services categorized under trademark classification?
- 1.95.0.2 3. Why is trademark classification essential during the registration process?
- 1.95.0.3 4. Can a trademark be registered under multiple classes?
- 1.95.0.4 5. What tools are available for trademark classification in India?
- 1.95.0.5 6. How does trademark classification help prevent legal conflicts?
- 1.95.0.6 7. What is the significance of the NICE classification system?
- 1.95.0.7 8. What are the benefits of correct trademark classification?
- 1.95.1 Related posts:
- 1.95.2 Related posts:
- 1.95.3 Related posts:
- 1.95.4 Related posts:
- 1.95.5 Related posts:
- 1.95.6 Related posts:
- 1.95.7 Related posts:
- 1.95.8 Related posts:
- 1.96 MCA Streamlines Cross-border Mergers for Reverse Flipping
- 1.97 Understanding Sovereign Green Bonds
- 1.98 Key Features of the IFSCA’s SGrB Scheme
- 1.99 We Are Problem Solvers. And Take Accountability.
Latest Posts


July 4, 2024 | Deal Street
IIT-M start-up Planys Technologies raises ₹43 crore in round led by investor Ashish Kacholia
Read More






















Thought Leadership



Non Disclosure Agreements in India – NDA Template, Types & Breach
Blog Content Overview
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What is a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)?
- 3 Types of Non-Disclosure Agreements in India
- 4 Essential Clauses in an NDA
- 5 Non Disclosure Agreements Format
- 6 Legal Validity of NDAs in India
- 7 Breach of NDAs: Consequences & Remedies
- 8 Importance of Customized NDAs for Businesses
- 9 FAQs on Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) in India
- 9.0.1 1. What is an NDA, and why is it important in business?
- 9.0.2 2. What are the types of NDAs commonly used in India?
- 9.0.3 3. What happens if someone breaches an NDA in India?
- 9.0.4 4. How can businesses draft an effective NDA?
- 9.0.5 5. Are NDAs legally enforceable in India?
- 9.0.6 7. Why is it essential to customize an NDA instead of using a generic one?
- 9.0.7 8. How long does an NDA remain valid?
Introduction
Security of sensitive business information, protection of intellectual property and trade secrets and trust in collaborations are critical aspects of business security in an increasingly competitive and data-driven market today. It is to this effect that businesses typically execute non disclosure agreement (“NDA”), which imposes a contractual obligation on the party receiving the protected information to not only keep the same confidential but to not disclose or divulge such information without permission from the disclosing party.
NDAs can relate to trade secrets, business models, or intellectual property; all of which help to ensure confidentiality and security in business partnerships. Fundamentally, this agreement ensures that the recipient of such confidential information is obligated to keep the same protected. As such, any breach of an NDA would typically build in mechanisms for compensation for damages caused by the party in breach of the NDA.
Overview of NDAs in Indian Law / Legal Environment
NDAs in India are enforceable as per the Indian Contract Act, 1872. They are very commonly employed across sectors and can be used for purposes ranging from technology/manufacturing to consulting to even labour or critical events requiring protection of sensitive information. An airtight NDA defines what is and is not confidential information, limits the use of such information, and outlines the consequences for a breach of the obligations. NDAs are widely used in India to guard proprietary information involving in commercial transactions, employment, or partnership. NDAs keep the most important business information private by:
- Security of proprietary information from unauthorized use or leakage.
- Developing intellectual property, trade secrets, and business plans protection laws.
- Establishing trust in relationships while going through mergers, acquisitions or negotiations.
NDAs by ensuring confidentiality preserve a business’s competitive edge and eliminate litigation.such as technology, manufacturing, and consulting. NDAs can be unilateral, mutual or multilateral, but for it to be effective they should meet Indian laws. The success of an NDA depends on its definitions, enforceable provisions and jurisdiction. A breach of an NDA can be financially and reputationally disastrous.
What is a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)?
A Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is a legally binding contract designed to safeguard sensitive and proprietary information shared between two or more parties. It establishes a confidential relationship by outlining the type of information that must remain undisclosed, the purpose of sharing the information, and the consequences of any breach. NDAs are integral to protecting intellectual property, trade secrets, and other business-critical data.
Definition of a Non-Disclosure Agreement
In simple terms, an NDA is a formal agreement where one party agrees not to disclose or misuse the confidential information provided by the other party. Colloquially also referred to as a confidentiality agreement, an NDA ensures that the disclosed information is used solely for the intended purpose and remains secure. NDAs are enforceable under the Indian Contract Act, 1872, making them a vital tool in safeguarding sensitive data in India.
Key Purposes and Objectives of NDAs
The primary goal of an NDA is to maintain the confidentiality of information and prevent its unauthorized use. Key objectives include:
- Protecting Intellectual Property: Ensuring that trade secrets, patents, and proprietary processes remain secure.
- Establishing Trust: Building a reliable relationship between parties, particularly in mergers, acquisitions, or joint ventures.
- Avoiding Misuse of Data: Preventing employees, contractors, or partners from sharing confidential details with competitors.
- Defining Legal Recourse: Outlining the consequences of a breach, including penalties and legal actions.
By clearly defining the scope of confidentiality, NDAs reduce the likelihood of disputes and offer a framework for resolution if a breach occurs.
Real-Life Examples of NDA Use in Business Scenarios
NDAs are widely used across various industries and situations, such as:
- Employment Agreements: Employers often require NDAs to protect internal policies, client lists, and proprietary methods from being disclosed by employees.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: During due diligence, NDAs secure sensitive financial and operational data exchanged between companies. This can also include restrictions on disclosure of investment by a party and prevention of any media release (as typically required by incubators).
- Technology and Innovation: Startups and tech companies frequently use NDAs to safeguard unique ideas, algorithms, or software codes when pitching to investors or collaborating with developers.
- Freelance and Consulting Projects: Freelancers or consultants working with confidential client data are bound by NDAs to prevent misuse.
- Vendor or Supplier Relationships: NDAs protect sensitive pricing strategies, product designs, or supply chain details shared with third-party vendors.
For example, a startup seeking funding may share its business model, product specifications and financial projections with potential investors under an NDA, ensuring these details remain confidential and protected from competitors.
Types of Non-Disclosure Agreements in India
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) come in various forms depending on the nature of the relationship and the flow of confidential information between parties. Understanding the types of NDAs is essential for selecting the most suitable agreement to safeguard sensitive information. Typically, an NDA will impose a total ban on disclosure, except where such disclosure is required by law or on order of any statutory authority. Below are the primary types of NDAs used in India:
1. Unilateral NDAs
A Unilateral NDA is a one-sided agreement where only one party discloses confidential information, and the receiving party agrees to protect it. This type of NDA is commonly used when a business shares proprietary information with employees, contractors, or third-party vendors who are not expected to reciprocate with their own confidential data.
Common Use Cases:
- Protecting trade secrets during product development.
- Sharing sensitive business data with potential investors.
- Securing intellectual property shared with a freelancer or consultant.
Example: A tech startup providing details of its proprietary algorithm to a marketing agency under a unilateral NDA.
2. Bilateral/Mutual NDAs
A Bilateral NDA, also known as a mutual NDA, involves two parties sharing confidential information with each other and agreeing to protect it. This type of agreement is ideal when both parties need to exchange sensitive data, such as in partnerships, collaborations, or joint ventures.
Common Use Cases:
- Collaborations between companies on a new product or service.
- Mergers and acquisitions where both entities share financial and operational data.
- Negotiations between two businesses for a potential partnership.
Example: Two pharmaceutical companies working together on developing a new drug may use a mutual NDA to safeguard their research and development data.
3. Multilateral NDAs
A Multilateral NDA is used when three or more parties need to share confidential information among themselves while ensuring mutual protection. This type of NDA simplifies the process by consolidating multiple bilateral agreements into a single document, reducing legal complexities and administrative overhead.
Common Use Cases:
- Consortiums or alliances in large-scale projects like infrastructure development.
- Joint ventures involving multiple stakeholders.
- Collaborative research projects between academic institutions and private companies.
Example: A group of IT companies collaborating on a government project to develop a unified digital platform may use a multilateral NDA to protect their individual contributions.
Essential Clauses in an NDA
A well-drafted Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is only as strong as the clauses it includes. Each clause serves a specific purpose in defining the rights and obligations of the parties, ensuring comprehensive protection of confidential information. Here are the key clauses every NDA should have:
1. Confidentiality Clause
The confidentiality clause is the cornerstone of an NDA. It explicitly defines what constitutes “confidential” or “privileged” or “sensitive” information, how it can be used, and the obligations of the receiving party to protect it.
Key Points to Include:
- Clearly specify the information considered confidential.
- Outline permissible uses of the information.
- Prohibit unauthorized sharing, reproduction, or disclosure.
2. Non-Compete Clause
A Non-Compete Clause prevents the receiving party from using the confidential information to gain a competitive advantage or engage in competing activities.
Key Points to Include:
- Define the duration of the non-compete obligation.
- Specify the geographic scope where competition is restricted.
- Ensure compliance with Indian laws to avoid enforceability issues.
Example: An NDA between a software company and a vendor may include a non-compete clause to prevent the vendor from replicating or selling similar software.
3. Duration and Scope of Confidentiality
This clause specifies how long the confidentiality obligation will remain in effect and the extent to which it applies.
Key Points to Include:
- Duration: Specify whether confidentiality is time-bound (e.g., 3-5 years) or indefinite.
- Scope: Clearly define the level of protection and the limitations of disclosure.
Tip: While most NDAs in India enforce confidentiality for a limited period, indefinite clauses are often used for trade secrets.
4. Dispute Resolution Clause
This clause outlines how disputes related to the NDA will be resolved. It ensures a smooth resolution process and avoids lengthy litigation.
Key Points to Include:
- Specify the jurisdiction under which disputes will be resolved.
- Choose between arbitration, mediation, or court proceedings.
- Define the governing laws (e.g., Indian Contract Act, 1872).
Example: An NDA might state that disputes will be resolved through arbitration under the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996.
5. Exclusions from Confidentiality
This clause identifies situations where confidentiality obligations do not apply.
Common Exclusions:
- Information already in the public domain.
- Information disclosed with prior consent.
- Data independently developed without using confidential information.
Including clear exclusions prevents ambiguity and protects the receiving party from unwarranted liability.
Tips for Drafting a Legally Sound NDA in India
- Be Specific: Avoid vague terms; clearly define confidential information and obligations.
- Customize the NDA: Tailor the agreement to the specific needs of your business and the type of relationship.
- Include Remedies for Breach: Specify monetary penalties or injunctive relief for violations.
- Use Simple Language: Avoid overly complex legal jargon to ensure all parties fully understand their obligations.
- Seek Professional Help: Consult legal experts to ensure compliance with Indian laws and enforceability in courts.
Adding these essential clauses strengthens the NDA, ensuring that confidential information remains secure and disputes are minimized.
Non Disclosure Agreements Format
Overview of an NDA Template in India
An NDA template serves as a standard framework for creating confidentiality agreements tailored to specific needs. While the format can vary depending on the context, every NDA must clearly define the scope of confidentiality, the parties involved, and the remedies in case of a breach. A professionally drafted NDA ensures enforceability under the Indian Contract Act, 1872.
Key Elements to Include in an NDA
- Parties to the Agreement
- Clearly identify the disclosing party and the receiving party.
- Include details such as names, designations, and addresses to eliminate ambiguity.
- For multilateral NDAs, list all parties involved.
Example: “This Agreement is entered into by ABC Pvt. Ltd. (Disclosing Party) and XYZ Pvt. Ltd. (Receiving Party) on [date].”
- Definition of Confidential Information
- Specify the information considered confidential, such as trade secrets, business strategies, or technical data.
- Use precise language to avoid disputes about the scope of confidentiality. The more detailed the scope of what constitutes “confidential information”, the better clarity that is brought about on the non-disclosure obligation.
Example: “Confidential Information includes but is not limited to financial data, client lists, marketing strategies, and proprietary software.”
- Obligations of the Receiving Party
- Detail the receiving party’s responsibilities to safeguard the information.
- Prohibit disclosure to third parties and unauthorized use.
Example: “The Receiving Party agrees not to disclose the Confidential Information to any third party without prior written consent of the Disclosing Party.”
- Consequences of Breach
- Define the penalties for unauthorized disclosure or misuse of confidential information.
- Specify remedies such as monetary damages, injunctions, or termination of the agreement.
Example: “In the event of a breach, the Receiving Party shall indemnify the Disclosing Party for all losses, including legal fees and damages.”
- Jurisdiction and Governing Law
- Specify the jurisdiction under which disputes will be resolved.
- Include the applicable legal framework, such as Indian Contract Act, 1872.
Example: “This Agreement shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of India, and disputes shall be subject to the exclusive jurisdiction of the courts in [city].”
Sample NDA Template for Download
To make the process easier, here’s a downloadable sample Non Disclosure Agreement PDF template for Indian businesses. The NDA Document includes all the main elements mentioned , ensuring compliance and clarity.
Download Sample Non Disclosure Agreement Format.
Legal Validity of NDAs in India
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) are widely used to protect sensitive information in India, but their enforceability depends on how well they align with the legal framework. Understanding the legal validity of NDAs is crucial for ensuring that these agreements hold up in a court of law.
Enforceability Under the Indian Contract Act, 1872
NDAs in India are governed by the Indian Contract Act, 1872, which mandates that:
- Lawful Consideration and Object: The agreement must not violate any existing laws or public policy.
- Free Consent: All parties must willingly agree to the terms without coercion, fraud, or misrepresentation.
- Definite and Certain Terms: The NDA must clearly define the confidential information, obligations, and consequences of a breach.
Key Point: NDAs with overly broad or vague clauses may be deemed unenforceable. Clauses such as “indefinite confidentiality for all types of information” are likely to be rejected by Indian courts.
Relevant Case Laws Supporting NDA Breaches in India
Case laws play a significant role in determining the enforceability of NDAs. Below are some landmark cases that highlight how Indian courts address NDA breaches, which have informed and clarified the interpretation of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 and its governance of non-disclosure agreements, including the enforceability of such agreements and their legal validity. These case laws have also informed the principle of “reasonableness” in enforcing such restrictions, from the perspective of protecting a business and its data:
- Niranjan Shankar Golikari v. Century Spinning & Manufacturing Co. Ltd. (1967):
- The Supreme Court upheld the validity of confidentiality clauses in employment contracts, ruling that such restrictions must be reasonable and protect legitimate business interests.
- Superintendence Company of India v. Krishan Murgai (1980):
- This case emphasized that NDAs and restrictive covenants must strike a balance between protecting business interests and not imposing unreasonable restrictions on an individual’s right to work.
- American Express Bank Ltd. v. Priya Puri (2006):
- The Delhi High Court ruled that NDAs signed by employees are enforceable, particularly when the disclosed information constitutes trade secrets or proprietary knowledge.
- Gujarat Bottling Co. Ltd. v. Coca-Cola Co. (1995):
- The court underscored that an injunction can be granted to prevent further disclosure of confidential information in case of a breach of an NDA.
Key Point: Courts often evaluate the reasonableness of the NDA’s terms and whether the breach caused material harm to the disclosing party.
Breach of NDAs: Consequences & Remedies
A breach of a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is a serious violation that can lead to significant legal, financial, and reputational damage. NDAs are legally binding contracts that ensure the confidentiality of sensitive information. Breaching an NDA can result in severe consequences, including legal actions, fines, and loss of business trust. This section explores common types of NDA breaches, legal remedies available in India, and ways to mitigate risks.
Common Types of Breaches
- Intentional Disclosure of Confidential Information
- This occurs when the receiving party intentionally discloses confidential information to unauthorized third parties.
- Example: An employee shares proprietary business strategies with a competitor to gain personal benefits.
- Accidental Breaches
- These breaches occur due to negligence, such as sending an email to the wrong person or failing to secure confidential files.
- Example: A company accidentally discloses confidential client information in an unsecured email.
What Happens If You Breach a Confidentiality Agreement?
A breach of the NDA is considered a civil offense in India. NDAs are legally enforceable contracts, and the receiving party is obligated to keep the disclosed information confidential. If the confidentiality clause is breached, several legal consequences may follow:
Legal Remedies for Breach of NDA
In the event of a breach, the NDA itself may outline remedies such as termination, injunctions, and indemnification.
- Injunctions
- The non-breaching party may seek a court order to stop the breaching party from further disclosing confidential information. Injunctions may be interim (temporary) or perpetual (permanent).
- Legal Basis: Governed by Order XXXIX Rule 1 and 2 of the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, and Section 38 of the Specific Relief Act, 1963.
- Indemnification and Damages
- The breaching party may be required to indemnify the non-breaching party for any losses, including court fees, legal costs, and actual damages incurred. This can include both compensatory and consequential damages.
- Compensatory Damages: These are calculated based on the actual financial loss suffered due to the breach.
- Example: If a business loses ₹50,000 due to a breach, compensatory damages may cover that loss.
- Consequential Damages: These damages include losses that occurred indirectly due to the breach, such as lost profits or opportunities.
- Example: A tour company loses potential sales after a breach prevents them from securing a necessary asset.
- Criminal Remedies
- In certain cases, criminal remedies may apply, particularly under the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- Section 72A of the IT Act, 2000 provides for imprisonment up to 3 years or fines up to ₹5 lakh for the unlawful disclosure of information obtained during a contractual relationship.
- In certain cases, criminal remedies may apply, particularly under the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and the Information Technology Act, 2000.
Why Should You Not Break a Confidentiality Agreement?
Breaking an NDA can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Legal and Financial Penalties
- NDAs often specify penalties for violations, including injunctions, indemnifications, and damages.
- A breach could result in substantial financial loss, not only in direct damages but also in reputational harm and loss of future business.
- Job Termination and Reputational Damage
- For employees or contractors, breaching an NDA may result in termination from their position and loss of professional reputation.
- Businesses that breach NDAs risk losing client trust and face the possibility of damaging their public image, which could lead to a loss of clients and future opportunities.
Different Types of Contract Breach Remedies
The remedy for a breach of NDA depends on the specific provisions in the agreement, the nature of the violation, and the facts of the case. Common remedies include:
- Damages for Compensation
- Compensatory Damages: The most common remedy, compensatory damages are calculated based on the actual losses suffered due to the breach, including expectation damages and consequential damages.
- Example: A business loses potential profits from a deal that fell through due to a breach.
- Specific Performance
- Courts may order the breaching party to fulfill its contractual obligations if monetary damages are insufficient. This remedy is more common for contracts involving unique or irreplaceable items.
- Example: A company may seek specific performance if the item breached is a unique asset that cannot be replaced.
- Injunctions
- Injunctions prevent the breaching party from further disclosing confidential information. These can be temporary or permanent, depending on the severity of the breach.
- Liquidated Damages
- A set amount specified in the NDA to cover the breach, particularly where it is difficult to quantify actual damages. Liquidated damages clauses are often used in construction contracts, real estate deals, and partnerships.
- Revocation
- The non-breaching party can rescind the contract, returning both parties to their original position. This remedy is typically used for significant breaches that go to the heart of the agreement.
How to Mitigate the Risk of NDA Breaches
- Draft Clear and Precise NDAs
- Ensure that the NDA clearly defines the scope of confidentiality and the consequences of a breach. Consider incorporating clauses for arbitration to resolve disputes efficiently.
- Implement Security Measures
- Use encryption, access restrictions, and secure systems to prevent accidental breaches.
- Regular Audits and Training
- Conduct periodic reviews of compliance and train employees and third parties on proper handling of confidential information.
- Legal Preparation
- Ensure that any breach is met with swift legal action through well-defined remedies in the NDA.
This proactive approach helps mitigate risks and maintain business integrity.
Importance of Customized NDAs for Businesses
A generic NDA may not always be effective in addressing the specific needs and risks of a business. Customized NDAs are essential for ensuring that the confidentiality, legal obligations, and remedies align with the unique aspects of each business relationship.
Benefits of Tailoring NDAs for Specific Business Needs
- Enhanced Protection of Sensitive Information
Custom NDAs allow businesses to define confidential information more precisely, ensuring better protection for proprietary data, trade secrets, and strategic plans. - Addressing Unique Business Risks
A tailored NDA can address the unique risks associated with different types of business relationships, such as vendor contracts, partnerships, or employee agreements, ensuring that all specific scenarios are covered. - Clearer Terms and Obligations
By customizing the terms and obligations, businesses can ensure both parties have a clear understanding of their responsibilities, reducing the potential for disputes. - Better Enforcement of Terms
A well-crafted NDA that aligns with business needs is easier to enforce in case of breach, as it clearly defines the scope of confidential information, obligations, and penalties for violation. - Minimized Legal Loopholes
Customization helps eliminate ambiguities and potential legal loopholes that could undermine the NDA’s effectiveness in protecting confidential information.
Wrapping up, Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) are a vital tool for businesses in India to protect confidential information and ensure that sensitive data remains secure. Whether it’s a unilateral, bilateral, or multilateral NDA, having the right type tailored to your specific needs is essential for safeguarding trade secrets, business strategies, and proprietary information. A well-drafted NDA template can serve as a solid foundation for any business relationship, offering clarity on obligations and consequences in case of breach. Understanding the legal framework surrounding NDAs, including remedies for breach, is crucial to ensure enforceability under Indian law. To maximize protection, it’s highly recommended to consult with a legal professional to draft a customized NDA that best suits your business’s unique requirements.
FAQs on Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) in India
1. What is an NDA, and why is it important in business?
A Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is a legally binding contract that protects confidential information shared between parties during business dealings. It ensures sensitive data like trade secrets, strategies, or intellectual property remains secure, preventing unauthorized disclosure and fostering trust in business relationships.
2. What are the types of NDAs commonly used in India?
The three main types of NDAs are:
- Unilateral NDA: One party discloses information to another.
- Bilateral (Mutual) NDA: Both parties share confidential information.
- Multilateral NDA: Multiple parties are involved in the agreement.
Each type caters to different business scenarios and ensures tailored protection.
3. What happens if someone breaches an NDA in India?
A breach of NDA can lead to serious consequences, including:
- Civil remedies: Injunctions, monetary damages, or compensation under the Indian Contract Act, 1872.
- Criminal penalties: Punishments under laws like the IT Act, 2000 for unauthorized data disclosure.
Legal actions ensure accountability and protect the affected party’s interests.
4. How can businesses draft an effective NDA?
Businesses should seek legal assistance to draft customized NDAs that address their specific needs. This includes tailoring clauses for confidentiality, scope, and remedies for breach, ensuring compliance with Indian laws for enforceability.
5. Are NDAs legally enforceable in India?
Yes, NDAs are enforceable under Indian laws, including the Indian Contract Act, 1872, Specific Relief Act, 1963, and other relevant statutes. Courts uphold NDAs as long as the terms are fair, reasonable, and not overly broad.
7. Why is it essential to customize an NDA instead of using a generic one?
A customized NDA addresses the unique risks and requirements of your business, ensuring better protection of sensitive information. Tailoring an NDA minimizes legal loopholes, clarifies obligations, and provides effective remedies for breach.
8. How long does an NDA remain valid?
The validity of an NDA depends on the terms set in the agreement. It can be for a fixed duration (e.g., 2-5 years) or remain indefinite, especially for trade secrets or proprietary information that requires long-term protection.


SaaS Blueprint – Unlocking India’s Potential with Industry Insights
Blog Content Overview
The Software as a Service (SaaS) industry is transforming how businesses operate, enabling organizations to scale rapidly, reduce costs, and enhance accessibility. India’s SaaS story is particularly compelling: once a nascent segment, the Indian SaaS market is now projected to reach $50 billion by 2030, contributing significantly to the global market valued at over $200 billion in 2024. The country is home to over 1,500 SaaS companies, several of which have achieved unicorn status, contributing to a market valued at approximately $13 billion in 2023.
In India, the SaaS ecosystem is experiencing an unprecedented boom, becoming a global hub for innovation, entrepreneurship, and investment. Treelife’s SaaS Blueprint: Unlocking India’s Potential with Industry Insights and Regulatory Guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the Indian SaaS landscape, delving into industry growth trends, regulatory frameworks, investment landscape, risk mitigation strategies, and key government initiatives driving the sector. Whether you’re an entrepreneur, investor, or an industry observer, this handbook provides actionable insights and a clear roadmap to navigate the opportunities in this vibrant and fast growing ecosystem.
If you have any questions or need further clarity, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us at [email protected]
Why SaaS is the Future of Technology
The Indian SaaS sector stands at the intersection of global opportunity and local ingenuity, ready to redefine industries with cutting-edge solutions. As businesses embrace technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and machine learning, the potential for innovation and impact is limitless. The SaaS model is projected to surpass $300 billion globally by 2026 – a testament to its scalability and adaptability. From CRM and ERP solutions to AI-driven platforms and industry-specific tools, SaaS caters to diverse business needs. In India, the sector’s growth is equally remarkable, with the market expected to reach $50 billion by 2030. Fueled by affordable cloud infrastructure, a highly skilled workforce, and supportive government policies, the Indian SaaS sector has become a powerhouse of global significance.
However, navigating the complexities of regulation, compliance, and market dynamics is essential for long-term success. With actionable insights and a deep dive into the regulatory framework, this handbook equips businesses and stakeholders to harness the immense potential of SaaS while staying compliant and resilient.
Inside the SaaS Blueprint – Key Highlights
1. A Comprehensive Industry Overview
The handbook provides an analysis of the SaaS industry’s evolution, market size, and the role of technology in driving transformation. Key highlights include:
- The global rise of SaaS, driven by innovations in AI, machine learning, and cloud computing.
- Insights into the Indian SaaS market, which is home to over 1,500 companies generating $13 billion in annual revenue, with 70% of revenue generated in international markets.
- An exploration of key SaaS segments like Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), cybersecurity, fintech, and more, showcasing India’s ability to serve both local and global markets.
2. Regulatory and Legal Framework
The legal and regulatory landscape for SaaS businesses is complex, with both domestic and international considerations. The handbook covers:
- Contract Law: SaaS agreements such as subscription, service level, and licensing agreements, and the importance of safeguarding intellectual property (IP).
- Data Protection and Privacy: Navigating India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, and ensuring compliance with global laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Securing patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets to protect proprietary technology.
- Taxation: Detailed insights into GST implications, equalization levy updates, and income tax considerations for SaaS businesses operating domestically and internationally.
3. Investment Landscape
India’s SaaS sector has emerged as an attractive destination for venture capital and private equity investment, with the handbook providing:
- The growing preference for vertical SaaS solutions catering to niche industries like agritech and climate tech.
- Key investment trends, including the role of AI in creating new SaaS categories like software testing, predictive analytics, and automation.
- Challenges such as founder dilution and valuation pressures, with strategies for navigating these hurdles while attracting sustainable funding.
4. Mitigating Risks and Building Resilience
The digital nature of SaaS exposes companies to unique risks, including data breaches and operational disruptions. Learn more about strategies to mitigate risk and build resilience through::
- Enhancing data security through encryption, access controls, and compliance with local and global regulations.
- Building operational resilience with disaster recovery plans, fault-tolerant infrastructure, and robust incident response and reporting frameworks.
- Addressing third-party risks by vetting external vendors and ensuring alignment with security standards like SOC 2 and ISO 27001.
5. Government Initiatives Supporting SaaS
Aimed at fostering innovation and promoting adoption of SaaS, the Government of India has launched multiple initiatives and policies, the most prominent of which are below:
- MeghRaj Initiative: Accelerating cloud adoption in public services to improve efficiency and scalability.
- National Policy on Software Products (NPSP): Supporting 10,000 startups and developing clusters for software product innovation.
- Government eMarketplace (GeM): Enabling SaaS companies to tap into public sector procurement opportunities.
- SAMRIDH Program: Connecting startups with resources for scaling and growth.
Key Takeaways for Stakeholders
Whether you’re an entrepreneur, investor, or policymaker, this handbook provides actionable insights to navigate the opportunities and challenges of the SaaS ecosystem. Key takeaways include:
- The roadmap to build and scale a successful SaaS business in India.
- Strategies to ensure compliance with complex regulatory frameworks.
- Insights into investment trends and funding opportunities in SaaS.
- A detailed analysis of risks and resilience strategies to future-proof your business.
Download the SaaS Blueprint today and take the next step in shaping the future of SaaS in India. For inquiries or further guidance, reach out to us at [email protected].



Mergers & Acquisitions in India – Meaning, Difference, Types, M&A Examples
Blog Content Overview
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What are Mergers and Acquisitions?
- 3 Key Differences Between Mergers and Acquisitions
- 4 Types of Mergers and Acquisitions
- 5 Merger and Acquisition Process
- 6 Benefits and Challenges of Mergers and Acquisitions
- 7 Recent and Latest Mergers and Acquisitions in India
- 8 Legal and Regulatory Framework Governing M&A in India
- 9 Examples of Successful M&A Deals in India
- 10 Reasons for Mergers and Acquisitions
- 11 Future of Mergers and Acquisitions in India
- 12 Conclusion
- 13 FAQs on Mergers & Acquisitions in India
- 13.0.1 1. What is the meaning of mergers and acquisitions in India?
- 13.0.2 2. What is the difference between a merger and an acquisition?
- 13.0.3 3. What are the main types of mergers and acquisitions?
- 13.0.4 4. Why do companies pursue mergers and acquisitions in India?
- 13.0.5 6. What are the challenges in the M&A process in India?
- 13.0.6 7. How do synergies work in mergers and acquisitions?
Introduction
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) have emerged as transformative business strategies in the Indian economic landscape, reshaping industries and fostering innovation. At its core, mergers involve the integration of two companies into a single entity, while acquisitions refer to one company taking control over another. Together, these strategies drive growth, create synergies, and enhance competitiveness in an increasingly dynamic marketplace.
India, with its burgeoning economy and government initiatives such as Ease of Doing Business, offers a fertile ground for M&A activities. Key factors driving this trend include globalization, technological advancements, and the need for businesses to scale operations and access new markets. From tech startups to traditional manufacturing giants, M&A plays a pivotal role in aligning businesses with evolving market demands.
As a result, the importance of M&A in the Indian economy cannot be overstated. It enables companies to achieve operational efficiencies, expand product portfolios, and enter untapped markets. For the Indian economy at large, M&A fosters job creation, encourages foreign investments, and enhances the global standing of Indian enterprises. Notable examples like the Flipkart-Walmart deal and the Disney India-Reliance (JioCinema) mergers highlight how such transactions have not only transformed the businesses involved but also impacted entire industries and consequently, the Indian consumer experience.
As India continues to position itself as a global economic powerhouse, mergers and acquisitions remain a cornerstone of its corporate strategy, driving innovation, market consolidation, and economic progress.
What are Mergers and Acquisitions?
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) are strategic corporate actions that businesses undertake to achieve growth, gain competitive advantages, or drive value creation. While often discussed together, mergers and acquisitions have distinct definitions and implications in the corporate world.
Definition of Mergers
A merger occurs when two companies combine to form a single, unified entity. This is often done to pool resources, share expertise, and achieve operational efficiencies, or to expand the reach a business has in the relevant market. In a merger, the entities involved are typically of similar size, and the integration is seen as a collaborative effort. For example, the merger of Vodafone India and Idea Cellular created one of the largest telecom operators in India, Vodafone Idea.
Definition of Acquisitions
An acquisition, on the other hand, happens when one company takes control of another. This can involve purchasing a majority stake or acquiring the entire business. Acquisitions can be either friendly or hostile, depending on whether the target company agrees to the deal. A well-known acquisition in India is Walmart’s takeover of Flipkart, which helped Walmart enter the Indian e-commerce market.
Reasons for Mergers and Acquisitions
Companies pursue mergers and acquisitions for several strategic reasons, including:
- Market Expansion:
M&A enables businesses to enter new geographical regions, tap into different customer bases, and expand their market share. For example, in the financial year of 2023-2024, Reliance Industries acquired the retail, wholesale, logistics and warehousing businesses of Future Group. This deal is projected to consequently expand the reach of Reliance Industries’ retail arm in India. - Cost Savings:
Consolidation often results in economies of scale, reducing production costs, streamlining operations, and enhancing profitability. - Diversification:
By acquiring companies in different sectors, businesses reduce risk and ensure a steady revenue flow even in volatile markets. This trend can be seen in Zomato’s acquisition of grocery delivery company Blinkit (formerly known as Grofers). The acquisition greatly benefited Zomato, leading to 169% returns in the trailing year. - Access to Technology and Talent:
M&A helps organizations acquire cutting-edge technology, intellectual property, and skilled workforce without building these capabilities from scratch. For example, in F.Y. 2023-2024, Tata Motors announced a strategic partnership with Tesla Inc. whereby Tesla’s advanced battery technology and autonomous driving features could be introduced into Tata Motors’ EV lineup in India, in exchange for a 20% stake valued at USD 2 billion. - Synergies:
Perhaps the most significant reason for M&A is achieving synergies—the enhanced value generated when two companies combine.
Synergies in Mergers and Acquisitions
Synergies in mergers and acquisitions refer to the financial and operational benefits derived from combining two businesses. Synergies can take several forms:
- Cost Synergies:
Achieved by eliminating duplicate roles, sharing resources, and optimizing operations to reduce overall expenses. - Revenue Synergies:
Created when the combined entity generates higher sales due to a broader customer base, complementary products, or better market positioning. - Financial Synergies:
Resulting from better access to funding, improved credit ratings, and enhanced financial stability.
For example, the merger of Daimler-Benz and Chrysler aimed to combine their expertise and resources, creating one of the largest automotive manufacturers with significant operational and cost synergies. Similarly in India, the Disney India-Reliance media asset merger will see not only continued survival of the streaming platform offered by Disney India, but will also enable the merged entity to provide a more comprehensive service to Indian consumers, thereby ensuring a steady synergy between the two companies.
Key Differences Between Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions are often used interchangeably, but they are fundamentally different in their structure, purpose, and impact. Understanding these differences is essential for businesses evaluating their growth strategies and for stakeholders aiming to interpret these corporate moves.
What is the Difference Between a Merger and an Acquisition?
Mergers and acquisitions differ across several dimensions, including their operational goals, legal requirements, and financial implications. Below is a detailed table explaining these differences:
| Aspect | Merger | Acquisition |
| Definition | Combining two companies into a single, unified entity. | One company takes control of another by purchasing its shares or assets. |
| Objective | To achieve mutual growth by sharing resources and market opportunities. | To expand market presence, gain assets, or eliminate competition. |
| Legal Process | Involves mutual agreement and shareholder approval from both entities. A scheme of merger will also require approval from the National Company Law Tribunal and (where the applicable thresholds are attracted) approval from the Competition Commission of India and/or the Reserve Bank of India/Securities and Exchange Board of India. | The acquiring company gains ownership, which can be friendly or hostile. This is typically done by way of business transfer agreements or slump sales. |
| Control and Ownership | Ownership is typically shared between the merged companies. | The acquiring company retains control; the target company loses autonomy erstwhile enjoyed. |
| Cultural Impact | Requires integration of organizational cultures and systems. | The target company often adopts the culture and processes of the acquirer. |
| Size of Companies | Usually, companies of similar size merge. | The acquiring company is generally larger and financially stronger. |
| Financial Impact | Often viewed as a collaborative growth strategy with shared benefits. | Can lead to financial domination by the acquiring company over the acquired. |
| Examples in India | Vodafone & Idea Cellular (merger to form Vodafone Idea). | Walmart acquiring Flipkart for market entry into India. |
Real-Life Examples to Highlight the Differences
Merger Example: Vodafone & Idea Cellular
The merger between Vodafone India and Idea Cellular in 2018 created Vodafone Idea Limited, a single entity to counter the rising competition in India’s telecom sector. This was a collaborative decision to combine their resources and customer base, resulting in a larger market share and operational synergies.
Acquisition Example: Walmart & Flipkart
In 2018, Walmart acquired a 77% stake in Flipkart for $16 billion. This acquisition marked Walmart’s entry into the Indian e-commerce space, allowing it to compete with Amazon and leverage Flipkart’s established market presence. The acquisition was strategic, as Walmart gained complete control while Flipkart operated under its umbrella.
The difference between merger and acquisition lies in their structure, purpose, and execution. While mergers aim for collaboration and mutual growth, acquisitions are often driven by strategic takeovers to enhance competitiveness or expand market reach.
Types of Mergers and Acquisitions
Depending on the strategic goals of the companies involved, M&A transactions are classified into various types. These types not only reflect the nature of the deal but also its potential impact on the market, operations, and competitive positioning.
a. Types of Mergers
- Horizontal Merger
- A horizontal merger occurs when two companies operating in the same industry and often as direct competitors combine forces.
- Objective: To gain market share, eliminate competition, and achieve economies of scale.
- Example: The merger of Vodafone India and Idea Cellular to create Vodafone Idea aimed to strengthen their position in the telecom market.
- Vertical Merger
- A vertical merger involves the combination of companies operating at different levels of the supply chain (e.g., a supplier and a buyer).
- Objective: To ensure better control over the supply chain, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
- Example: Reliance Industries’ acquisition of Den Networks and Hathway Cable to expand its Jio broadband services.
- Conglomerate Merger
- A conglomerate merger happens between companies from completely unrelated industries.
- Objective: To diversify business operations and mitigate risks associated with a single market.
- Example: The Tata Group’s acquisition of Tetley Tea, which diversified its operations into the beverage sector.
- Market Extension Merger
- Combines companies offering similar products in different geographical markets.
- Objective: To expand market reach and access new customer bases.
- Example: Airtel acquiring Zain Telecom’s African operations.
- Product Extension Merger
- Involves companies that deal with related products merging to expand their product lines.
- Objective: To offer complementary products and enhance market penetration.
- Example: Facebook’s acquisition of Instagram to broaden its social media portfolio.
b. Types of Acquisitions
- Friendly Acquisitions
- These are mutually agreed deals where the acquiring and target companies collaborate on the transaction.
- Example: Tata Steel’s acquisition of Bhushan Steel to enhance its production capacity.
- Hostile Takeovers
- Occur when the acquiring company takes control of the target company without its consent, often by purchasing a majority of its shares.
- Example: L&T’s hostile takeover of Mindtree.
- Reverse Mergers
- In this scenario, a private company acquires a public company to bypass the lengthy IPO process and become publicly traded.
- Example: The reverse merger of Vedanta Resources into Sterlite Industries.
c. Theories of Mergers and Acquisitions
- Efficiency Theory
- Suggests that M&A transactions are driven by the desire to increase operational efficiency.
- Focus: Cost reduction, revenue enhancement, and resource optimization.
- Example: Companies merging to reduce redundant departments and cut costs.
- Monopoly Theory
- Argues that M&As are often pursued to eliminate competition and gain a dominant market position.
- Focus: Market power and the ability to influence pricing and industry standards.
- Example: The acquisition of WhatsApp by Facebook to dominate the messaging space.
- Valuation Theory
- Suggests that companies engage in M&A when the target company’s market value is lower than its perceived intrinsic value.
- Focus: Acquiring undervalued businesses to create financial gains.
- Example: Reliance Industries acquiring multiple startups to tap into high-growth sectors.
Merger and Acquisition Process
The merger and acquisition process is a multifaceted journey that requires meticulous planning and execution. Each phase of the process plays a vital role in ensuring the success of the transaction, minimizing risks, and maximizing value. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the key stages involved:
1. Strategic Planning
- This is the foundational stage where companies identify their objectives for the merger or acquisition.
- Key Activities:
- Define clear goals: market expansion, cost efficiency, or diversification.
- Identify potential target companies.
- Assess alignment with long-term business strategies.
- Importance: Strategic clarity ensures the M&A aligns with the company’s vision and delivers value.
2. Due Diligence
- A critical stage involving an in-depth evaluation of the target company.
- Key Areas of Assessment:
- Financial performance, including revenue and debt.
- Legal compliance and potential liabilities.
- Market position, competition, and operational efficiency.
- Importance: Identifies potential risks and validates the decision to proceed with the transaction.
3. Valuation and Negotiation
- This phase determines the value of the target company and sets the terms of the deal.
- Key Activities:
- Assess the company’s intrinsic and market value.
- Negotiate terms such as purchase price, payment structure, and contingencies.
- Importance: Accurate valuation prevents overpayment and ensures the deal’s financial viability.
4. Legal and Regulatory Approvals
- Securing necessary permissions from governing bodies to ensure compliance with local and international laws.
- Key Activities:
- Review by legal teams for compliance with corporate, tax, and antitrust laws.
- Obtain approvals from regulatory bodies like National Company Law Tribunal, SEBI, RBI, or the Competition Commission of India (CCI).
- Importance: Ensures the deal is legally sound and avoids future legal challenges.
5. Integration Planning
- Preparing a roadmap to merge the operations, cultures, and systems of the two entities.
- Key Activities:
- Define integration objectives and timelines.
- Plan the merging of HR, IT, operations, and finance systems.
- Importance: Effective planning minimizes disruptions and facilitates a seamless transition.
6. Post-Merger Integration
- The final and often most challenging phase where the actual integration takes place.
- Key Activities:
- Align organizational cultures and team structures.
- Monitor and evaluate the performance of the combined entity.
- Address stakeholder concerns and maintain morale.
- Importance: Ensures the realization of synergies and the success of the M&A.
Benefits and Challenges of Mergers and Acquisitions
a. Benefits of Mergers and Acquisitions
- Increased Market Share
- M&A allows companies to consolidate their position in existing markets and expand into new ones.
- Example: The Flipkart-Walmart acquisition strengthened Walmart’s presence in India’s e-commerce sector.
- Operational Synergies
- Combining resources and expertise leads to cost savings, improved efficiency, and higher productivity.
- Example: The Vodafone-Idea merger achieved economies of scale in operations.
- Enhanced Financial Performance
- M&A enables companies to leverage combined assets for greater profitability and improved cash flow.
- Example: HDFC Bank and HDFC Limited merger enhanced their financial services portfolio.
b. Advantages and Disadvantages of Mergers and Acquisitions
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Economies of Scale: Cost reduction through shared resources and streamlined operations. | Cultural Clashes: Differences in organizational cultures can disrupt operations. |
| Access to New Markets: Entering untapped geographical or demographic markets. | High Costs: Significant financial investment for valuations, legal fees, and integrations. |
| Improved Competitiveness: Enhanced ability to compete in global or local markets. | Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with complex legal and antitrust requirements can take a significant period of time to obtain approvals, causing delays in closing deals. |
Recent and Latest Mergers and Acquisitions in India
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in India have become a pivotal part of the business landscape, reflecting the country’s growing economy and diverse industry sectors. The latest M&A deals in India showcase how companies are using strategic consolidations to enhance market presence, strengthen financials, and expand their portfolios. Here are a few significant recent and latest mergers and acquisitions in India:
1. Walmart & Flipkart
- Overview: Walmart’s acquisition of Flipkart in 2018 for $16 billion was one of the largest deals in India’s e-commerce sector.
- Strategic Impact: Walmart gained a significant foothold in the Indian market, enabling it to compete with Amazon in the growing online retail space. Flipkart benefited from Walmart’s deep financial resources and global supply chain expertise.
- Importance: This acquisition exemplifies a classic example of market expansion and securing a dominant position in the Indian e-commerce market.
2. HDFC Bank & HDFC Ltd.
- Overview: In 2022, HDFC Bank announced the acquisition of HDFC Ltd., creating India’s largest private sector bank by assets.
- Strategic Impact: This merger aims to create synergies in banking and housing finance, providing integrated financial services to customers and improving operational efficiencies.
- Importance: The merger is expected to drive substantial growth for the bank, enabling cross-selling opportunities and increasing market share in financial services.
3. Tata Consumer & Bisleri (Proposed)
- Overview: Tata Consumer Products, which owns Tata Tea and other popular brands, is in talks to acquire Bisleri, a leading bottled water brand in India.
- Strategic Impact: The acquisition would strengthen Tata Consumer’s position in the beverage sector, particularly in the bottled water market, one of the fastest-growing segments in India.
- Importance: If the deal goes through, it would mark a major consolidation in the FMCG sector, combining two strong brands and expanding Tata Consumer’s portfolio of products.
Trends in Recent Mergers and Acquisitions in India
- Industry Consolidation: M&A deals in India are becoming more common in sectors such as e-commerce, banking, and FMCG, as companies look to diversify and expand their offerings.
- Cross-border Acquisitions: Increasingly, Indian companies are acquiring foreign firms to access international markets and new technologies. For instance, Tata Group’s acquisition of Air India was a major step toward reviving the airline and increasing global market reach.
- Strategic Alliances: Companies are forming alliances through mergers and acquisitions to enhance competitive advantages, such as better financial performance and market entry in new regions.
Legal and Regulatory Framework Governing M&A in India
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in India are governed by a complex and detailed legal and regulatory framework. Companies looking to execute M&A transactions must comply with various laws and regulations to ensure that the deal is legally sound and does not face any future legal challenges. Below is an overview of the key legislations, regulatory bodies, and tax implications involved in M&A in India.
Key Legislations Governing M&A in India
- Companies Act, 2013
- The Companies Act, 2013 serves as the principal legislation for governing corporate transactions, including mergers and acquisitions, in India. It outlines the procedures for mergers, demergers, and corporate restructuring, including the approval process by shareholders, creditors, and the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT).
- Important Provisions:
- Sections 230 to 232 of the Companies Act deal with the process of mergers and demergers. Robust mechanisms are put in place to ensure greater transparency and accountability, ensuring protection of stakeholders.
- Provisions related to the protection of minority shareholders and creditors during the M&A process.
- SEBI Guidelines
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates M&A deals involving listed companies to ensure transparency and protect the interests of investors.
- Key SEBI Regulations:
- SEBI (Substantial Acquisition of Shares and Takeovers) Regulations, 2011: Governs the process of acquiring control or a substantial amount of shares in a listed company.
- SEBI (Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations: Applies to the issuance of securities in the case of mergers, especially if the transaction involves a public offer.
- SEBI ensures that M&A deals involving public companies comply with disclosure norms and prevent market manipulation. This ensures greater accountability and transparency to protect the ultimate public interest in such entities and deals.
- Competition Act, 2002
- The Competition Act regulates mergers and acquisitions to prevent any anti-competitive practices that may harm the market or consumers.
- Key Provisions:
- Section 5 and Section 6: Deals with the merger control provisions, ensuring that any M&A transaction does not create a dominant market position that could reduce competition.
- Role of CCI: The Competition Commission of India (CCI) reviews mergers and acquisitions crossing a certain financial threshold to evaluate their impact on market competition and consumer welfare.
- FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act), 1999
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) governs foreign investments in India and controls the cross-border flow of capital.
- Important Provisions:
- FEMA regulations come into play when foreign companies or individuals are involved in the M&A transaction.
- Approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is required for foreign investments exceeding certain thresholds.
Regulatory Bodies Overseeing M&A in India
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- SEBI plays a pivotal role in overseeing M&A transactions involving publicly traded companies. It ensures compliance with disclosure norms and regulates takeover bids, ensuring fair practices and transparency in the securities market.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- RBI regulates foreign investment in Indian companies under the FEMA guidelines. Any cross-border mergers, acquisitions, or investments require approval from RBI, especially if the transaction exceeds the prescribed limit.
- Competition Commission of India (CCI)
- The CCI examines and evaluates the competition aspects of M&A transactions to ensure that such deals do not result in market monopolies or anti-competitive behavior. The CCI has the authority to block or modify deals that are deemed detrimental to market competition.
- National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)
- The NCLT is a judicial body that adjudicates disputes related to mergers, demergers, and corporate restructuring. It is also the final authority in approving the merger or acquisition process once shareholders and creditors approve the deal. Any appeals against a ruling of the NCLT will be taken up to the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (authority on par with jurisdictional high courts in India) and thereafter, to the Supreme Court by way of special leave petitions.
Tax Implications and Compliance Challenges in M&A
M&A transactions in India also involve significant tax implications that businesses must navigate carefully to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
- Income Tax Act, 1961
- Capital Gains Tax: If the target company’s shares are sold or transferred during the M&A, capital gains tax may be levied based on the holding period and the value of the shares.
- Tax-Free Reorganization: Certain mergers and acquisitions can qualify as tax-free reorganizations under Section 47 of the Income Tax Act if the transaction meets specific conditions.
- GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- M&A Transactions: Goods and Services Tax (GST) applies to the transfer of business assets during mergers or acquisitions. However, the transfer of shares in a merger is generally exempt from GST.
- Stamp Duty
- M&A transactions involving the transfer of shares or assets are subject to stamp duty, which varies based on the state in which the deal is executed.
Examples of Successful M&A Deals in India
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in India have played a significant role in shaping the country’s business landscape. Successful M&A deals have not only expanded market share but also led to innovation, enhanced competitiveness, and strategic growth. Below are some notable mergers and acquisitions in India that have been instrumental in transforming industries.
1. Tata Steel & Corus
- Deal Overview:
In 2007, Tata Steel, one of India’s largest steel manufacturers, acquired Corus, a UK-based steel giant, for approximately $12 billion. This acquisition was one of the largest overseas acquisitions by an Indian company at the time. - Strategic Impact:
- Tata Steel gained access to Corus’s advanced steel technology, expanding its presence in Europe.
- The deal allowed Tata Steel to diversify its product offerings and strengthen its position as a global player in the steel industry.
- Lessons Learned:
- Cultural Integration: While the deal was strategically sound, cultural integration was a challenge, as Tata Steel had to align its operations with the Western approach to business.
- Long-Term Vision: Tata Steel’s vision of becoming a global leader in steel was achieved by securing Corus’s resources, expanding its production capacity, and penetrating the European market.
2. Vodafone & Idea (Vi)
- Deal Overview:
In 2018, Vodafone India and Idea Cellular merged to create Vi (Vodafone Idea), one of India’s largest telecom operators, with a combined market share of over 40%. The deal was valued at approximately $23 billion. - Strategic Impact:
- The merger allowed both companies to compete effectively with industry leaders Airtel and Reliance Jio, especially in the face of declining revenue and increasing competition.
- By pooling resources, both companies were able to share infrastructure, reduce costs, and focus on customer acquisition.
- Lessons Learned:
- Regulatory Hurdles: The deal was subject to regulatory scrutiny and approval from the Competition Commission of India (CCI). It highlighted the importance of navigating regulatory challenges in large-scale M&A transactions.
- Post-Merger Integration: Post-merger challenges included integrating networks, streamlining operations, and retaining customers amidst fierce competition.
3. Zomato & Blinkit
- Deal Overview:
In 2022, Zomato, the food delivery giant, acquired Blinkit (formerly Grofers), an online grocery delivery platform, for $568 million. This move aimed to enhance Zomato’s presence in the rapidly growing quick commerce (Q-commerce) space. - Strategic Impact:
- The acquisition enabled Zomato to diversify its portfolio by venturing into grocery delivery, tapping into the expanding demand for fast delivery services.
- Blinkit’s established customer base and supply chain expertise in grocery logistics complemented Zomato’s food delivery network, making it a strong contender in the Q-commerce market.
- Lessons Learned:
- Diversification: Zomato’s move into the grocery segment shows the importance of diversification in capturing new growth opportunities.
- Market Trends: Understanding market trends, like the increasing demand for faster grocery delivery, helped Zomato gain a competitive edge in an emerging segment.
Reasons for Mergers and Acquisitions
Here are the common reasons for mergers and acquisitions that drive companies to pursue such deals:
1. Expanding Market Reach
One of the most common reasons for mergers and acquisitions is to expand market reach. By acquiring or merging with another company, businesses can enter new geographical regions, reach untapped customer segments, or gain access to a broader market.
- Example: A company may merge with a local competitor in a different region to increase its presence without having to build an entirely new distribution network.
2. Diversifying Product Portfolio
M&A allows companies to diversify their product portfolio by adding complementary or entirely new products to their offerings. This helps reduce dependence on a single product line and spreads business risk.
- Example: A tech company acquiring a software company to offer a full suite of products, from hardware to software, providing customers with a complete solution.
3. Reducing Operational Costs
By merging with or acquiring another business, companies can achieve economies of scale, streamline operations, and reduce overall costs. This can include sharing infrastructure, cutting redundant staff, or integrating supply chains for better efficiency.
- Example: Two manufacturing companies may merge to optimize production facilities, reduce supply chain costs, and achieve higher purchasing power.
Future of Mergers and Acquisitions in India
The future of mergers and acquisitions in India looks promising, driven by evolving market dynamics and global trends. As the country continues to grow economically, M&A activities are expected to remain a key strategy for companies looking to expand, diversify, and optimize operations.
Trends and Predictions in M&A Activities
- Increased Cross-Border M&As: With India’s growing influence on the global stage, cross-border mergers and acquisitions are expected to rise, especially in sectors like technology and finance.
- Private Equity and Venture Capital: The involvement of private equity firms and venture capitalists in M&A is expected to grow as they seek opportunities in high-growth sectors.
Emerging Sectors for M&A
- Technology: The digital transformation wave in India will drive M&A in the tech sector, particularly in software, fintech, and AI startups.
- Finance: The growing demand for financial products and services will lead to consolidation in the banking, insurance, and fintech sectors.
- Healthcare: With rising healthcare needs, mergers and acquisitions in healthcare services, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology are expected to surge.
Impact of Globalization and Technology on M&A Deals
- Globalization: As Indian companies expand globally, M&A will continue to be a preferred route for market entry and acquiring new capabilities.
- Technology: Advancements in digital platforms and AI will streamline M&A processes, making them faster and more efficient while opening new avenues for innovation.
Conclusion
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in India are pivotal to the growth and evolution of businesses, offering opportunities for market expansion, cost reduction, and increased competitiveness. Understanding the meaning of mergers and acquisitions, the key differences between mergers and acquisitions, and the various types of M&A can provide valuable insights for companies looking to optimize their strategies. Real-world examples, such as the Tata Steel & Corus deal and Vodafone & Idea merger, highlight the strategic importance of M&A in India’s business landscape.
As M&A continues to shape industries across sectors like technology, finance, and healthcare, companies must stay informed about M&A processes, legal frameworks, and emerging trends. The future of mergers and acquisitions in India remains bright, driven by evolving market dynamics and technological advancements. Understanding these concepts is essential for businesses aiming to succeed in an increasingly competitive global economy.
FAQs on Mergers & Acquisitions in India
1. What is the meaning of mergers and acquisitions in India?
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in India refer to the process where two companies combine (merger) or one company takes over another (acquisition). These transactions are often undertaken to achieve growth, expand market reach, or diversify product portfolios.
2. What is the difference between a merger and an acquisition?
A merger involves two companies combining to form a new entity, while an acquisition occurs when one company takes over another, with the acquired company becoming part of the acquiring company. Mergers are typically seen as a mutual agreement, whereas acquisitions can be friendly or hostile.
3. What are the main types of mergers and acquisitions?
There are several types of mergers and acquisitions:
- Horizontal Merger: Between competitors in the same industry.
- Vertical Merger: Between companies in the supply chain (suppliers and buyers).
- Conglomerate Merger: Between unrelated businesses.
- Friendly Acquisition: Where both companies agree to the deal.
- Hostile Takeover: When one company acquires another against the wishes of the target company’s management.
4. Why do companies pursue mergers and acquisitions in India?
Companies pursue mergers and acquisitions to expand their market reach, diversify their product offerings, achieve economies of scale, reduce operational costs, and stay competitive in the evolving market.
6. What are the challenges in the M&A process in India?
Challenges in the merger and acquisition process in India include regulatory approvals, cultural integration, maintaining brand identity, and aligning the financial goals of both companies. Legal complexities and compliance with various laws like the Competition Act and SEBI regulations can also pose difficulties.
7. How do synergies work in mergers and acquisitions?
Synergies in mergers and acquisitions refer to the combined benefits that result from the merger or acquisition, such as cost savings, improved efficiencies, increased market share, and enhanced revenue generation. Synergies often drive the value of an M&A deal, making it beneficial for both companies involved.


Compliances for LLP in India – List, Benefits, Penalties
Blog Content Overview
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What is LLP in India?
- 3 What are Compliances for LLP in India?
- 4 Importance of LLP Compliance
- 5 One-Time Mandatory Compliance for LLPs
- 6 Mandatory Compliances for LLPs in India
- 7 Compliances for Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) in India (Checklist)
- 8 Benefits of LLP Compliance
- 9 Steps to Ensure LLP Compliance
- 10 How to File LLP Compliances in India
- 11 FAQs on Compliances for Limited Liability Partnership in India
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced business environment, choosing the right legal structure is pivotal for business owners in India. One such popular structure is the Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) which essentially functions as a hybrid of a partnership and a corporate entity. The key benefit to the LLP structure is that the business can retain the benefits of limited liability while retaining operational flexibility. Consequently, LLPs have gained immense traction among entrepreneurs and professionals for their simplicity and efficiency in operation.
However, with this flexibility comes the responsibility of maintaining LLP compliances in India, which are mandatory for safeguarding the legal standing and operational credibility of the entity. Adhering to these compliances for LLPs ensures that the LLP operates within the framework of the law, avoids hefty penalties, and maintains its goodwill among stakeholders and regulatory bodies. Failing to comply with these regulations can lead to severe repercussions, including financial penalties, legal disputes, and even the dissolution of the LLP. Therefore, understanding and adhering to LLP filing requirements and deadlines is not just a legal obligation but also a cornerstone of sustainable business management. This blog serves as a comprehensive guide to LLP annual compliance and filing requirements in India, detailing the steps, benefits, and consequences of non-compliance.
What is LLP in India?
LLPs in India are governed by the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 (“LLP Act”). As defined thereunder, an LLP is a separate legal entity distinct from its partners. This means that the LLP can own assets, incur liabilities, and enter into contracts in its name, providing a level of security and independence not found in traditional partnerships. One of its hallmark features is limited liability, ensuring that the personal assets of the partners are not at risk beyond their agreed contributions to the business.
An LLP is further governed by an LLP agreement executed between the partners and filed as part of the incorporation documents to be provided to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs under the LLP Act. Accordingly, critical terms such as the extent of liability, obligations of each partner and their capital contributions to the LLP are captured therein.
Key Characteristics of an LLP
- Separate Legal Entity: An LLP has its own legal identity, distinct from its partners, allowing it to function independently.
- Limited Liability: The partners’ liabilities are limited to their contributions, offering a layer of financial protection.
- Flexibility in Management: Unlike corporations, LLPs provide greater flexibility in internal operations and decision-making processes.
- No Minimum Capital Requirement: LLPs do not mandate a minimum capital requirement, making them accessible for startups and small businesses.
How is an LLP Different from a Private Limited Company?
While both LLPs and Private Limited Companies offer limited liability protection, they differ in various ways:
- Ownership and Control: In an LLP, the partners manage the business directly, whereas in a Private Limited Company, directors manage operations on behalf of shareholders.
- Compliance Burden: LLPs have fewer compliance requirements and lower operational costs compared to Private Limited Companies.
- Tax Advantages: LLPs generally benefit from a simplified tax structure, avoiding dividend distribution tax applicable to Private Limited Companies.
Regulatory Oversight
LLPs in India fall under the purview of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), as designated by the LLP Act. Key regulations include registration, annual filings, and periodic updates for changes in partnership structure or business operations. The Registrar of Companies (RoC) monitors compliance, ensuring that LLPs adhere to the legal framework established under the LLP Act.
By combining the best aspects of partnerships and corporations, LLPs have emerged as a favored structure for entrepreneurs seeking a balance of flexibility, liability protection, and operational efficiency.
What are Compliances for LLP in India?
Compliances for Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) in India refer to the set of mandatory legal, financial, and procedural obligations that LLPs must adhere to in order to maintain their legal standing and operational credibility. Governed by the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008, these compliances ensure that LLPs operate transparently, fulfill their tax obligations, and align with the regulations set by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
Importance of LLP Compliance
Maintaining compliance for a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is not just a legal obligation—it’s a cornerstone for ensuring the smooth operation and longevity of the business. LLP compliance encompasses all the mandatory filings and procedural requirements that safeguard the LLP’s legal standing and financial integrity.
Why Compliance is Crucial for an LLP
- Preserving Legal Status
Timely compliance is essential to uphold an LLP’s status as a legally recognized entity. Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences, such as disqualification of partners, restrictions on business activities, and even the dissolution of the LLP by regulatory authorities. - Ensuring Smooth Business Operations
Compliance helps in maintaining organized and transparent business practices. Adhering to LLP filing requirements, such as submitting financial statements and annual returns, ensures that the LLP operates within the boundaries of the law, minimizing disruptions. - Avoiding Penalties and Legal Complications
Non-compliance with mandatory LLP requirements can result in hefty penalties, with additional penalty levied on a per day basis for any delays/contraventions that are not rectified. Additionally, prolonged non-compliance can escalate into legal complications, tarnishing the LLP’s reputation and creating obstacles for future business dealings. It is crucial to note that the ROC through the LLP Act, is empowered to strike off LLPs that are deemed to be defunct or not carrying on operations in accordance with the LLP Act.
The Role of Timely Filings
- Maintaining Transparency
Filing annual returns (Form 11) and financial statements (Form 8) on time fosters transparency in financial and operational activities. This builds trust among stakeholders, clients, and regulatory bodies. - Enhancing Credibility
A compliant LLP is viewed as reliable and trustworthy, which can be a critical factor when securing investments, loans, or partnerships. Timely compliance reflects professionalism and adherence to business ethics. - Tax Benefits
Compliance also plays a significant role in tax planning and benefits. Filing accurate income tax returns on time helps avoid interest, penalties, and scrutiny from tax authorities. LLPs that adhere to tax filing requirements can also access incentives and deductions applicable to compliant businesses.
One-Time Mandatory Compliance for LLPs
When establishing a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) in India, there are specific one-time compliance requirements that ensure a strong legal and operational foundation. These steps must be completed immediately after incorporation to maintain transparency and align with regulatory expectations.
1. LLP Form-3: Filing the LLP Agreement
The LLP Agreement serves as the governing document for the partnership, outlining the roles, responsibilities, and operational rules for the partners. As per the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008, this agreement must be filed using Form-3 with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) within 30 days of incorporation.
- Why it’s important: Filing the LLP Agreement ensures clarity in the partnership’s functioning and establishes legal protections for all partners.
- Failure to file: Delays in filing Form-3 attract penalties, which can escalate daily until the agreement is submitted.
2. Opening a Current Bank Account
To streamline financial transactions and maintain accountability, every LLP must open a current bank account in its name with a recognized bank in India.
- Purpose: This account is essential for conducting all business-related financial activities, from payments to receipts.
- Transparency in operations: Using a dedicated LLP bank account ensures clear separation of personal and business transactions, reducing the risk of financial discrepancies.
3. Obtaining PAN and TAN Numbers
Each LLP must obtain a Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN) from the Income Tax Department.
- Ease of compliance: With the introduction of the LLP (Second Amendment) Rules, 2022, PAN and TAN numbers are now automatically generated and issued alongside the Certificate of Incorporation, simplifying this step.
- Purpose of PAN and TAN: PAN is required for income tax filings, while TAN is mandatory for deducting and remitting tax at source (TDS) when applicable.
4. GST Registration (If Applicable)
While not mandatory at the time of incorporation, an LLP must obtain GST registration if its annual turnover exceeds ₹40 lakhs (or ₹20 lakhs for service providers).
- When to register: LLPs can register under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Act as soon as their turnover threshold is crossed.
- Benefits of GST compliance: Timely GST registration allows LLPs to claim input tax credits and ensures they comply with tax collection and remittance requirements.
Mandatory Compliances for LLPs in India
For Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) in India, adhering to mandatory compliance requirements is crucial for maintaining their legal standing and ensuring smooth operations. These obligations, governed by the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008, apply to all LLPs, irrespective of their business activity or scale. Below is a comprehensive list of the mandatory filings and compliance requirements that every LLP must meet.
1. Annual Return Filing (Form 11)
Every LLP must file Form 11 annually, even if it has not conducted any business during the year.
- What it includes: Form 11 provides a summary of the LLP’s management affairs, including details about its partners.
- Deadline: This form must be filed by May 30th each year.
- Penalty for non-compliance: Failing to file Form 11 on time results in a fine of ₹100 per day until compliance is achieved.
2. Statement of Accounts and Solvency (Form 8)
Form 8 is a critical compliance requirement, documenting the LLP’s financial performance and solvency status.
- What it includes: It covers profit-and-loss statements, balance sheets, and a declaration of solvency.
- Audit requirement: LLPs with a turnover exceeding ₹40 lakhs or a contribution exceeding ₹25 lakhs must get their accounts audited by a Chartered Accountant (CA).
- Deadline: Form 8 must be filed within 30 days from the end of six months of the financial year, i.e., by October 30th.
- Penalty for non-compliance: Missing the deadline incurs a penalty of ₹100 per day, which continues until the filing is completed.
3. Income Tax Filing (ITR-5)
Filing Income Tax Returns (ITR-5) is mandatory for all LLPs, with deadlines varying based on the need for a tax audit.
- Deadline for non-audited LLPs: LLPs not requiring a tax audit must file their ITR by July 31st.
- Deadline for audited LLPs: LLPs requiring an audit must complete their ITR filing by September 30th after the audit is performed by a practicing CA.
- Special cases: LLPs engaged in international or specified domestic transactions must file Form 3CEB and complete their tax filing by November 30th.
4. Other Miscellaneous Compliances
In addition to the major filings, LLPs must meet several routine compliance requirements, including:
- Director Identification Number (DIN) Updates: Ensuring that DINs of all designated partners remain active and updated.
- Event-Based Filings: Filing relevant forms with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) for changes such as partner additions or exits, amendments to the LLP agreement, or changes in contributions.
- Maintenance of Statutory Records: LLPs must maintain accurate and updated records of financial transactions, partner details, and minutes of meetings.
Compliances for Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) in India (Checklist)
| Compliance Requirement | Form Associated | Deadline | Frequency | Penalties for Non- Compliance | Other Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Return Filing | Form 11 | May 30th every year | Annual | ₹100 per day until compliance | Mandatory for all LLPs, irrespective of business activity. Provides a summary of LLP’s management affairs. |
| Statement of Accounts and Solvency | Form 8 | October 30th every year | Annual | ₹100 per day until compliance | Must include profit-and-loss statements and balance sheets. Audit required for LLPs with turnover > ₹40 lakhs or contribution > ₹25 lakhs. |
| Income Tax Filing | ITR-5 | July 31st (non-audited LLPs) | Annual | Interest on due tax, penalties, and legal consequences for non-filing | Tax-audited LLPs must file by September 30th. LLPs with international/domestic transactions must file Form 3CEB and complete filing by November 30th. |
| LLP Agreement Filing | Form-3 | Within 30 days of incorporation | One-Time | ₹100 per day until compliance | Filing the LLP Agreement ensures clarity in roles, responsibilities, and rules of operation. |
| GST Registration | GST Registration Form | Upon reaching turnover threshold of ₹40L/₹20L | Event-Based | Penalty of 10% of the tax amount due (minimum ₹10,000) | Not mandatory at incorporation. Registration is required when annual turnover exceeds ₹40 lakhs (₹20 lakhs for service providers). |
| DIN Updates | NA | As required | Event-Based | NA | Ensure Director Identification Numbers (DINs) are active and updated for all designated partners. |
| Event-Based Filings | Various MCA Forms | Within the prescribed timeline | Event-Based | ₹100 per day until compliance | Applies to changes in LLP agreement, partner details, or contributions. |
| Form 3CEB Filing | Form 3CEB | November 30th (if applicable) | Annual (if applicable) | Penalties and scrutiny by tax authorities | Mandatory for LLPs engaged in international or specific domestic transactions. |
Key Insights:
- Timeliness is critical: Most filings have daily penalties for delays, so adhering to deadlines is crucial to avoid unnecessary financial burdens.
- Audit requirements: LLPs with higher turnover or contributions must have their accounts audited by a Chartered Accountant.
- Professional assistance recommended: Engaging a CA or compliance expert, like Treelife can help LLPs stay on top of all legal and tax obligations.
Benefits of LLP Compliance
Timely compliance with regulatory requirements offers several advantages for an LLP:
- Legal Protection: Compliance helps maintain the limited liability status of partners, ensuring the business remains a separate legal entity and protecting personal assets.
- Credibility: Meeting filing deadlines boosts the credibility of the LLP with clients, investors, and regulatory bodies, enhancing trust and reputation.
- Avoiding Penalties: Adhering to compliance prevents costly fines, interest charges, and legal consequences, helping avoid disruptions to business operations.
- Tax Benefits: Timely filing of income tax returns and maintaining proper records can provide tax advantages, including deductions and exemptions, reducing the business’s tax liability.
Steps to Ensure LLP Compliance
To maintain a compliant LLP, following a structured approach is crucial. Here’s an LLP compliance safety checklist to help your business stay on track:
- Regular Bookkeeping: Accurate financial record-keeping is essential. Even if no business activity occurs, LLPs must maintain detailed books throughout the year. This ensures readiness for filings and audits, and helps avoid penalties for non-compliance.
- Set Reminders for Filing Deadlines: It’s important to establish a system to track key filing dates. Use calendar alerts or professional services to ensure timely submission of required returns and documents to avoid delays and fines.
- Engage Professionals: Consult with a Chartered Accountant (CA) or compliance expert to manage filings, audits, and overall compliance. Professionals can guide you through complex regulatory requirements, ensuring that your LLP adheres to all legal obligations.
- Stay Updated: Regularly update your LLP’s forms with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) whenever there are changes in partners, capital contributions, or corporate structure. Timely updates prevent issues with legal filings and keep your records accurate.
By following these steps to ensure LLP compliance, you can avoid legal pitfalls and maintain smooth business operations.
How to File LLP Compliances in India
Filing LLP compliances in India involves several important steps to ensure your business adheres to regulatory requirements. Here’s a guide on how to file LLP returns and the LLP compliance filing process:
- Filing the Statement of Accounts & Solvency (Form 8):
To file Form 8 online on the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) portal, follow these steps:- Login to the MCA portal (https://www.mca.gov.in/content/mca/global/en/home.html) using your credentials.


- Navigate to the ‘e-Forms’ section and select Form 8.
- Fill in details like LLP’s financial status, assets, liabilities, and solvency.
- Attach the certification from a practicing Chartered Accountant (CA) confirming the accuracy of the details.
- Submit the form and pay the filing fees.
This form must be filed annually to confirm the financial health of the LLP.
- Filing Annual Return (Form 11):
To file Form 11, follow these steps:- Log in to the MCA portal (https://www.mca.gov.in/content/mca/global/en/mca/llp-e-filling.html).
- Select Form 11 under the ‘e-Forms’ section.
- Fill in details about the LLP’s registered office, partners, and capital contributions.
- Submit the form along with the prescribed fees. This form provides the government with an annual update on the LLP’s operational status and structure.
- Income Tax Filing (ITR-5):
For filing income tax returns for an LLP, follow these steps:- Prepare the financial records and details for ITR-5, which is specifically designed for LLPs.
- Ensure that the LLP’s digital signature is ready for filing.
- Visit the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal and log in.
- Choose ITR-5 from the available forms and fill in the necessary details.
- Submit the return after ensuring all the required information is accurately entered.
LLPs must file their tax returns by the due date to avoid penalties.
- Form 3CEB Filing:
If your LLP is involved in international or domestic transactions subject to transfer pricing regulations, you may need to file Form 3CEB. To file this form:- Engage a CA to certify the transfer pricing report.
- Prepare the form by providing details on the transactions with related parties.
- Submit the form through the MCA portal as part of your compliance.
LLP e-filing streamlines these processes, making it easier for businesses to stay compliant. By following these steps and filing the necessary forms, you ensure that your LLP remains in good standing with regulatory authorities in India.
Filing and Audit Requirements Under the Income Tax Act
Understanding the filing requirements for LLPs under the Income Tax Act is crucial for maintaining compliance and avoiding penalties. Here’s a breakdown of key LLP tax audit and filing requirements:
- Audit Requirements for LLPs:
According to the LLP Act, 2008, any LLP with a turnover exceeding Rs. 40 lakhs or capital contributions exceeding Rs. 25 lakhs is required to have its books audited. The audit must be conducted by a qualified Chartered Accountant (CA) to ensure financial transparency and compliance with statutory regulations. - Income Tax Filing Deadlines:
LLPs must adhere to specific deadlines for filing income tax returns:- For audited LLPs, the filing deadline is September 30th of the assessment year.
- For non-audited LLPs, the deadline is July 31st.
Filing after these dates can result in penalties and interest charges, so it’s essential to keep track of these important dates.
- Tax Audit Threshold:
The threshold for a tax audit under the Income Tax Act has changed in recent years. Starting from the financial year 2020-21, the limit has increased from Rs. 1 crore to Rs. 5 crore for LLPs with cash receipts and payments exceeding the specified limit. This change means that LLPs with a turnover of Rs. 5 crore or less may not require a tax audit, provided their cash transactions remain within the prescribed limits. - Form 3CEB Filing:
If your LLP engages in specified transactions (such as international or domestic transactions involving related parties), you are required to file Form 3CEB. This form, certified by a Chartered Accountant, provides details on the transfer pricing policies and transactions. It must be filed along with the income tax return.
Wrapping things up, LLP compliance in India is essential for ensuring smooth business operations and legal protection. By adhering to the required compliances, such as filing annual returns, maintaining proper financial records, and conducting audits, an LLP can enjoy significant benefits, including legal protection, increased credibility, and tax advantages. Timely compliance also helps avoid penalties and legal consequences that could disrupt business growth. Understanding the LLP compliance checklist and meeting the necessary filing deadlines is crucial for maintaining regulatory adherence and safeguarding your business’s future in India.
FAQs on Compliances for Limited Liability Partnership in India
- What are the key compliances for LLP in India?
Key compliances for LLPs in India include filing the annual return (Form 11), submitting the Statement of Accounts & Solvency (Form 8), income tax filings (ITR-5), and conducting an annual audit if required. - What are the benefits of LLP compliance in India?
LLP compliance offers several benefits, including legal protection for partners, enhanced credibility with clients and investors, tax advantages, and the avoidance of penalties and legal issues. - What are the penalties for non-compliance by an LLP in India?
Non-compliance with LLP regulations can result in penalties, fines, interest charges, or legal consequences, which can harm the business’s reputation and disrupt operations. - How do I ensure timely compliance for my LLP in India?
To ensure timely compliance, maintain regular bookkeeping, set reminders for filing deadlines, consult professionals like Chartered Accountants (CAs), and stay updated with regulatory changes from the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA). - What is the tax audit threshold for an LLP in India?
The tax audit threshold for LLPs under the Income Tax Act has been increased from Rs. 1 crore to Rs. 5 crore for financial transactions involving cash receipts and payments, starting from FY 2020-21. - What forms are required for LLP compliance in India?
Essential forms for LLP compliance include Form 11 (Annual Return), Form 8 (Statement of Accounts & Solvency), Form 3CEB (for transfer pricing), and ITR-5 (Income Tax Return). - How do I file LLP returns in India?
LLP returns in India can be filed online through the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) portal. The process includes submitting Form 11 (Annual Return), Form 8 (Statement of Accounts & Solvency), and ITR-5 (Income Tax Return) with the necessary certifications, such as from a Chartered Accountant (CA). - What is the deadline for filing LLP compliance documents in India?
The deadline for filing LLP compliance documents varies: Form 11 (Annual Return) must be filed by May 30th, Form 8 (Statement of Accounts & Solvency) by October 30th, and income tax returns (ITR-5) by July 31st for non-audited LLPs and September 30th for audited LLPs.



Trademark Registration in India – Meaning, Online Process, Documents
Blog Content Overview
- 1 Introduction to Trademark Registration in India
- 2 What is Trademark Registration?
- 3 Types of Trademarks in India
- 4 Procedure for Online Trademark Registration in India
- 4.1 Step 1: Choose a Unique Trademark and Conduct a Trademark Registration Search
- 4.2 Step 2: Prepare and Submit the Application (Online/Offline)
- 4.3 Step 3: Verification of Application and Documents
- 4.4 Step 4: Trademark Journal Publication and Opposition
- 4.5 Step 5: Approval and Issuance of Trademark Registration Certificate
- 4.6 Additional Points to Note
- 5 Documents Required for Trademark Registration in India
- 6 Costs and Fees for Trademark Registration in India
- 7 How to Check Trademark Registration Status
- 8 Common Grounds for Refusal of Trademark Registration in India
- 9 Renewing a Trademark in India
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Trademark Registration in India
Introduction to Trademark Registration in India
In today’s competitive market, building a strong brand identity is vital for success. It is in this context that trademarks become a critical asset to distinguish a business’ products or services from others, ensuring they stand out and are instantly recognizable to a consumer. Consequently, protection of the trademark through trademark registration in India is a crucial step for businesses aiming to protect their brand identity and establish legal ownership over their logos, names, and symbols – all of which constitute intellectual property of the business. As a result, whether it’s a logo, name, slogan, or unique design, registering a trademark provides legal protection against infringement of intellectual property and legitimizes the brand’s ownership of such intellectual property.
In India, the process of registering a trademark is governed by the Trade Marks Act, 1999, and is overseen by the Trade Marks Registry. The Trade Marks Registry was established in 1940, and was followed by the passing of the Trademark Act in 1999. The Head Office of the Trade Marks Registry is located in Mumbai and regional offices in Ahmedabad, Chennai, Delhi, and Kolkata.
A registered trademark offers exclusive rights of use to the owner, preventing unauthorized use of the mark by others and providing a legal mechanism to pursue recourse against infringement. Additionally, registration helps avoid potential legal conflicts or claim of the mark by a third party, and protects the business from unfair competition.
The answer to question – How to Register Trademark in India? is relatively straightforward, but it requires careful attention to detail to ensure compliance with legal requirements. It involves several steps, including a trademark search, filing the application, examination, publication, and ultimately the issuance of the registration certificate. Throughout this process, it is crucial to ensure that the trademark is distinct, does not conflict with existing marks, and is used in a way that is representative of the business’ activities.
What is Trademark Registration?
Trademark registration is a legal process that grants exclusive rights to a brand or business to use a specific mark, symbol, logo, name, or design to distinguish its products or services from others in the market. A registered trademark becomes an integral part of a company’s intellectual property portfolio, offering both legal protection and a competitive edge.
In India, trademarks are governed by the Trade Marks Act, 1999, which provides the framework for registering, protecting, and enforcing trademark rights.
Definition of a Trademark
A trademark is a distinct sign, symbol, word, or combination of these elements that represents a brand and differentiates its offerings from others. Trademarks are not just limited to logos or names; they can include slogans, colors, sounds, or even packaging styles that uniquely identify a product or service. In India, trademarks are protected under the Trade Marks Act, 1999, offering exclusive rights to the owner.
For example:
- The golden arches of McDonald’s are a globally recognized logo trademark.
- The tagline “Just Do It” is an example of a registered “wordmark” by Nike.
Trademarks are classified into 45 trademark classes, which group various goods and services to streamline the registration process. Businesses must choose the relevant class that aligns with their offerings during registration.
Intellectual Property Rights Symbols and Their Significance: ™, ℠, ®
Understanding the symbols associated with trademarks is crucial for businesses and consumers alike:
- ™ (Trademark):
- This symbol indicates that the mark is being used as a trademark, but it is not yet registered.
- It signifies intent to protect the brand and discourages misuse.
- ℠ (Service Mark):
- Used for service-based businesses to highlight unregistered marks.
- Common in industries like hospitality, consulting, and IT services.
- ® (Registered Trademark):
- Denotes that the trademark is officially registered with the government.
- Provides legal protection and exclusive rights to use the mark in its registered category.
Using the correct symbol helps businesses communicate their trademark status while deterring infringement and ensuring legal enforceability.
Importance of Trademark Registration
Trademark registration is essential for businesses looking to secure their brand identity. It ensures legal protection and provides exclusive rights to the owner to use the mark for their goods or services. Key reasons why trademark registration is important include:
- Brand Protection: Prevents competitors from using similar names, logos, or designs that could mislead customers.
- Legal Recognition: Grants official ownership under Indian law, ensuring your rights are safeguarded.
- Customer Trust: A trademark adds credibility to your brand, making it easier for customers to identify and trust your products or services.
- Asset Creation: Registered trademarks are intangible assets that can be licensed, franchised, or sold for business growth.
- Global Reach: Trademark registration in India can facilitate international trademark recognition, helping businesses expand globally.
Benefits of Registering a Trademark in India
The benefits of trademark registration extend beyond legal protection. Here are the key advantages:
- Exclusive Rights: Registration provides exclusive rights to the owner, ensuring the trademark cannot be legally used by others in the registered class.
- Competitive Edge: A trademark helps establish a distinct identity in the market, giving your business a competitive advantage.
- Prevention of Infringement: Protects against unauthorized use of your brand name, logo, or design.
- Market Goodwill: Builds trust and goodwill with customers, enhancing brand loyalty.
- Ease of Business Expansion: A registered trademark facilitates licensing or franchising, opening doors for business growth.
- Strong Legal Position: In the event of disputes, a registered trademark provides a strong legal standing.
Brief Overview of the Trademark Registration Process in India
The procedure for trademark registration in India is systematic and straightforward. Here’s a quick overview:
- Trademark Search: Conduct a trademark registration search to ensure the desired trademark is unique and not already registered.
- Application Filing: Submit the trademark application online or offline with all required documents, including ID proofs, business registration details, and the logo (if applicable).
- Examination and Review: Authorities review the application and may raise objections, which must be addressed within the stipulated time.
- Publication: The trademark is published in the Trademark Journal, allowing for public objections.
- Approval and Registration: If no objections are raised or resolved satisfactorily, the trademark is approved and the trademark registration certificate is issued.
Registering a trademark not only provides legal protection but also secures your brand’s future, ensuring long-term growth and recognition in the market.
Types of Trademarks in India
Trademarks in India are categorized into general and specific types, each serving different purposes to protect distinct aspects of a brand’s identity.
General Trademarks
- Generic Mark: Refers to common terms or names that describe a product or service. These marks are not eligible for registration as they lack uniqueness (e.g., “Milk” for dairy products).
- Suggestive Mark: Indicates the nature or quality of the goods or services indirectly, requiring imagination to connect with the product (e.g., “Netflix” suggests internet-based flicks).
- Descriptive Mark: Describes the product or service but must acquire distinctiveness to qualify for registration (e.g., “Best Rice”).
- Arbitrary Mark: Uses common words in an unrelated context, making them distinctive (e.g., “Apple” for electronics).
- Fanciful Mark: Invented words with no prior meaning, offering the highest level of protection (e.g., “Google”).
Specific Trademarks
- Service Mark: Identifies and protects services rather than goods (e.g., logos of consulting firms).
- Certification Mark: Indicates that the product meets established standards (e.g., ISI mark).
- Collective Mark: Used by a group of entities to signify membership or collective ownership (e.g., “CA” for Chartered Accountants).
- Trade Dress: Protects the visual appearance or packaging of a product, such as color schemes or layouts (e.g., Coca-Cola bottle shape).
- Sound Mark: Protects unique sounds associated with a brand (e.g., the Nokia tune).
Other types include Pattern Marks, Position Marks, and Hologram Marks, which add further layers of protection to unique brand elements.
Who can Apply for Trademark?
Anyone can apply for trademark registration, including individuals, companies, and LLPs. The person listed as the applicant in the trademark registration form will be recognized as the trademark owner once the registration is complete. This process allows businesses and individuals to protect their brand identity under trademark law.
Procedure for Online Trademark Registration in India
Trademark registration in India involves a detailed and systematic process that ensures legal protection for your brand. Below is a step-by-step guide to the procedure:
Step 1: Choose a Unique Trademark and Conduct a Trademark Registration Search
- Begin by selecting a unique and distinctive trademark that effectively represents your brand. It could be a logo, wordmark, slogan, or even a combination of elements.
- Ensure your trademark aligns with your business’s trademark class. There are 45 classes under which trademarks can be registered:
- Classes 1-34 cover goods.
- Classes 35-45 cover services.
- Conduct a trademark registration search using the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks’ online database. This ensures your chosen mark isn’t already in use or similar to an existing trademark, avoiding potential objections or rejections.
Step 2: Prepare and Submit the Application (Online/Offline)
- Application Form: File Form TM-A, which allows registration for one or multiple classes.
- Required Documents:
- Business Registration Proof (e.g., GST certificate or incorporation document).
- Identity and address proof of the applicant (e.g., PAN, Aadhaar).
- A clear digital image of the trademark (dimensions: 9 cm x 5 cm).
- Proof of claim, if the mark has been used previously in another country.
- Power of Attorney, if an agent is filing on your behalf.
- Filing Options:
- Manual Filing: Submit the form at the nearest Trademark Registry Office (Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, or Ahmedabad).
- Acknowledgment takes 15-20 days.
- Online Filing: Faster and efficient, with instant acknowledgment via the IP India portal (https://ipindia.gov.in/).
- Manual Filing: Submit the form at the nearest Trademark Registry Office (Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, or Ahmedabad).



- Government Fees for Trademark Registration (as on date):
- ₹4,500 (e-filing) or ₹5,000 (manual filing) for individuals, startups, and small businesses.
- ₹9,000 (e-filing) or ₹10,000 (manual filing) for others.
Step 3: Verification of Application and Documents
- The Registrar of Trademarks examines the application to ensure compliance with the Trademark Act of 1999 and relevant guidelines.
- If any issues arise, such as incomplete information or similarity with an existing mark, the Registrar raises an objection and sends a notice to the applicant.
- Applicants must respond to objections within the stipulated timeframe, providing justifications or additional documentation.
Step 4: Trademark Journal Publication and Opposition
- Once cleared, the trademark is published in the Indian Trademark Journal, inviting public feedback.
- Opposition Period:
- Third parties have four months to file an opposition if they believe the trademark conflicts with their rights.
- If opposition arises, both parties present their evidence, and the Registrar conducts a hearing to resolve the matter.
Step 5: Approval and Issuance of Trademark Registration Certificate
- If there are no objections or oppositions (or they are resolved), the Registrar approves the trademark.
- A Trademark Registration Certificate is issued, officially granting the applicant the right to use the ® symbol alongside their trademark.
Additional Points to Note
- The entire trademark registration process in India can take 6 months to 2 years, depending on the objections or oppositions.
- During the registration process, you can use the ™ symbol to indicate a pending trademark application. Once the certificate is issued, switch to the ® symbol, denoting a registered trademark.
By following this step-by-step guide, businesses can protect their brand, build trust, and enjoy exclusive rights to their trademark in India. Ensure proper documentation and legal assistance for a smoother registration process.
Documents Required for Trademark Registration in India
To successfully register a trademark in India, specific documents must be submitted. These documents establish the applicant’s identity, business details, and trademark uniqueness. Here’s a concise list with key details:
1. Business Registration Proof
- Sole Proprietorship: GST Certificate or Business Registration Certificate.
- Partnership Firm: Partnership Deed or Registration Certificate.
- Company/LLP: Incorporation Certificate and Company PAN card.
2. Identity and Address Proof
- Individuals/Sole Proprietors: PAN Card, Aadhaar Card, or Passport.
- Companies/LLPs: Identity proof of directors/partners and registered office address proof.
3. Trademark Representation
- A clear digital image of the trademark (logo, wordmark, or slogan) with dimensions of 9 cm x 5 cm.
4. Power of Attorney (Form TM-48)
- A signed Power of Attorney authorizing an agent or attorney to file the trademark application.
5. Proof of Prior Usage (If Applicable)
- Evidence such as invoices, advertisements, or product labels showing prior use of the trademark.
6. Udyog Aadhaar or MSME Certificate
- Required for startups, small businesses, and individuals to avail reduced trademark registration fees.
7. Class-Specific Details
- Declaration of the class of goods or services (from 45 available trademark classes).
8. Address Proof of Business
- Recent utility bills, lease agreements, or ownership documents as proof of the business location.
By ensuring all these documents for trademark registration are complete and accurate, applicants can avoid delays and simplify the registration process. Proper documentation is key to protecting your brand identity in India.
Costs and Fees for Trademark Registration in India
Understanding of the costs involved in trademark registration in India is needed for businesses and individuals planning to protect their intellectual property. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
1. Government Fees for Trademark Registration (as on date)
- Individuals, Startups, and Small Enterprises:
- ₹4,500 for e-filing.
- ₹5,000 for physical filing.
- Others (Companies, LLPs, etc.):
- ₹9,000 for e-filing.
- ₹10,000 for physical filing.
2. Additional Costs for Professional Services
- Hiring a trademark attorney or agent may involve additional charges depending on the complexity of the application and services provided.
3. Factors Affecting Trademark Registration Costs
- Number of Classes: Registering under multiple trademark classes increases the fees.
- Type of Trademark: Filing for a collective trademark or series mark incurs higher costs.
- Opposition Proceedings: If objections are raised, handling opposition can add to the expenses.
Planning your trademark registration carefully can help you manage costs effectively while ensuring maximum protection for your brand.
How to Check Trademark Registration Status
After filing your application, it’s essential to monitor its status regularly to avoid delays. Here’s how you can do it:



1. Online Methods to Check Trademark Status
- Visit the official website of the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks.
- Navigate to the “Trademark Status” option or visit https://tmrsearch.ipindia.gov.in/eregister/eregister.aspx .
- Enter your application number or trademark details.
- View the current status, including examination, opposition, or registration updates.
2. Common Reasons for Delays
- Incomplete Documentation: Missing or incorrect documents can lead to processing delays.
- Objections or Oppositions: Objections raised by the Trademark Office or third-party oppositions require resolution, prolonging the process.
- Backlog at Trademark Office: High volume of applications can slow down the approval process.
3. Resolving Delays
- Ensure that all documents are complete and accurate during submission.
- Respond promptly to objections or opposition notices.
- Seek professional assistance to expedite the process.
By staying informed about the trademark registration status and addressing issues proactively, you can secure your trademark efficiently and avoid unnecessary complications.
Common Grounds for Refusal of Trademark Registration in India
When applying for trademark registration in India, the application may be refused based on certain grounds. It’s essential to understand these absolute grounds for refusal to avoid issues during the process.
1. Absolute Grounds for Refusal
These are the reasons that may lead to the rejection of a trademark application even if no other parties oppose it. They include:
- Lack of Distinctiveness: A trademark must be unique and capable of distinguishing the goods or services of one entity from another. Generic or descriptive marks are often refused.
- Deceptive or Misleading Marks: Trademarks that mislead consumers about the nature or quality of the goods or services are not eligible for registration.
- Conflict with Public Order or Morality: Trademarks that go against public morality or religious beliefs can be refused.
- Confusion with Existing Trademarks: Trademarks that are too similar to an already registered mark or a pending application will be rejected.
2. Examples of Trademarks That May Be Rejected
- Descriptive Marks: For example, “Sweet Cake” for a bakery.
- Generic Terms: Words like “Apple” for computer-related products or “Coffee” for coffee-related services.
- Marks That Resemble Flags, Emblems, or National Symbols: Trademarks that resemble state or national flags or symbols.
By understanding these grounds, applicants can avoid common mistakes and improve their chances of approval.
Renewing a Trademark in India
Once your trademark is registered, it remains valid for a specific period. However, it must be renewed to continue enjoying protection under the law.
1. Validity Period of a Trademark
In India, a trademark is valid for 10 years from the date of registration. After this period, the trademark owner must renew the registration to maintain its exclusive rights.
2. Procedure and Timeline for Trademark Renewal
- Filing for Renewal: The application for renewal must be filed before the expiration of the 10-year validity period. It can be done within 6 months before or after the expiration date.
- Online Filing: The process can be done through the official website of the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks. You need to fill out the appropriate form (Form TM-R) and pay the renewal fees.
- Timeline: The renewal process is typically completed within 1–2 months, depending on the workload of the Trademark Office.
3. Costs Involved in Trademark Renewal
- The renewal fees for individuals, startups, and small businesses are typically ₹4,500 for e-filing and ₹5,000 for physical filing.
- For companies, LLPs, and other organizations, the renewal fees are ₹9,000 for e-filing and ₹10,000 for physical filing.
By renewing your trademark on time, you ensure continued protection and exclusive rights to your brand name and logo in India. Regular renewal is key to maintaining the integrity of your intellectual property and protecting your business identity.
Hence, trademark registration in India is essential for businesses aiming to protect their intellectual property and strengthen their brand presence. Registering a trademark provides exclusive rights to your brand name, logo, or symbol, preventing unauthorized use and offering legal protection. The trademark registration process is simple, starting with a trademark search, followed by filing an application and addressing any objections or oppositions. Renewing your trademark ensures ongoing protection and secures your brand’s identity for years to come. With trademark registration in India, businesses, whether startups or established companies, can build trust, create valuable assets, and safeguard their brand in the competitive market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Trademark Registration in India
1. Is trademark registration mandatory in India?
No, trademark registration is not mandatory in India. However, registering your trademark provides several benefits, such as legal protection, exclusive rights to use the mark, and the ability to take legal action in case of infringement. It also prevents others from using a similar mark and adds value to your brand by enhancing its credibility.
2. Who can apply for trademark registration in India?
Any individual, business entity, or legal entity claiming to be the proprietor of the trademark can apply for registration. The application can be filed either on a “used” or “proposed to be used” basis. Trademark applications can be filed online through the official IP India portal or at one of the regional trademark offices located in Delhi, Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Kolkata, or Chennai.
3. What are the benefits of trademark registration in India?
Trademark registration offers exclusive rights to use the trademark for the registered goods or services. It protects your brand from unauthorized use, provides legal backing in case of infringement, and allows you to use the ™ and ® symbols. It also enhances brand recognition and helps in building a trustworthy reputation in the market.
4. How long does it take to register a trademark in India?
Trademark registration in India typically takes between 8-15 months. This duration may vary depending on the complexity of the case and whether any objections or oppositions are raised during the process. If there are no complications, registration is usually completed within this time frame.
5. What documents are required for trademark registration in India?
Key documents required include a clear representation of the trademark (logo or wordmark), proof of business registration, identity and address proof (e.g., PAN, Aadhaar), and relevant certificates (for startups or small enterprises). If filing through an agent, a Power of Attorney may also be required.
6. How much does trademark registration cost in India?
The trademark registration fee varies based on the type of applicant. For individuals, startups, and small enterprises, the fee is ₹4,500 for e-filing and ₹5,000 for physical filing. For others, the fee is ₹9,000 for e-filing and ₹10,000 for physical filing. Additional professional fees may apply if you choose to hire legal assistance.
7. Where do I apply for trademark registration in India?
Trademark registration applications can be submitted online through the official IP India website or filed at one of the regional trademark offices in Delhi, Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Kolkata, or Chennai. E-filing provides instant acknowledgment, while physical filing may take 15-20 days to receive acknowledgment.
8. Why should I register my trademark if it’s not mandatory?
Although not mandatory, trademark registration offers several advantages, including legal protection, exclusive rights to your mark, and the ability to use the ® symbol. It also boosts your brand’s credibility and safeguards your intellectual property against infringement.
9. What is the typical timeline for trademark registration in India?
Trademark registration generally takes 8-15 months in uncomplicated cases. However, if objections or oppositions arise, the process may take longer due to the need to resolve these issues.
10. How can I check the status of my trademark registration application?
You can easily check the status of your trademark registration online through the IP India website. It will provide updates on the status of your application, including any objections or progress on its approval.
11. What are common reasons for the refusal of trademark registration?
Trademarks may be refused on absolute grounds if they are too generic, descriptive, offensive, or conflict with an already registered trademark. Marks that lack distinctiveness or mislead the public may also face rejection by the authorities.
12. How do I renew my trademark in India?
Trademark registration in India is valid for 10 years. To renew your trademark, you need to file a renewal application before the expiry date and pay the renewal fee. Renewing your trademark on time ensures continued protection of your intellectual property rights.



Non Disclosure Agreements in India – NDA Template, Types & Breach
Blog Content Overview
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What is a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)?
- 3 Types of Non-Disclosure Agreements in India
- 4 Essential Clauses in an NDA
- 5 Non Disclosure Agreements Format
- 6 Legal Validity of NDAs in India
- 7 Breach of NDAs: Consequences & Remedies
- 8 Importance of Customized NDAs for Businesses
- 9 FAQs on Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) in India
- 9.0.1 1. What is an NDA, and why is it important in business?
- 9.0.2 2. What are the types of NDAs commonly used in India?
- 9.0.3 3. What happens if someone breaches an NDA in India?
- 9.0.4 4. How can businesses draft an effective NDA?
- 9.0.5 5. Are NDAs legally enforceable in India?
- 9.0.6 7. Why is it essential to customize an NDA instead of using a generic one?
- 9.0.7 8. How long does an NDA remain valid?
Introduction
Security of sensitive business information, protection of intellectual property and trade secrets and trust in collaborations are critical aspects of business security in an increasingly competitive and data-driven market today. It is to this effect that businesses typically execute non disclosure agreement (“NDA”), which imposes a contractual obligation on the party receiving the protected information to not only keep the same confidential but to not disclose or divulge such information without permission from the disclosing party.
NDAs can relate to trade secrets, business models, or intellectual property; all of which help to ensure confidentiality and security in business partnerships. Fundamentally, this agreement ensures that the recipient of such confidential information is obligated to keep the same protected. As such, any breach of an NDA would typically build in mechanisms for compensation for damages caused by the party in breach of the NDA.
Overview of NDAs in Indian Law / Legal Environment
NDAs in India are enforceable as per the Indian Contract Act, 1872. They are very commonly employed across sectors and can be used for purposes ranging from technology/manufacturing to consulting to even labour or critical events requiring protection of sensitive information. An airtight NDA defines what is and is not confidential information, limits the use of such information, and outlines the consequences for a breach of the obligations. NDAs are widely used in India to guard proprietary information involving in commercial transactions, employment, or partnership. NDAs keep the most important business information private by:
- Security of proprietary information from unauthorized use or leakage.
- Developing intellectual property, trade secrets, and business plans protection laws.
- Establishing trust in relationships while going through mergers, acquisitions or negotiations.
NDAs by ensuring confidentiality preserve a business’s competitive edge and eliminate litigation.such as technology, manufacturing, and consulting. NDAs can be unilateral, mutual or multilateral, but for it to be effective they should meet Indian laws. The success of an NDA depends on its definitions, enforceable provisions and jurisdiction. A breach of an NDA can be financially and reputationally disastrous.
What is a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)?
A Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is a legally binding contract designed to safeguard sensitive and proprietary information shared between two or more parties. It establishes a confidential relationship by outlining the type of information that must remain undisclosed, the purpose of sharing the information, and the consequences of any breach. NDAs are integral to protecting intellectual property, trade secrets, and other business-critical data.
Definition of a Non-Disclosure Agreement
In simple terms, an NDA is a formal agreement where one party agrees not to disclose or misuse the confidential information provided by the other party. Colloquially also referred to as a confidentiality agreement, an NDA ensures that the disclosed information is used solely for the intended purpose and remains secure. NDAs are enforceable under the Indian Contract Act, 1872, making them a vital tool in safeguarding sensitive data in India.
Key Purposes and Objectives of NDAs
The primary goal of an NDA is to maintain the confidentiality of information and prevent its unauthorized use. Key objectives include:
- Protecting Intellectual Property: Ensuring that trade secrets, patents, and proprietary processes remain secure.
- Establishing Trust: Building a reliable relationship between parties, particularly in mergers, acquisitions, or joint ventures.
- Avoiding Misuse of Data: Preventing employees, contractors, or partners from sharing confidential details with competitors.
- Defining Legal Recourse: Outlining the consequences of a breach, including penalties and legal actions.
By clearly defining the scope of confidentiality, NDAs reduce the likelihood of disputes and offer a framework for resolution if a breach occurs.
Real-Life Examples of NDA Use in Business Scenarios
NDAs are widely used across various industries and situations, such as:
- Employment Agreements: Employers often require NDAs to protect internal policies, client lists, and proprietary methods from being disclosed by employees.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: During due diligence, NDAs secure sensitive financial and operational data exchanged between companies. This can also include restrictions on disclosure of investment by a party and prevention of any media release (as typically required by incubators).
- Technology and Innovation: Startups and tech companies frequently use NDAs to safeguard unique ideas, algorithms, or software codes when pitching to investors or collaborating with developers.
- Freelance and Consulting Projects: Freelancers or consultants working with confidential client data are bound by NDAs to prevent misuse.
- Vendor or Supplier Relationships: NDAs protect sensitive pricing strategies, product designs, or supply chain details shared with third-party vendors.
For example, a startup seeking funding may share its business model, product specifications and financial projections with potential investors under an NDA, ensuring these details remain confidential and protected from competitors.
Types of Non-Disclosure Agreements in India
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) come in various forms depending on the nature of the relationship and the flow of confidential information between parties. Understanding the types of NDAs is essential for selecting the most suitable agreement to safeguard sensitive information. Typically, an NDA will impose a total ban on disclosure, except where such disclosure is required by law or on order of any statutory authority. Below are the primary types of NDAs used in India:
1. Unilateral NDAs
A Unilateral NDA is a one-sided agreement where only one party discloses confidential information, and the receiving party agrees to protect it. This type of NDA is commonly used when a business shares proprietary information with employees, contractors, or third-party vendors who are not expected to reciprocate with their own confidential data.
Common Use Cases:
- Protecting trade secrets during product development.
- Sharing sensitive business data with potential investors.
- Securing intellectual property shared with a freelancer or consultant.
Example: A tech startup providing details of its proprietary algorithm to a marketing agency under a unilateral NDA.
2. Bilateral/Mutual NDAs
A Bilateral NDA, also known as a mutual NDA, involves two parties sharing confidential information with each other and agreeing to protect it. This type of agreement is ideal when both parties need to exchange sensitive data, such as in partnerships, collaborations, or joint ventures.
Common Use Cases:
- Collaborations between companies on a new product or service.
- Mergers and acquisitions where both entities share financial and operational data.
- Negotiations between two businesses for a potential partnership.
Example: Two pharmaceutical companies working together on developing a new drug may use a mutual NDA to safeguard their research and development data.
3. Multilateral NDAs
A Multilateral NDA is used when three or more parties need to share confidential information among themselves while ensuring mutual protection. This type of NDA simplifies the process by consolidating multiple bilateral agreements into a single document, reducing legal complexities and administrative overhead.
Common Use Cases:
- Consortiums or alliances in large-scale projects like infrastructure development.
- Joint ventures involving multiple stakeholders.
- Collaborative research projects between academic institutions and private companies.
Example: A group of IT companies collaborating on a government project to develop a unified digital platform may use a multilateral NDA to protect their individual contributions.
Essential Clauses in an NDA
A well-drafted Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is only as strong as the clauses it includes. Each clause serves a specific purpose in defining the rights and obligations of the parties, ensuring comprehensive protection of confidential information. Here are the key clauses every NDA should have:
1. Confidentiality Clause
The confidentiality clause is the cornerstone of an NDA. It explicitly defines what constitutes “confidential” or “privileged” or “sensitive” information, how it can be used, and the obligations of the receiving party to protect it.
Key Points to Include:
- Clearly specify the information considered confidential.
- Outline permissible uses of the information.
- Prohibit unauthorized sharing, reproduction, or disclosure.
2. Non-Compete Clause
A Non-Compete Clause prevents the receiving party from using the confidential information to gain a competitive advantage or engage in competing activities.
Key Points to Include:
- Define the duration of the non-compete obligation.
- Specify the geographic scope where competition is restricted.
- Ensure compliance with Indian laws to avoid enforceability issues.
Example: An NDA between a software company and a vendor may include a non-compete clause to prevent the vendor from replicating or selling similar software.
3. Duration and Scope of Confidentiality
This clause specifies how long the confidentiality obligation will remain in effect and the extent to which it applies.
Key Points to Include:
- Duration: Specify whether confidentiality is time-bound (e.g., 3-5 years) or indefinite.
- Scope: Clearly define the level of protection and the limitations of disclosure.
Tip: While most NDAs in India enforce confidentiality for a limited period, indefinite clauses are often used for trade secrets.
4. Dispute Resolution Clause
This clause outlines how disputes related to the NDA will be resolved. It ensures a smooth resolution process and avoids lengthy litigation.
Key Points to Include:
- Specify the jurisdiction under which disputes will be resolved.
- Choose between arbitration, mediation, or court proceedings.
- Define the governing laws (e.g., Indian Contract Act, 1872).
Example: An NDA might state that disputes will be resolved through arbitration under the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996.
5. Exclusions from Confidentiality
This clause identifies situations where confidentiality obligations do not apply.
Common Exclusions:
- Information already in the public domain.
- Information disclosed with prior consent.
- Data independently developed without using confidential information.
Including clear exclusions prevents ambiguity and protects the receiving party from unwarranted liability.
Tips for Drafting a Legally Sound NDA in India
- Be Specific: Avoid vague terms; clearly define confidential information and obligations.
- Customize the NDA: Tailor the agreement to the specific needs of your business and the type of relationship.
- Include Remedies for Breach: Specify monetary penalties or injunctive relief for violations.
- Use Simple Language: Avoid overly complex legal jargon to ensure all parties fully understand their obligations.
- Seek Professional Help: Consult legal experts to ensure compliance with Indian laws and enforceability in courts.
Adding these essential clauses strengthens the NDA, ensuring that confidential information remains secure and disputes are minimized.
Non Disclosure Agreements Format
Overview of an NDA Template in India
An NDA template serves as a standard framework for creating confidentiality agreements tailored to specific needs. While the format can vary depending on the context, every NDA must clearly define the scope of confidentiality, the parties involved, and the remedies in case of a breach. A professionally drafted NDA ensures enforceability under the Indian Contract Act, 1872.
Key Elements to Include in an NDA
- Parties to the Agreement
- Clearly identify the disclosing party and the receiving party.
- Include details such as names, designations, and addresses to eliminate ambiguity.
- For multilateral NDAs, list all parties involved.
Example: “This Agreement is entered into by ABC Pvt. Ltd. (Disclosing Party) and XYZ Pvt. Ltd. (Receiving Party) on [date].”
- Definition of Confidential Information
- Specify the information considered confidential, such as trade secrets, business strategies, or technical data.
- Use precise language to avoid disputes about the scope of confidentiality. The more detailed the scope of what constitutes “confidential information”, the better clarity that is brought about on the non-disclosure obligation.
Example: “Confidential Information includes but is not limited to financial data, client lists, marketing strategies, and proprietary software.”
- Obligations of the Receiving Party
- Detail the receiving party’s responsibilities to safeguard the information.
- Prohibit disclosure to third parties and unauthorized use.
Example: “The Receiving Party agrees not to disclose the Confidential Information to any third party without prior written consent of the Disclosing Party.”
- Consequences of Breach
- Define the penalties for unauthorized disclosure or misuse of confidential information.
- Specify remedies such as monetary damages, injunctions, or termination of the agreement.
Example: “In the event of a breach, the Receiving Party shall indemnify the Disclosing Party for all losses, including legal fees and damages.”
- Jurisdiction and Governing Law
- Specify the jurisdiction under which disputes will be resolved.
- Include the applicable legal framework, such as Indian Contract Act, 1872.
Example: “This Agreement shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of India, and disputes shall be subject to the exclusive jurisdiction of the courts in [city].”
Sample NDA Template for Download
To make the process easier, here’s a downloadable sample Non Disclosure Agreement PDF template for Indian businesses. The NDA Document includes all the main elements mentioned , ensuring compliance and clarity.
Download Sample Non Disclosure Agreement Format.
Legal Validity of NDAs in India
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) are widely used to protect sensitive information in India, but their enforceability depends on how well they align with the legal framework. Understanding the legal validity of NDAs is crucial for ensuring that these agreements hold up in a court of law.
Enforceability Under the Indian Contract Act, 1872
NDAs in India are governed by the Indian Contract Act, 1872, which mandates that:
- Lawful Consideration and Object: The agreement must not violate any existing laws or public policy.
- Free Consent: All parties must willingly agree to the terms without coercion, fraud, or misrepresentation.
- Definite and Certain Terms: The NDA must clearly define the confidential information, obligations, and consequences of a breach.
Key Point: NDAs with overly broad or vague clauses may be deemed unenforceable. Clauses such as “indefinite confidentiality for all types of information” are likely to be rejected by Indian courts.
Relevant Case Laws Supporting NDA Breaches in India
Case laws play a significant role in determining the enforceability of NDAs. Below are some landmark cases that highlight how Indian courts address NDA breaches, which have informed and clarified the interpretation of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 and its governance of non-disclosure agreements, including the enforceability of such agreements and their legal validity. These case laws have also informed the principle of “reasonableness” in enforcing such restrictions, from the perspective of protecting a business and its data:
- Niranjan Shankar Golikari v. Century Spinning & Manufacturing Co. Ltd. (1967):
- The Supreme Court upheld the validity of confidentiality clauses in employment contracts, ruling that such restrictions must be reasonable and protect legitimate business interests.
- Superintendence Company of India v. Krishan Murgai (1980):
- This case emphasized that NDAs and restrictive covenants must strike a balance between protecting business interests and not imposing unreasonable restrictions on an individual’s right to work.
- American Express Bank Ltd. v. Priya Puri (2006):
- The Delhi High Court ruled that NDAs signed by employees are enforceable, particularly when the disclosed information constitutes trade secrets or proprietary knowledge.
- Gujarat Bottling Co. Ltd. v. Coca-Cola Co. (1995):
- The court underscored that an injunction can be granted to prevent further disclosure of confidential information in case of a breach of an NDA.
Key Point: Courts often evaluate the reasonableness of the NDA’s terms and whether the breach caused material harm to the disclosing party.
Breach of NDAs: Consequences & Remedies
A breach of a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is a serious violation that can lead to significant legal, financial, and reputational damage. NDAs are legally binding contracts that ensure the confidentiality of sensitive information. Breaching an NDA can result in severe consequences, including legal actions, fines, and loss of business trust. This section explores common types of NDA breaches, legal remedies available in India, and ways to mitigate risks.
Common Types of Breaches
- Intentional Disclosure of Confidential Information
- This occurs when the receiving party intentionally discloses confidential information to unauthorized third parties.
- Example: An employee shares proprietary business strategies with a competitor to gain personal benefits.
- Accidental Breaches
- These breaches occur due to negligence, such as sending an email to the wrong person or failing to secure confidential files.
- Example: A company accidentally discloses confidential client information in an unsecured email.
What Happens If You Breach a Confidentiality Agreement?
A breach of the NDA is considered a civil offense in India. NDAs are legally enforceable contracts, and the receiving party is obligated to keep the disclosed information confidential. If the confidentiality clause is breached, several legal consequences may follow:
Legal Remedies for Breach of NDA
In the event of a breach, the NDA itself may outline remedies such as termination, injunctions, and indemnification.
- Injunctions
- The non-breaching party may seek a court order to stop the breaching party from further disclosing confidential information. Injunctions may be interim (temporary) or perpetual (permanent).
- Legal Basis: Governed by Order XXXIX Rule 1 and 2 of the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, and Section 38 of the Specific Relief Act, 1963.
- Indemnification and Damages
- The breaching party may be required to indemnify the non-breaching party for any losses, including court fees, legal costs, and actual damages incurred. This can include both compensatory and consequential damages.
- Compensatory Damages: These are calculated based on the actual financial loss suffered due to the breach.
- Example: If a business loses ₹50,000 due to a breach, compensatory damages may cover that loss.
- Consequential Damages: These damages include losses that occurred indirectly due to the breach, such as lost profits or opportunities.
- Example: A tour company loses potential sales after a breach prevents them from securing a necessary asset.
- Criminal Remedies
- In certain cases, criminal remedies may apply, particularly under the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- Section 72A of the IT Act, 2000 provides for imprisonment up to 3 years or fines up to ₹5 lakh for the unlawful disclosure of information obtained during a contractual relationship.
- In certain cases, criminal remedies may apply, particularly under the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and the Information Technology Act, 2000.
Why Should You Not Break a Confidentiality Agreement?
Breaking an NDA can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Legal and Financial Penalties
- NDAs often specify penalties for violations, including injunctions, indemnifications, and damages.
- A breach could result in substantial financial loss, not only in direct damages but also in reputational harm and loss of future business.
- Job Termination and Reputational Damage
- For employees or contractors, breaching an NDA may result in termination from their position and loss of professional reputation.
- Businesses that breach NDAs risk losing client trust and face the possibility of damaging their public image, which could lead to a loss of clients and future opportunities.
Different Types of Contract Breach Remedies
The remedy for a breach of NDA depends on the specific provisions in the agreement, the nature of the violation, and the facts of the case. Common remedies include:
- Damages for Compensation
- Compensatory Damages: The most common remedy, compensatory damages are calculated based on the actual losses suffered due to the breach, including expectation damages and consequential damages.
- Example: A business loses potential profits from a deal that fell through due to a breach.
- Specific Performance
- Courts may order the breaching party to fulfill its contractual obligations if monetary damages are insufficient. This remedy is more common for contracts involving unique or irreplaceable items.
- Example: A company may seek specific performance if the item breached is a unique asset that cannot be replaced.
- Injunctions
- Injunctions prevent the breaching party from further disclosing confidential information. These can be temporary or permanent, depending on the severity of the breach.
- Liquidated Damages
- A set amount specified in the NDA to cover the breach, particularly where it is difficult to quantify actual damages. Liquidated damages clauses are often used in construction contracts, real estate deals, and partnerships.
- Revocation
- The non-breaching party can rescind the contract, returning both parties to their original position. This remedy is typically used for significant breaches that go to the heart of the agreement.
How to Mitigate the Risk of NDA Breaches
- Draft Clear and Precise NDAs
- Ensure that the NDA clearly defines the scope of confidentiality and the consequences of a breach. Consider incorporating clauses for arbitration to resolve disputes efficiently.
- Implement Security Measures
- Use encryption, access restrictions, and secure systems to prevent accidental breaches.
- Regular Audits and Training
- Conduct periodic reviews of compliance and train employees and third parties on proper handling of confidential information.
- Legal Preparation
- Ensure that any breach is met with swift legal action through well-defined remedies in the NDA.
This proactive approach helps mitigate risks and maintain business integrity.
Importance of Customized NDAs for Businesses
A generic NDA may not always be effective in addressing the specific needs and risks of a business. Customized NDAs are essential for ensuring that the confidentiality, legal obligations, and remedies align with the unique aspects of each business relationship.
Benefits of Tailoring NDAs for Specific Business Needs
- Enhanced Protection of Sensitive Information
Custom NDAs allow businesses to define confidential information more precisely, ensuring better protection for proprietary data, trade secrets, and strategic plans. - Addressing Unique Business Risks
A tailored NDA can address the unique risks associated with different types of business relationships, such as vendor contracts, partnerships, or employee agreements, ensuring that all specific scenarios are covered. - Clearer Terms and Obligations
By customizing the terms and obligations, businesses can ensure both parties have a clear understanding of their responsibilities, reducing the potential for disputes. - Better Enforcement of Terms
A well-crafted NDA that aligns with business needs is easier to enforce in case of breach, as it clearly defines the scope of confidential information, obligations, and penalties for violation. - Minimized Legal Loopholes
Customization helps eliminate ambiguities and potential legal loopholes that could undermine the NDA’s effectiveness in protecting confidential information.
Wrapping up, Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) are a vital tool for businesses in India to protect confidential information and ensure that sensitive data remains secure. Whether it’s a unilateral, bilateral, or multilateral NDA, having the right type tailored to your specific needs is essential for safeguarding trade secrets, business strategies, and proprietary information. A well-drafted NDA template can serve as a solid foundation for any business relationship, offering clarity on obligations and consequences in case of breach. Understanding the legal framework surrounding NDAs, including remedies for breach, is crucial to ensure enforceability under Indian law. To maximize protection, it’s highly recommended to consult with a legal professional to draft a customized NDA that best suits your business’s unique requirements.
FAQs on Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) in India
1. What is an NDA, and why is it important in business?
A Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is a legally binding contract that protects confidential information shared between parties during business dealings. It ensures sensitive data like trade secrets, strategies, or intellectual property remains secure, preventing unauthorized disclosure and fostering trust in business relationships.
2. What are the types of NDAs commonly used in India?
The three main types of NDAs are:
- Unilateral NDA: One party discloses information to another.
- Bilateral (Mutual) NDA: Both parties share confidential information.
- Multilateral NDA: Multiple parties are involved in the agreement.
Each type caters to different business scenarios and ensures tailored protection.
3. What happens if someone breaches an NDA in India?
A breach of NDA can lead to serious consequences, including:
- Civil remedies: Injunctions, monetary damages, or compensation under the Indian Contract Act, 1872.
- Criminal penalties: Punishments under laws like the IT Act, 2000 for unauthorized data disclosure.
Legal actions ensure accountability and protect the affected party’s interests.
4. How can businesses draft an effective NDA?
Businesses should seek legal assistance to draft customized NDAs that address their specific needs. This includes tailoring clauses for confidentiality, scope, and remedies for breach, ensuring compliance with Indian laws for enforceability.
5. Are NDAs legally enforceable in India?
Yes, NDAs are enforceable under Indian laws, including the Indian Contract Act, 1872, Specific Relief Act, 1963, and other relevant statutes. Courts uphold NDAs as long as the terms are fair, reasonable, and not overly broad.
7. Why is it essential to customize an NDA instead of using a generic one?
A customized NDA addresses the unique risks and requirements of your business, ensuring better protection of sensitive information. Tailoring an NDA minimizes legal loopholes, clarifies obligations, and provides effective remedies for breach.
8. How long does an NDA remain valid?
The validity of an NDA depends on the terms set in the agreement. It can be for a fixed duration (e.g., 2-5 years) or remain indefinite, especially for trade secrets or proprietary information that requires long-term protection.



Mergers & Acquisitions in India – Meaning, Difference, Types, M&A Examples
Blog Content Overview
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What are Mergers and Acquisitions?
- 3 Key Differences Between Mergers and Acquisitions
- 4 Types of Mergers and Acquisitions
- 5 Merger and Acquisition Process
- 6 Benefits and Challenges of Mergers and Acquisitions
- 7 Recent and Latest Mergers and Acquisitions in India
- 8 Legal and Regulatory Framework Governing M&A in India
- 9 Examples of Successful M&A Deals in India
- 10 Reasons for Mergers and Acquisitions
- 11 Future of Mergers and Acquisitions in India
- 12 Conclusion
- 13 FAQs on Mergers & Acquisitions in India
- 13.0.1 1. What is the meaning of mergers and acquisitions in India?
- 13.0.2 2. What is the difference between a merger and an acquisition?
- 13.0.3 3. What are the main types of mergers and acquisitions?
- 13.0.4 4. Why do companies pursue mergers and acquisitions in India?
- 13.0.5 6. What are the challenges in the M&A process in India?
- 13.0.6 7. How do synergies work in mergers and acquisitions?
Introduction
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) have emerged as transformative business strategies in the Indian economic landscape, reshaping industries and fostering innovation. At its core, mergers involve the integration of two companies into a single entity, while acquisitions refer to one company taking control over another. Together, these strategies drive growth, create synergies, and enhance competitiveness in an increasingly dynamic marketplace.
India, with its burgeoning economy and government initiatives such as Ease of Doing Business, offers a fertile ground for M&A activities. Key factors driving this trend include globalization, technological advancements, and the need for businesses to scale operations and access new markets. From tech startups to traditional manufacturing giants, M&A plays a pivotal role in aligning businesses with evolving market demands.
As a result, the importance of M&A in the Indian economy cannot be overstated. It enables companies to achieve operational efficiencies, expand product portfolios, and enter untapped markets. For the Indian economy at large, M&A fosters job creation, encourages foreign investments, and enhances the global standing of Indian enterprises. Notable examples like the Flipkart-Walmart deal and the Disney India-Reliance (JioCinema) mergers highlight how such transactions have not only transformed the businesses involved but also impacted entire industries and consequently, the Indian consumer experience.
As India continues to position itself as a global economic powerhouse, mergers and acquisitions remain a cornerstone of its corporate strategy, driving innovation, market consolidation, and economic progress.
What are Mergers and Acquisitions?
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) are strategic corporate actions that businesses undertake to achieve growth, gain competitive advantages, or drive value creation. While often discussed together, mergers and acquisitions have distinct definitions and implications in the corporate world.
Definition of Mergers
A merger occurs when two companies combine to form a single, unified entity. This is often done to pool resources, share expertise, and achieve operational efficiencies, or to expand the reach a business has in the relevant market. In a merger, the entities involved are typically of similar size, and the integration is seen as a collaborative effort. For example, the merger of Vodafone India and Idea Cellular created one of the largest telecom operators in India, Vodafone Idea.
Definition of Acquisitions
An acquisition, on the other hand, happens when one company takes control of another. This can involve purchasing a majority stake or acquiring the entire business. Acquisitions can be either friendly or hostile, depending on whether the target company agrees to the deal. A well-known acquisition in India is Walmart’s takeover of Flipkart, which helped Walmart enter the Indian e-commerce market.
Reasons for Mergers and Acquisitions
Companies pursue mergers and acquisitions for several strategic reasons, including:
- Market Expansion:
M&A enables businesses to enter new geographical regions, tap into different customer bases, and expand their market share. For example, in the financial year of 2023-2024, Reliance Industries acquired the retail, wholesale, logistics and warehousing businesses of Future Group. This deal is projected to consequently expand the reach of Reliance Industries’ retail arm in India. - Cost Savings:
Consolidation often results in economies of scale, reducing production costs, streamlining operations, and enhancing profitability. - Diversification:
By acquiring companies in different sectors, businesses reduce risk and ensure a steady revenue flow even in volatile markets. This trend can be seen in Zomato’s acquisition of grocery delivery company Blinkit (formerly known as Grofers). The acquisition greatly benefited Zomato, leading to 169% returns in the trailing year. - Access to Technology and Talent:
M&A helps organizations acquire cutting-edge technology, intellectual property, and skilled workforce without building these capabilities from scratch. For example, in F.Y. 2023-2024, Tata Motors announced a strategic partnership with Tesla Inc. whereby Tesla’s advanced battery technology and autonomous driving features could be introduced into Tata Motors’ EV lineup in India, in exchange for a 20% stake valued at USD 2 billion. - Synergies:
Perhaps the most significant reason for M&A is achieving synergies—the enhanced value generated when two companies combine.
Synergies in Mergers and Acquisitions
Synergies in mergers and acquisitions refer to the financial and operational benefits derived from combining two businesses. Synergies can take several forms:
- Cost Synergies:
Achieved by eliminating duplicate roles, sharing resources, and optimizing operations to reduce overall expenses. - Revenue Synergies:
Created when the combined entity generates higher sales due to a broader customer base, complementary products, or better market positioning. - Financial Synergies:
Resulting from better access to funding, improved credit ratings, and enhanced financial stability.
For example, the merger of Daimler-Benz and Chrysler aimed to combine their expertise and resources, creating one of the largest automotive manufacturers with significant operational and cost synergies. Similarly in India, the Disney India-Reliance media asset merger will see not only continued survival of the streaming platform offered by Disney India, but will also enable the merged entity to provide a more comprehensive service to Indian consumers, thereby ensuring a steady synergy between the two companies.
Key Differences Between Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions are often used interchangeably, but they are fundamentally different in their structure, purpose, and impact. Understanding these differences is essential for businesses evaluating their growth strategies and for stakeholders aiming to interpret these corporate moves.
What is the Difference Between a Merger and an Acquisition?
Mergers and acquisitions differ across several dimensions, including their operational goals, legal requirements, and financial implications. Below is a detailed table explaining these differences:
| Aspect | Merger | Acquisition |
| Definition | Combining two companies into a single, unified entity. | One company takes control of another by purchasing its shares or assets. |
| Objective | To achieve mutual growth by sharing resources and market opportunities. | To expand market presence, gain assets, or eliminate competition. |
| Legal Process | Involves mutual agreement and shareholder approval from both entities. A scheme of merger will also require approval from the National Company Law Tribunal and (where the applicable thresholds are attracted) approval from the Competition Commission of India and/or the Reserve Bank of India/Securities and Exchange Board of India. | The acquiring company gains ownership, which can be friendly or hostile. This is typically done by way of business transfer agreements or slump sales. |
| Control and Ownership | Ownership is typically shared between the merged companies. | The acquiring company retains control; the target company loses autonomy erstwhile enjoyed. |
| Cultural Impact | Requires integration of organizational cultures and systems. | The target company often adopts the culture and processes of the acquirer. |
| Size of Companies | Usually, companies of similar size merge. | The acquiring company is generally larger and financially stronger. |
| Financial Impact | Often viewed as a collaborative growth strategy with shared benefits. | Can lead to financial domination by the acquiring company over the acquired. |
| Examples in India | Vodafone & Idea Cellular (merger to form Vodafone Idea). | Walmart acquiring Flipkart for market entry into India. |
Real-Life Examples to Highlight the Differences
Merger Example: Vodafone & Idea Cellular
The merger between Vodafone India and Idea Cellular in 2018 created Vodafone Idea Limited, a single entity to counter the rising competition in India’s telecom sector. This was a collaborative decision to combine their resources and customer base, resulting in a larger market share and operational synergies.
Acquisition Example: Walmart & Flipkart
In 2018, Walmart acquired a 77% stake in Flipkart for $16 billion. This acquisition marked Walmart’s entry into the Indian e-commerce space, allowing it to compete with Amazon and leverage Flipkart’s established market presence. The acquisition was strategic, as Walmart gained complete control while Flipkart operated under its umbrella.
The difference between merger and acquisition lies in their structure, purpose, and execution. While mergers aim for collaboration and mutual growth, acquisitions are often driven by strategic takeovers to enhance competitiveness or expand market reach.
Types of Mergers and Acquisitions
Depending on the strategic goals of the companies involved, M&A transactions are classified into various types. These types not only reflect the nature of the deal but also its potential impact on the market, operations, and competitive positioning.
a. Types of Mergers
- Horizontal Merger
- A horizontal merger occurs when two companies operating in the same industry and often as direct competitors combine forces.
- Objective: To gain market share, eliminate competition, and achieve economies of scale.
- Example: The merger of Vodafone India and Idea Cellular to create Vodafone Idea aimed to strengthen their position in the telecom market.
- Vertical Merger
- A vertical merger involves the combination of companies operating at different levels of the supply chain (e.g., a supplier and a buyer).
- Objective: To ensure better control over the supply chain, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
- Example: Reliance Industries’ acquisition of Den Networks and Hathway Cable to expand its Jio broadband services.
- Conglomerate Merger
- A conglomerate merger happens between companies from completely unrelated industries.
- Objective: To diversify business operations and mitigate risks associated with a single market.
- Example: The Tata Group’s acquisition of Tetley Tea, which diversified its operations into the beverage sector.
- Market Extension Merger
- Combines companies offering similar products in different geographical markets.
- Objective: To expand market reach and access new customer bases.
- Example: Airtel acquiring Zain Telecom’s African operations.
- Product Extension Merger
- Involves companies that deal with related products merging to expand their product lines.
- Objective: To offer complementary products and enhance market penetration.
- Example: Facebook’s acquisition of Instagram to broaden its social media portfolio.
b. Types of Acquisitions
- Friendly Acquisitions
- These are mutually agreed deals where the acquiring and target companies collaborate on the transaction.
- Example: Tata Steel’s acquisition of Bhushan Steel to enhance its production capacity.
- Hostile Takeovers
- Occur when the acquiring company takes control of the target company without its consent, often by purchasing a majority of its shares.
- Example: L&T’s hostile takeover of Mindtree.
- Reverse Mergers
- In this scenario, a private company acquires a public company to bypass the lengthy IPO process and become publicly traded.
- Example: The reverse merger of Vedanta Resources into Sterlite Industries.
c. Theories of Mergers and Acquisitions
- Efficiency Theory
- Suggests that M&A transactions are driven by the desire to increase operational efficiency.
- Focus: Cost reduction, revenue enhancement, and resource optimization.
- Example: Companies merging to reduce redundant departments and cut costs.
- Monopoly Theory
- Argues that M&As are often pursued to eliminate competition and gain a dominant market position.
- Focus: Market power and the ability to influence pricing and industry standards.
- Example: The acquisition of WhatsApp by Facebook to dominate the messaging space.
- Valuation Theory
- Suggests that companies engage in M&A when the target company’s market value is lower than its perceived intrinsic value.
- Focus: Acquiring undervalued businesses to create financial gains.
- Example: Reliance Industries acquiring multiple startups to tap into high-growth sectors.
Merger and Acquisition Process
The merger and acquisition process is a multifaceted journey that requires meticulous planning and execution. Each phase of the process plays a vital role in ensuring the success of the transaction, minimizing risks, and maximizing value. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the key stages involved:
1. Strategic Planning
- This is the foundational stage where companies identify their objectives for the merger or acquisition.
- Key Activities:
- Define clear goals: market expansion, cost efficiency, or diversification.
- Identify potential target companies.
- Assess alignment with long-term business strategies.
- Importance: Strategic clarity ensures the M&A aligns with the company’s vision and delivers value.
2. Due Diligence
- A critical stage involving an in-depth evaluation of the target company.
- Key Areas of Assessment:
- Financial performance, including revenue and debt.
- Legal compliance and potential liabilities.
- Market position, competition, and operational efficiency.
- Importance: Identifies potential risks and validates the decision to proceed with the transaction.
3. Valuation and Negotiation
- This phase determines the value of the target company and sets the terms of the deal.
- Key Activities:
- Assess the company’s intrinsic and market value.
- Negotiate terms such as purchase price, payment structure, and contingencies.
- Importance: Accurate valuation prevents overpayment and ensures the deal’s financial viability.
4. Legal and Regulatory Approvals
- Securing necessary permissions from governing bodies to ensure compliance with local and international laws.
- Key Activities:
- Review by legal teams for compliance with corporate, tax, and antitrust laws.
- Obtain approvals from regulatory bodies like National Company Law Tribunal, SEBI, RBI, or the Competition Commission of India (CCI).
- Importance: Ensures the deal is legally sound and avoids future legal challenges.
5. Integration Planning
- Preparing a roadmap to merge the operations, cultures, and systems of the two entities.
- Key Activities:
- Define integration objectives and timelines.
- Plan the merging of HR, IT, operations, and finance systems.
- Importance: Effective planning minimizes disruptions and facilitates a seamless transition.
6. Post-Merger Integration
- The final and often most challenging phase where the actual integration takes place.
- Key Activities:
- Align organizational cultures and team structures.
- Monitor and evaluate the performance of the combined entity.
- Address stakeholder concerns and maintain morale.
- Importance: Ensures the realization of synergies and the success of the M&A.
Benefits and Challenges of Mergers and Acquisitions
a. Benefits of Mergers and Acquisitions
- Increased Market Share
- M&A allows companies to consolidate their position in existing markets and expand into new ones.
- Example: The Flipkart-Walmart acquisition strengthened Walmart’s presence in India’s e-commerce sector.
- Operational Synergies
- Combining resources and expertise leads to cost savings, improved efficiency, and higher productivity.
- Example: The Vodafone-Idea merger achieved economies of scale in operations.
- Enhanced Financial Performance
- M&A enables companies to leverage combined assets for greater profitability and improved cash flow.
- Example: HDFC Bank and HDFC Limited merger enhanced their financial services portfolio.
b. Advantages and Disadvantages of Mergers and Acquisitions
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Economies of Scale: Cost reduction through shared resources and streamlined operations. | Cultural Clashes: Differences in organizational cultures can disrupt operations. |
| Access to New Markets: Entering untapped geographical or demographic markets. | High Costs: Significant financial investment for valuations, legal fees, and integrations. |
| Improved Competitiveness: Enhanced ability to compete in global or local markets. | Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with complex legal and antitrust requirements can take a significant period of time to obtain approvals, causing delays in closing deals. |
Recent and Latest Mergers and Acquisitions in India
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in India have become a pivotal part of the business landscape, reflecting the country’s growing economy and diverse industry sectors. The latest M&A deals in India showcase how companies are using strategic consolidations to enhance market presence, strengthen financials, and expand their portfolios. Here are a few significant recent and latest mergers and acquisitions in India:
1. Walmart & Flipkart
- Overview: Walmart’s acquisition of Flipkart in 2018 for $16 billion was one of the largest deals in India’s e-commerce sector.
- Strategic Impact: Walmart gained a significant foothold in the Indian market, enabling it to compete with Amazon in the growing online retail space. Flipkart benefited from Walmart’s deep financial resources and global supply chain expertise.
- Importance: This acquisition exemplifies a classic example of market expansion and securing a dominant position in the Indian e-commerce market.
2. HDFC Bank & HDFC Ltd.
- Overview: In 2022, HDFC Bank announced the acquisition of HDFC Ltd., creating India’s largest private sector bank by assets.
- Strategic Impact: This merger aims to create synergies in banking and housing finance, providing integrated financial services to customers and improving operational efficiencies.
- Importance: The merger is expected to drive substantial growth for the bank, enabling cross-selling opportunities and increasing market share in financial services.
3. Tata Consumer & Bisleri (Proposed)
- Overview: Tata Consumer Products, which owns Tata Tea and other popular brands, is in talks to acquire Bisleri, a leading bottled water brand in India.
- Strategic Impact: The acquisition would strengthen Tata Consumer’s position in the beverage sector, particularly in the bottled water market, one of the fastest-growing segments in India.
- Importance: If the deal goes through, it would mark a major consolidation in the FMCG sector, combining two strong brands and expanding Tata Consumer’s portfolio of products.
Trends in Recent Mergers and Acquisitions in India
- Industry Consolidation: M&A deals in India are becoming more common in sectors such as e-commerce, banking, and FMCG, as companies look to diversify and expand their offerings.
- Cross-border Acquisitions: Increasingly, Indian companies are acquiring foreign firms to access international markets and new technologies. For instance, Tata Group’s acquisition of Air India was a major step toward reviving the airline and increasing global market reach.
- Strategic Alliances: Companies are forming alliances through mergers and acquisitions to enhance competitive advantages, such as better financial performance and market entry in new regions.
Legal and Regulatory Framework Governing M&A in India
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in India are governed by a complex and detailed legal and regulatory framework. Companies looking to execute M&A transactions must comply with various laws and regulations to ensure that the deal is legally sound and does not face any future legal challenges. Below is an overview of the key legislations, regulatory bodies, and tax implications involved in M&A in India.
Key Legislations Governing M&A in India
- Companies Act, 2013
- The Companies Act, 2013 serves as the principal legislation for governing corporate transactions, including mergers and acquisitions, in India. It outlines the procedures for mergers, demergers, and corporate restructuring, including the approval process by shareholders, creditors, and the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT).
- Important Provisions:
- Sections 230 to 232 of the Companies Act deal with the process of mergers and demergers. Robust mechanisms are put in place to ensure greater transparency and accountability, ensuring protection of stakeholders.
- Provisions related to the protection of minority shareholders and creditors during the M&A process.
- SEBI Guidelines
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates M&A deals involving listed companies to ensure transparency and protect the interests of investors.
- Key SEBI Regulations:
- SEBI (Substantial Acquisition of Shares and Takeovers) Regulations, 2011: Governs the process of acquiring control or a substantial amount of shares in a listed company.
- SEBI (Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations: Applies to the issuance of securities in the case of mergers, especially if the transaction involves a public offer.
- SEBI ensures that M&A deals involving public companies comply with disclosure norms and prevent market manipulation. This ensures greater accountability and transparency to protect the ultimate public interest in such entities and deals.
- Competition Act, 2002
- The Competition Act regulates mergers and acquisitions to prevent any anti-competitive practices that may harm the market or consumers.
- Key Provisions:
- Section 5 and Section 6: Deals with the merger control provisions, ensuring that any M&A transaction does not create a dominant market position that could reduce competition.
- Role of CCI: The Competition Commission of India (CCI) reviews mergers and acquisitions crossing a certain financial threshold to evaluate their impact on market competition and consumer welfare.
- FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act), 1999
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) governs foreign investments in India and controls the cross-border flow of capital.
- Important Provisions:
- FEMA regulations come into play when foreign companies or individuals are involved in the M&A transaction.
- Approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is required for foreign investments exceeding certain thresholds.
Regulatory Bodies Overseeing M&A in India
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- SEBI plays a pivotal role in overseeing M&A transactions involving publicly traded companies. It ensures compliance with disclosure norms and regulates takeover bids, ensuring fair practices and transparency in the securities market.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- RBI regulates foreign investment in Indian companies under the FEMA guidelines. Any cross-border mergers, acquisitions, or investments require approval from RBI, especially if the transaction exceeds the prescribed limit.
- Competition Commission of India (CCI)
- The CCI examines and evaluates the competition aspects of M&A transactions to ensure that such deals do not result in market monopolies or anti-competitive behavior. The CCI has the authority to block or modify deals that are deemed detrimental to market competition.
- National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)
- The NCLT is a judicial body that adjudicates disputes related to mergers, demergers, and corporate restructuring. It is also the final authority in approving the merger or acquisition process once shareholders and creditors approve the deal. Any appeals against a ruling of the NCLT will be taken up to the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (authority on par with jurisdictional high courts in India) and thereafter, to the Supreme Court by way of special leave petitions.
Tax Implications and Compliance Challenges in M&A
M&A transactions in India also involve significant tax implications that businesses must navigate carefully to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
- Income Tax Act, 1961
- Capital Gains Tax: If the target company’s shares are sold or transferred during the M&A, capital gains tax may be levied based on the holding period and the value of the shares.
- Tax-Free Reorganization: Certain mergers and acquisitions can qualify as tax-free reorganizations under Section 47 of the Income Tax Act if the transaction meets specific conditions.
- GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- M&A Transactions: Goods and Services Tax (GST) applies to the transfer of business assets during mergers or acquisitions. However, the transfer of shares in a merger is generally exempt from GST.
- Stamp Duty
- M&A transactions involving the transfer of shares or assets are subject to stamp duty, which varies based on the state in which the deal is executed.
Examples of Successful M&A Deals in India
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in India have played a significant role in shaping the country’s business landscape. Successful M&A deals have not only expanded market share but also led to innovation, enhanced competitiveness, and strategic growth. Below are some notable mergers and acquisitions in India that have been instrumental in transforming industries.
1. Tata Steel & Corus
- Deal Overview:
In 2007, Tata Steel, one of India’s largest steel manufacturers, acquired Corus, a UK-based steel giant, for approximately $12 billion. This acquisition was one of the largest overseas acquisitions by an Indian company at the time. - Strategic Impact:
- Tata Steel gained access to Corus’s advanced steel technology, expanding its presence in Europe.
- The deal allowed Tata Steel to diversify its product offerings and strengthen its position as a global player in the steel industry.
- Lessons Learned:
- Cultural Integration: While the deal was strategically sound, cultural integration was a challenge, as Tata Steel had to align its operations with the Western approach to business.
- Long-Term Vision: Tata Steel’s vision of becoming a global leader in steel was achieved by securing Corus’s resources, expanding its production capacity, and penetrating the European market.
2. Vodafone & Idea (Vi)
- Deal Overview:
In 2018, Vodafone India and Idea Cellular merged to create Vi (Vodafone Idea), one of India’s largest telecom operators, with a combined market share of over 40%. The deal was valued at approximately $23 billion. - Strategic Impact:
- The merger allowed both companies to compete effectively with industry leaders Airtel and Reliance Jio, especially in the face of declining revenue and increasing competition.
- By pooling resources, both companies were able to share infrastructure, reduce costs, and focus on customer acquisition.
- Lessons Learned:
- Regulatory Hurdles: The deal was subject to regulatory scrutiny and approval from the Competition Commission of India (CCI). It highlighted the importance of navigating regulatory challenges in large-scale M&A transactions.
- Post-Merger Integration: Post-merger challenges included integrating networks, streamlining operations, and retaining customers amidst fierce competition.
3. Zomato & Blinkit
- Deal Overview:
In 2022, Zomato, the food delivery giant, acquired Blinkit (formerly Grofers), an online grocery delivery platform, for $568 million. This move aimed to enhance Zomato’s presence in the rapidly growing quick commerce (Q-commerce) space. - Strategic Impact:
- The acquisition enabled Zomato to diversify its portfolio by venturing into grocery delivery, tapping into the expanding demand for fast delivery services.
- Blinkit’s established customer base and supply chain expertise in grocery logistics complemented Zomato’s food delivery network, making it a strong contender in the Q-commerce market.
- Lessons Learned:
- Diversification: Zomato’s move into the grocery segment shows the importance of diversification in capturing new growth opportunities.
- Market Trends: Understanding market trends, like the increasing demand for faster grocery delivery, helped Zomato gain a competitive edge in an emerging segment.
Reasons for Mergers and Acquisitions
Here are the common reasons for mergers and acquisitions that drive companies to pursue such deals:
1. Expanding Market Reach
One of the most common reasons for mergers and acquisitions is to expand market reach. By acquiring or merging with another company, businesses can enter new geographical regions, reach untapped customer segments, or gain access to a broader market.
- Example: A company may merge with a local competitor in a different region to increase its presence without having to build an entirely new distribution network.
2. Diversifying Product Portfolio
M&A allows companies to diversify their product portfolio by adding complementary or entirely new products to their offerings. This helps reduce dependence on a single product line and spreads business risk.
- Example: A tech company acquiring a software company to offer a full suite of products, from hardware to software, providing customers with a complete solution.
3. Reducing Operational Costs
By merging with or acquiring another business, companies can achieve economies of scale, streamline operations, and reduce overall costs. This can include sharing infrastructure, cutting redundant staff, or integrating supply chains for better efficiency.
- Example: Two manufacturing companies may merge to optimize production facilities, reduce supply chain costs, and achieve higher purchasing power.
Future of Mergers and Acquisitions in India
The future of mergers and acquisitions in India looks promising, driven by evolving market dynamics and global trends. As the country continues to grow economically, M&A activities are expected to remain a key strategy for companies looking to expand, diversify, and optimize operations.
Trends and Predictions in M&A Activities
- Increased Cross-Border M&As: With India’s growing influence on the global stage, cross-border mergers and acquisitions are expected to rise, especially in sectors like technology and finance.
- Private Equity and Venture Capital: The involvement of private equity firms and venture capitalists in M&A is expected to grow as they seek opportunities in high-growth sectors.
Emerging Sectors for M&A
- Technology: The digital transformation wave in India will drive M&A in the tech sector, particularly in software, fintech, and AI startups.
- Finance: The growing demand for financial products and services will lead to consolidation in the banking, insurance, and fintech sectors.
- Healthcare: With rising healthcare needs, mergers and acquisitions in healthcare services, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology are expected to surge.
Impact of Globalization and Technology on M&A Deals
- Globalization: As Indian companies expand globally, M&A will continue to be a preferred route for market entry and acquiring new capabilities.
- Technology: Advancements in digital platforms and AI will streamline M&A processes, making them faster and more efficient while opening new avenues for innovation.
Conclusion
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in India are pivotal to the growth and evolution of businesses, offering opportunities for market expansion, cost reduction, and increased competitiveness. Understanding the meaning of mergers and acquisitions, the key differences between mergers and acquisitions, and the various types of M&A can provide valuable insights for companies looking to optimize their strategies. Real-world examples, such as the Tata Steel & Corus deal and Vodafone & Idea merger, highlight the strategic importance of M&A in India’s business landscape.
As M&A continues to shape industries across sectors like technology, finance, and healthcare, companies must stay informed about M&A processes, legal frameworks, and emerging trends. The future of mergers and acquisitions in India remains bright, driven by evolving market dynamics and technological advancements. Understanding these concepts is essential for businesses aiming to succeed in an increasingly competitive global economy.
FAQs on Mergers & Acquisitions in India
1. What is the meaning of mergers and acquisitions in India?
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in India refer to the process where two companies combine (merger) or one company takes over another (acquisition). These transactions are often undertaken to achieve growth, expand market reach, or diversify product portfolios.
2. What is the difference between a merger and an acquisition?
A merger involves two companies combining to form a new entity, while an acquisition occurs when one company takes over another, with the acquired company becoming part of the acquiring company. Mergers are typically seen as a mutual agreement, whereas acquisitions can be friendly or hostile.
3. What are the main types of mergers and acquisitions?
There are several types of mergers and acquisitions:
- Horizontal Merger: Between competitors in the same industry.
- Vertical Merger: Between companies in the supply chain (suppliers and buyers).
- Conglomerate Merger: Between unrelated businesses.
- Friendly Acquisition: Where both companies agree to the deal.
- Hostile Takeover: When one company acquires another against the wishes of the target company’s management.
4. Why do companies pursue mergers and acquisitions in India?
Companies pursue mergers and acquisitions to expand their market reach, diversify their product offerings, achieve economies of scale, reduce operational costs, and stay competitive in the evolving market.
6. What are the challenges in the M&A process in India?
Challenges in the merger and acquisition process in India include regulatory approvals, cultural integration, maintaining brand identity, and aligning the financial goals of both companies. Legal complexities and compliance with various laws like the Competition Act and SEBI regulations can also pose difficulties.
7. How do synergies work in mergers and acquisitions?
Synergies in mergers and acquisitions refer to the combined benefits that result from the merger or acquisition, such as cost savings, improved efficiencies, increased market share, and enhanced revenue generation. Synergies often drive the value of an M&A deal, making it beneficial for both companies involved.



Trademark Registration in India – Meaning, Online Process, Documents
Blog Content Overview
- 1 Introduction to Trademark Registration in India
- 2 What is Trademark Registration?
- 3 Types of Trademarks in India
- 4 Procedure for Online Trademark Registration in India
- 4.1 Step 1: Choose a Unique Trademark and Conduct a Trademark Registration Search
- 4.2 Step 2: Prepare and Submit the Application (Online/Offline)
- 4.3 Step 3: Verification of Application and Documents
- 4.4 Step 4: Trademark Journal Publication and Opposition
- 4.5 Step 5: Approval and Issuance of Trademark Registration Certificate
- 4.6 Additional Points to Note
- 5 Documents Required for Trademark Registration in India
- 6 Costs and Fees for Trademark Registration in India
- 7 How to Check Trademark Registration Status
- 8 Common Grounds for Refusal of Trademark Registration in India
- 9 Renewing a Trademark in India
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Trademark Registration in India
Introduction to Trademark Registration in India
In today’s competitive market, building a strong brand identity is vital for success. It is in this context that trademarks become a critical asset to distinguish a business’ products or services from others, ensuring they stand out and are instantly recognizable to a consumer. Consequently, protection of the trademark through trademark registration in India is a crucial step for businesses aiming to protect their brand identity and establish legal ownership over their logos, names, and symbols – all of which constitute intellectual property of the business. As a result, whether it’s a logo, name, slogan, or unique design, registering a trademark provides legal protection against infringement of intellectual property and legitimizes the brand’s ownership of such intellectual property.
In India, the process of registering a trademark is governed by the Trade Marks Act, 1999, and is overseen by the Trade Marks Registry. The Trade Marks Registry was established in 1940, and was followed by the passing of the Trademark Act in 1999. The Head Office of the Trade Marks Registry is located in Mumbai and regional offices in Ahmedabad, Chennai, Delhi, and Kolkata.
A registered trademark offers exclusive rights of use to the owner, preventing unauthorized use of the mark by others and providing a legal mechanism to pursue recourse against infringement. Additionally, registration helps avoid potential legal conflicts or claim of the mark by a third party, and protects the business from unfair competition.
The answer to question – How to Register Trademark in India? is relatively straightforward, but it requires careful attention to detail to ensure compliance with legal requirements. It involves several steps, including a trademark search, filing the application, examination, publication, and ultimately the issuance of the registration certificate. Throughout this process, it is crucial to ensure that the trademark is distinct, does not conflict with existing marks, and is used in a way that is representative of the business’ activities.
What is Trademark Registration?
Trademark registration is a legal process that grants exclusive rights to a brand or business to use a specific mark, symbol, logo, name, or design to distinguish its products or services from others in the market. A registered trademark becomes an integral part of a company’s intellectual property portfolio, offering both legal protection and a competitive edge.
In India, trademarks are governed by the Trade Marks Act, 1999, which provides the framework for registering, protecting, and enforcing trademark rights.
Definition of a Trademark
A trademark is a distinct sign, symbol, word, or combination of these elements that represents a brand and differentiates its offerings from others. Trademarks are not just limited to logos or names; they can include slogans, colors, sounds, or even packaging styles that uniquely identify a product or service. In India, trademarks are protected under the Trade Marks Act, 1999, offering exclusive rights to the owner.
For example:
- The golden arches of McDonald’s are a globally recognized logo trademark.
- The tagline “Just Do It” is an example of a registered “wordmark” by Nike.
Trademarks are classified into 45 trademark classes, which group various goods and services to streamline the registration process. Businesses must choose the relevant class that aligns with their offerings during registration.
Intellectual Property Rights Symbols and Their Significance: ™, ℠, ®
Understanding the symbols associated with trademarks is crucial for businesses and consumers alike:
- ™ (Trademark):
- This symbol indicates that the mark is being used as a trademark, but it is not yet registered.
- It signifies intent to protect the brand and discourages misuse.
- ℠ (Service Mark):
- Used for service-based businesses to highlight unregistered marks.
- Common in industries like hospitality, consulting, and IT services.
- ® (Registered Trademark):
- Denotes that the trademark is officially registered with the government.
- Provides legal protection and exclusive rights to use the mark in its registered category.
Using the correct symbol helps businesses communicate their trademark status while deterring infringement and ensuring legal enforceability.
Importance of Trademark Registration
Trademark registration is essential for businesses looking to secure their brand identity. It ensures legal protection and provides exclusive rights to the owner to use the mark for their goods or services. Key reasons why trademark registration is important include:
- Brand Protection: Prevents competitors from using similar names, logos, or designs that could mislead customers.
- Legal Recognition: Grants official ownership under Indian law, ensuring your rights are safeguarded.
- Customer Trust: A trademark adds credibility to your brand, making it easier for customers to identify and trust your products or services.
- Asset Creation: Registered trademarks are intangible assets that can be licensed, franchised, or sold for business growth.
- Global Reach: Trademark registration in India can facilitate international trademark recognition, helping businesses expand globally.
Benefits of Registering a Trademark in India
The benefits of trademark registration extend beyond legal protection. Here are the key advantages:
- Exclusive Rights: Registration provides exclusive rights to the owner, ensuring the trademark cannot be legally used by others in the registered class.
- Competitive Edge: A trademark helps establish a distinct identity in the market, giving your business a competitive advantage.
- Prevention of Infringement: Protects against unauthorized use of your brand name, logo, or design.
- Market Goodwill: Builds trust and goodwill with customers, enhancing brand loyalty.
- Ease of Business Expansion: A registered trademark facilitates licensing or franchising, opening doors for business growth.
- Strong Legal Position: In the event of disputes, a registered trademark provides a strong legal standing.
Brief Overview of the Trademark Registration Process in India
The procedure for trademark registration in India is systematic and straightforward. Here’s a quick overview:
- Trademark Search: Conduct a trademark registration search to ensure the desired trademark is unique and not already registered.
- Application Filing: Submit the trademark application online or offline with all required documents, including ID proofs, business registration details, and the logo (if applicable).
- Examination and Review: Authorities review the application and may raise objections, which must be addressed within the stipulated time.
- Publication: The trademark is published in the Trademark Journal, allowing for public objections.
- Approval and Registration: If no objections are raised or resolved satisfactorily, the trademark is approved and the trademark registration certificate is issued.
Registering a trademark not only provides legal protection but also secures your brand’s future, ensuring long-term growth and recognition in the market.
Types of Trademarks in India
Trademarks in India are categorized into general and specific types, each serving different purposes to protect distinct aspects of a brand’s identity.
General Trademarks
- Generic Mark: Refers to common terms or names that describe a product or service. These marks are not eligible for registration as they lack uniqueness (e.g., “Milk” for dairy products).
- Suggestive Mark: Indicates the nature or quality of the goods or services indirectly, requiring imagination to connect with the product (e.g., “Netflix” suggests internet-based flicks).
- Descriptive Mark: Describes the product or service but must acquire distinctiveness to qualify for registration (e.g., “Best Rice”).
- Arbitrary Mark: Uses common words in an unrelated context, making them distinctive (e.g., “Apple” for electronics).
- Fanciful Mark: Invented words with no prior meaning, offering the highest level of protection (e.g., “Google”).
Specific Trademarks
- Service Mark: Identifies and protects services rather than goods (e.g., logos of consulting firms).
- Certification Mark: Indicates that the product meets established standards (e.g., ISI mark).
- Collective Mark: Used by a group of entities to signify membership or collective ownership (e.g., “CA” for Chartered Accountants).
- Trade Dress: Protects the visual appearance or packaging of a product, such as color schemes or layouts (e.g., Coca-Cola bottle shape).
- Sound Mark: Protects unique sounds associated with a brand (e.g., the Nokia tune).
Other types include Pattern Marks, Position Marks, and Hologram Marks, which add further layers of protection to unique brand elements.
Who can Apply for Trademark?
Anyone can apply for trademark registration, including individuals, companies, and LLPs. The person listed as the applicant in the trademark registration form will be recognized as the trademark owner once the registration is complete. This process allows businesses and individuals to protect their brand identity under trademark law.
Procedure for Online Trademark Registration in India
Trademark registration in India involves a detailed and systematic process that ensures legal protection for your brand. Below is a step-by-step guide to the procedure:
Step 1: Choose a Unique Trademark and Conduct a Trademark Registration Search
- Begin by selecting a unique and distinctive trademark that effectively represents your brand. It could be a logo, wordmark, slogan, or even a combination of elements.
- Ensure your trademark aligns with your business’s trademark class. There are 45 classes under which trademarks can be registered:
- Classes 1-34 cover goods.
- Classes 35-45 cover services.
- Conduct a trademark registration search using the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks’ online database. This ensures your chosen mark isn’t already in use or similar to an existing trademark, avoiding potential objections or rejections.
Step 2: Prepare and Submit the Application (Online/Offline)
- Application Form: File Form TM-A, which allows registration for one or multiple classes.
- Required Documents:
- Business Registration Proof (e.g., GST certificate or incorporation document).
- Identity and address proof of the applicant (e.g., PAN, Aadhaar).
- A clear digital image of the trademark (dimensions: 9 cm x 5 cm).
- Proof of claim, if the mark has been used previously in another country.
- Power of Attorney, if an agent is filing on your behalf.
- Filing Options:
- Manual Filing: Submit the form at the nearest Trademark Registry Office (Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, or Ahmedabad).
- Acknowledgment takes 15-20 days.
- Online Filing: Faster and efficient, with instant acknowledgment via the IP India portal (https://ipindia.gov.in/).
- Manual Filing: Submit the form at the nearest Trademark Registry Office (Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, or Ahmedabad).



- Government Fees for Trademark Registration (as on date):
- ₹4,500 (e-filing) or ₹5,000 (manual filing) for individuals, startups, and small businesses.
- ₹9,000 (e-filing) or ₹10,000 (manual filing) for others.
Step 3: Verification of Application and Documents
- The Registrar of Trademarks examines the application to ensure compliance with the Trademark Act of 1999 and relevant guidelines.
- If any issues arise, such as incomplete information or similarity with an existing mark, the Registrar raises an objection and sends a notice to the applicant.
- Applicants must respond to objections within the stipulated timeframe, providing justifications or additional documentation.
Step 4: Trademark Journal Publication and Opposition
- Once cleared, the trademark is published in the Indian Trademark Journal, inviting public feedback.
- Opposition Period:
- Third parties have four months to file an opposition if they believe the trademark conflicts with their rights.
- If opposition arises, both parties present their evidence, and the Registrar conducts a hearing to resolve the matter.
Step 5: Approval and Issuance of Trademark Registration Certificate
- If there are no objections or oppositions (or they are resolved), the Registrar approves the trademark.
- A Trademark Registration Certificate is issued, officially granting the applicant the right to use the ® symbol alongside their trademark.
Additional Points to Note
- The entire trademark registration process in India can take 6 months to 2 years, depending on the objections or oppositions.
- During the registration process, you can use the ™ symbol to indicate a pending trademark application. Once the certificate is issued, switch to the ® symbol, denoting a registered trademark.
By following this step-by-step guide, businesses can protect their brand, build trust, and enjoy exclusive rights to their trademark in India. Ensure proper documentation and legal assistance for a smoother registration process.
Documents Required for Trademark Registration in India
To successfully register a trademark in India, specific documents must be submitted. These documents establish the applicant’s identity, business details, and trademark uniqueness. Here’s a concise list with key details:
1. Business Registration Proof
- Sole Proprietorship: GST Certificate or Business Registration Certificate.
- Partnership Firm: Partnership Deed or Registration Certificate.
- Company/LLP: Incorporation Certificate and Company PAN card.
2. Identity and Address Proof
- Individuals/Sole Proprietors: PAN Card, Aadhaar Card, or Passport.
- Companies/LLPs: Identity proof of directors/partners and registered office address proof.
3. Trademark Representation
- A clear digital image of the trademark (logo, wordmark, or slogan) with dimensions of 9 cm x 5 cm.
4. Power of Attorney (Form TM-48)
- A signed Power of Attorney authorizing an agent or attorney to file the trademark application.
5. Proof of Prior Usage (If Applicable)
- Evidence such as invoices, advertisements, or product labels showing prior use of the trademark.
6. Udyog Aadhaar or MSME Certificate
- Required for startups, small businesses, and individuals to avail reduced trademark registration fees.
7. Class-Specific Details
- Declaration of the class of goods or services (from 45 available trademark classes).
8. Address Proof of Business
- Recent utility bills, lease agreements, or ownership documents as proof of the business location.
By ensuring all these documents for trademark registration are complete and accurate, applicants can avoid delays and simplify the registration process. Proper documentation is key to protecting your brand identity in India.
Costs and Fees for Trademark Registration in India
Understanding of the costs involved in trademark registration in India is needed for businesses and individuals planning to protect their intellectual property. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
1. Government Fees for Trademark Registration (as on date)
- Individuals, Startups, and Small Enterprises:
- ₹4,500 for e-filing.
- ₹5,000 for physical filing.
- Others (Companies, LLPs, etc.):
- ₹9,000 for e-filing.
- ₹10,000 for physical filing.
2. Additional Costs for Professional Services
- Hiring a trademark attorney or agent may involve additional charges depending on the complexity of the application and services provided.
3. Factors Affecting Trademark Registration Costs
- Number of Classes: Registering under multiple trademark classes increases the fees.
- Type of Trademark: Filing for a collective trademark or series mark incurs higher costs.
- Opposition Proceedings: If objections are raised, handling opposition can add to the expenses.
Planning your trademark registration carefully can help you manage costs effectively while ensuring maximum protection for your brand.
How to Check Trademark Registration Status
After filing your application, it’s essential to monitor its status regularly to avoid delays. Here’s how you can do it:



1. Online Methods to Check Trademark Status
- Visit the official website of the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks.
- Navigate to the “Trademark Status” option or visit https://tmrsearch.ipindia.gov.in/eregister/eregister.aspx .
- Enter your application number or trademark details.
- View the current status, including examination, opposition, or registration updates.
2. Common Reasons for Delays
- Incomplete Documentation: Missing or incorrect documents can lead to processing delays.
- Objections or Oppositions: Objections raised by the Trademark Office or third-party oppositions require resolution, prolonging the process.
- Backlog at Trademark Office: High volume of applications can slow down the approval process.
3. Resolving Delays
- Ensure that all documents are complete and accurate during submission.
- Respond promptly to objections or opposition notices.
- Seek professional assistance to expedite the process.
By staying informed about the trademark registration status and addressing issues proactively, you can secure your trademark efficiently and avoid unnecessary complications.
Common Grounds for Refusal of Trademark Registration in India
When applying for trademark registration in India, the application may be refused based on certain grounds. It’s essential to understand these absolute grounds for refusal to avoid issues during the process.
1. Absolute Grounds for Refusal
These are the reasons that may lead to the rejection of a trademark application even if no other parties oppose it. They include:
- Lack of Distinctiveness: A trademark must be unique and capable of distinguishing the goods or services of one entity from another. Generic or descriptive marks are often refused.
- Deceptive or Misleading Marks: Trademarks that mislead consumers about the nature or quality of the goods or services are not eligible for registration.
- Conflict with Public Order or Morality: Trademarks that go against public morality or religious beliefs can be refused.
- Confusion with Existing Trademarks: Trademarks that are too similar to an already registered mark or a pending application will be rejected.
2. Examples of Trademarks That May Be Rejected
- Descriptive Marks: For example, “Sweet Cake” for a bakery.
- Generic Terms: Words like “Apple” for computer-related products or “Coffee” for coffee-related services.
- Marks That Resemble Flags, Emblems, or National Symbols: Trademarks that resemble state or national flags or symbols.
By understanding these grounds, applicants can avoid common mistakes and improve their chances of approval.
Renewing a Trademark in India
Once your trademark is registered, it remains valid for a specific period. However, it must be renewed to continue enjoying protection under the law.
1. Validity Period of a Trademark
In India, a trademark is valid for 10 years from the date of registration. After this period, the trademark owner must renew the registration to maintain its exclusive rights.
2. Procedure and Timeline for Trademark Renewal
- Filing for Renewal: The application for renewal must be filed before the expiration of the 10-year validity period. It can be done within 6 months before or after the expiration date.
- Online Filing: The process can be done through the official website of the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks. You need to fill out the appropriate form (Form TM-R) and pay the renewal fees.
- Timeline: The renewal process is typically completed within 1–2 months, depending on the workload of the Trademark Office.
3. Costs Involved in Trademark Renewal
- The renewal fees for individuals, startups, and small businesses are typically ₹4,500 for e-filing and ₹5,000 for physical filing.
- For companies, LLPs, and other organizations, the renewal fees are ₹9,000 for e-filing and ₹10,000 for physical filing.
By renewing your trademark on time, you ensure continued protection and exclusive rights to your brand name and logo in India. Regular renewal is key to maintaining the integrity of your intellectual property and protecting your business identity.
Hence, trademark registration in India is essential for businesses aiming to protect their intellectual property and strengthen their brand presence. Registering a trademark provides exclusive rights to your brand name, logo, or symbol, preventing unauthorized use and offering legal protection. The trademark registration process is simple, starting with a trademark search, followed by filing an application and addressing any objections or oppositions. Renewing your trademark ensures ongoing protection and secures your brand’s identity for years to come. With trademark registration in India, businesses, whether startups or established companies, can build trust, create valuable assets, and safeguard their brand in the competitive market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Trademark Registration in India
1. Is trademark registration mandatory in India?
No, trademark registration is not mandatory in India. However, registering your trademark provides several benefits, such as legal protection, exclusive rights to use the mark, and the ability to take legal action in case of infringement. It also prevents others from using a similar mark and adds value to your brand by enhancing its credibility.
2. Who can apply for trademark registration in India?
Any individual, business entity, or legal entity claiming to be the proprietor of the trademark can apply for registration. The application can be filed either on a “used” or “proposed to be used” basis. Trademark applications can be filed online through the official IP India portal or at one of the regional trademark offices located in Delhi, Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Kolkata, or Chennai.
3. What are the benefits of trademark registration in India?
Trademark registration offers exclusive rights to use the trademark for the registered goods or services. It protects your brand from unauthorized use, provides legal backing in case of infringement, and allows you to use the ™ and ® symbols. It also enhances brand recognition and helps in building a trustworthy reputation in the market.
4. How long does it take to register a trademark in India?
Trademark registration in India typically takes between 8-15 months. This duration may vary depending on the complexity of the case and whether any objections or oppositions are raised during the process. If there are no complications, registration is usually completed within this time frame.
5. What documents are required for trademark registration in India?
Key documents required include a clear representation of the trademark (logo or wordmark), proof of business registration, identity and address proof (e.g., PAN, Aadhaar), and relevant certificates (for startups or small enterprises). If filing through an agent, a Power of Attorney may also be required.
6. How much does trademark registration cost in India?
The trademark registration fee varies based on the type of applicant. For individuals, startups, and small enterprises, the fee is ₹4,500 for e-filing and ₹5,000 for physical filing. For others, the fee is ₹9,000 for e-filing and ₹10,000 for physical filing. Additional professional fees may apply if you choose to hire legal assistance.
7. Where do I apply for trademark registration in India?
Trademark registration applications can be submitted online through the official IP India website or filed at one of the regional trademark offices in Delhi, Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Kolkata, or Chennai. E-filing provides instant acknowledgment, while physical filing may take 15-20 days to receive acknowledgment.
8. Why should I register my trademark if it’s not mandatory?
Although not mandatory, trademark registration offers several advantages, including legal protection, exclusive rights to your mark, and the ability to use the ® symbol. It also boosts your brand’s credibility and safeguards your intellectual property against infringement.
9. What is the typical timeline for trademark registration in India?
Trademark registration generally takes 8-15 months in uncomplicated cases. However, if objections or oppositions arise, the process may take longer due to the need to resolve these issues.
10. How can I check the status of my trademark registration application?
You can easily check the status of your trademark registration online through the IP India website. It will provide updates on the status of your application, including any objections or progress on its approval.
11. What are common reasons for the refusal of trademark registration?
Trademarks may be refused on absolute grounds if they are too generic, descriptive, offensive, or conflict with an already registered trademark. Marks that lack distinctiveness or mislead the public may also face rejection by the authorities.
12. How do I renew my trademark in India?
Trademark registration in India is valid for 10 years. To renew your trademark, you need to file a renewal application before the expiry date and pay the renewal fee. Renewing your trademark on time ensures continued protection of your intellectual property rights.


The Importance of Trademark Registration in India
Blog Content Overview
In today’s competitive business landscape, protecting intellectual property is crucial for building a strong brand and maintaining a competitive edge. Trademark registration is one of the most effective ways to safeguard your brand’s identity, ensuring that it remains unique and protected from infringement. In India, where the economy is booming with startups, small businesses, and large corporations alike, understanding the importance of trademark registration is paramount.
What is a Trademark?
A trademark is a unique symbol, word, phrase, logo, design, or combination thereof that identifies and distinguishes the goods or services of one entity from others. It is a vital aspect of branding and helps create a distinct identity in the minds of consumers.
For instance, iconic logos like the golden arches of McDonald’s or the swoosh of Nike are registered trademarks that symbolize their respective brands globally. Similarly, Indian brands like Tata, Reliance, and Flipkart rely heavily on trademarks to maintain their market dominance and consumer trust.
Why is Trademark Registration Important in India?
1. Legal Protection Against Infringement
Trademark registration provides legal protection under the Trademarks Act, 1999. If another business attempts to use your registered trademark without authorization, you can take legal action against them. This protection ensures that your brand’s identity remains intact and safeguarded.
2. Exclusive Rights
A registered trademark grants the owner exclusive rights to use the trademark for the goods or services it represents. It also prevents competitors from using similar marks that could confuse consumers.
3. Brand Recognition and Goodwill
A trademark acts as an asset that enhances brand recognition and builds consumer trust. Over time, a strong trademark becomes synonymous with quality and reliability, which contributes to long-term goodwill.
4. Market Differentiation
In a saturated market, a trademark helps distinguish your products or services from those of competitors. It establishes your brand’s unique identity and strengthens customer loyalty.
5. Asset Creation
A registered trademark is an intangible asset that can be sold, licensed, or franchised. This adds financial value to your business, making it an attractive proposition for investors or partners.
6. Global Expansion
Trademark registration in India can serve as the foundation for international trademark registration under treaties like the Madrid Protocol. This is especially important for businesses planning to expand globally.
Consequences of Not Registering a Trademark
Failure to register a trademark can expose your business to several risks:
- Risk of Infringement: Without registration, proving ownership of a trademark becomes challenging.
- Brand Dilution: Competitors might use similar marks, leading to loss of distinctiveness and consumer trust.
- Limited Legal Remedies: Unregistered trademarks are harder to defend in court.
- Missed Opportunities: A lack of trademark protection can hinder global expansion plans.
Steps to Register a Trademark in India
- Trademark Search: Conduct a thorough search to ensure that the trademark is unique and not already registered by someone else.
- Application Filing: Submit a trademark application with the necessary details, including the logo, class of goods or services, and owner details.
- Examination: The Trademark Registry examines the application to ensure compliance with legal requirements.
- Publication: The trademark is published in the Trademark Journal to invite objections, if any.
- Registration Certificate: If no objections are raised, or if objections are resolved, the trademark is registered, and a certificate is issued.
Costs and Duration
Trademark registration in India is a cost-effective process. The official fees depend on the nature of the applicant, with reduced fees for startups, individuals, and small businesses. The registration process typically takes 12-18 months, but the protection is valid for 10 years and can be renewed indefinitely.
Key Industries Benefiting from Trademark Registration
- E-commerce and Retail: Trademarks protect brand identity in a highly competitive digital marketplace.
- Pharmaceuticals: Ensures safety and trust by preventing counterfeit products.
- Technology Startups: Safeguards innovations and unique business models.
- Food and Beverage: Builds trust and loyalty through distinctive branding.
Conclusion
Trademark registration is not just a legal formality but a strategic move to protect and enhance your brand’s value. In a thriving economy like India, securing a trademark ensures that your brand stands out, builds trust, and enjoys long-term growth.
Investing in trademark registration today is a step toward safeguarding your business’s future. Don’t wait for competitors to claim what’s rightfully yours. Secure your brand’s identity and take it to new heights with the power of trademarks. If you’re ready to register your trademark or need expert guidance, reach out to Treelife for a consultation today.


Trademark Classification in India – Goods & Service Class Codes
Blog Content Overview
- 1 Introduction to Trademarks
- 2 Background of Trademarks in India
- 3 What is a Trademark Class?
- 4 Importance of Trademark Classification
- 5 Trademark Classification List
- 6 List of Trademark Classes of Goods in India (1-34 Classes)
- 7 List of Trademark Classes of Services in India (35-45 Classes)
- 8 Online Tools available for Classifying Trademarks
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 FAQs on Trademark Classification in India
- 10.0.1 2. How are goods and services categorized under trademark classification?
- 10.0.2 3. Why is trademark classification essential during the registration process?
- 10.0.3 4. Can a trademark be registered under multiple classes?
- 10.0.4 5. What tools are available for trademark classification in India?
- 10.0.5 6. How does trademark classification help prevent legal conflicts?
- 10.0.6 7. What is the significance of the NICE classification system?
- 10.0.7 8. What are the benefits of correct trademark classification?
Introduction to Trademarks
A trademark is a unique term, symbol, logo, design, phrase, or a combination of these elements that distinguishes a business’s products or services from those of its competitors in the market. Trademarks can take the form of text, graphics, or symbols and are commonly used on company letterheads, service banners, publicity brochures, and product packaging. By creating a distinct identity, trademarks play a vital role in building customer trust, enhancing brand recognition, and establishing a competitive edge.
As a form of intellectual property, a trademark grants its owner the exclusive rights to use the registered term, symbol, or design. No other individual, company, or organization can legally use the trademark without the owner’s consent. If unauthorized use occurs, the trademark owner can take legal action under the Trade Marks Act of 1999.
Registering your trademark as per trademark classification not only safeguards your brand identity but also prevents third parties from using it without authorization. It is a straightforward process in India, allowing businesses to protect their intellectual property and ensure their products or services stand out in the market.
Trademarks are categorized into various classes based on the goods or services they represent. Understanding the classification system is crucial to ensure proper protection. In this article, we will explore the legal framework for trademarks, the classification system, and the online tools available to identify the correct trademark class for your registration.
Background of Trademarks in India
The Trade Marks Registry, established in 1940, administers trademark regulations under the Trademarks Act of 1999 in India. This Act aims to protect trademarks, regulate their use, and prevent infringement. Registering a trademark is essential for businesses to safeguard their name, reputation, and goodwill, as well as to strengthen brand identity and build customer trust. Trademarks can be in the form of graphics, symbols, text, or a combination, commonly used on letterheads, service banners, brochures, and product packaging to stand out in the market.
The Trade Marks Registry has offices in Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Chennai, Delhi, and Kolkata to handle trademark applications. To apply for protection, businesses must classify their products or services under the NICE Classification (10th edition), a global system that ensures clarity in trademark registration.
The importance of trademark classification was emphasized in the Nandhini Deluxe v. Karnataka Co-operative Milk Producers Federation Ltd. (2018) case, where the Supreme Court clarified that visually distinct trademarks for unrelated goods or services are not “deceptively similar” and may be registered, even if they fall under the same class.
What is a Trademark Class?
Trademark classes are the categories into which goods and services are classified under the NICE Classification (NCL), an internationally recognized system created by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). This classification system is essential for businesses seeking trademark registration, as it ensures that each trademark application accurately reflects the nature of the goods or services it represents.
Types of Trademark Classes
The NICE Classification divides goods and services into 45 distinct trademark classes:
- Goods: Classes 1 to 34.
Goods type trademark classes, numbered 1 to 34, categorize products based on their nature. 1 This classification system helps businesses protect their brands by ensuring clear identification and preventing confusion in the marketplace. - Services: Classes 35 to 45.
Trademark classes 35-45 are dedicated to services, ranging from advertising and business management to education, healthcare, and legal services.
Each class represents a specific category of goods or services. For example: Class 13 for Firearms and explosives. Class 36 for Financial and insurance services.
How to Choose the Right Trademark Class?
When filing a trademark application, the applicant must carefully select the correct class that corresponds to the goods or services their business offers. This choice is crucial for avoiding potential trademark infringement and conducting effective trademark searches. During the trademark registration process, specifying the trademark classes or categories of products and services for which the trademark will be used is essential. It defines the mark and determines its usage in the industry, acting as an identifier for the mark. Choosing the right category and classification for a trade name is highly beneficial. The applicant can also apply for protection of the same mark under multiple classes if applicable.
Services are typically identified from the alphabetical list provided, using the divisions of operations indicated in the headers and their explanatory notes. For instance, rental facilities are categorized in the same class as the rented items.
Multiple Classes for Comprehensive Protection
Applicants can file for trademark protection under multiple classes if their goods or services span across different categories. For example, a business dealing in both clothing (Class 25) and retail services (Class 35) should register under both classes to ensure complete coverage.
Importance of Trademark Classification
The significance of a trademark class search to safeguarding a business’ intellectual property and brand cannot be overstated. In 2018, the Hon’ble Supreme Court highlighted the significance of categorizing trademarks under different classes in a landmark case involving the popular dairy brand “Nandhini Deluxe”1 in Karnataka. The court observed that two visually distinct and different marks cannot be called deceptively similar, especially when they are used for different goods and services. The Court also concluded that there is no provision of law that expressly prohibits the registration of a trademark which is similar to an existing trademark used for dissimilar goods, even when they fall under the same class.
Benefits of Classification
- Preventing Conflicts: Using a trademark class search makes it easier to find already-registered trademarks that could clash with your intended mark. This averts any legal conflicts and expensive lawsuits.
- Registration Success: You increase the likelihood of a successful registration by classifying your trademark correctly. The possibility of being rejected by the trademark office is reduced with an appropriate categorization.
- Protection of Brand Identity: You may operate with confidence knowing that your brand is protected within your industry by registering it in the correct class.
- Market Expansion: When your company develops, you may use a well-classified trademark to launch additional goods and services under the same way.
Trademark Classification List
The trademark class list consists of two types :-
- Trademark Classification for Goods
- Trademark Classification for Services
1. Trademark Classification for Goods
This trademark registration class of goods contains 34 classes.
- If a final product does not belong in any other class, the trademark is categorized according to its function and purpose.
- Products with several uses can be categorized into various types based on those uses.
- The categories list is classified according to the mode of transportation or the raw materials if the functions are not covered by other divisions.
- Based on the substance they are composed of, semi-finished goods and raw materials are categorised.
- When a product is composed of many components, it is categorized according to the substance that predominates.
2. Trademark Classification for Services
This trademark registration class of services contains 10 classes.
- The trademark class for services is divided into branches of activity. The same categorization applies to rental services.
- Services connected to advice or consultations are categorized according to the advice, consultation, or information’s subject.
Search Trademark Classes in India
List of Trademark Classes of Goods in India (1-34 Classes)
| Trademark Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Trademark Class 1 | Chemicals used in industry, science, and photography. |
| Trademark Class 2 | Paints, varnishes, lacquers, and preservatives against rust. |
| Trademark Class 3 | Cleaning, polishing, scouring, and abrasive preparations. |
| Trademark Class 4 | Industrial oils, greases, and fuels (including motor fuels). |
| Trademark Class 5 | Pharmaceuticals and other preparations for medical use. |
| Trademark Class 6 | Common metals and their alloys, metal building materials. |
| Trademark Class 7 | Machines, machine tools, and motors (except vehicles). |
| Trademark Class 8 | Hand tools and implements, cutlery, and razors. |
| Trademark Class 9 | Scientific, photographic, and measuring instruments. |
| Trademark Class 10 | Medical and veterinary apparatus and instruments. |
| Trademark Class 11 | Apparatus for lighting, heating, and cooking. |
| Trademark Class 12 | Vehicles and parts thereof. |
| Trademark Class 13 | Firearms and explosives. |
| Trademark Class 14 | Precious metals and jewelry. |
| Trademark Class 15 | Musical instruments. |
| Trademark Class 16 | Paper, stationery, and printed materials. |
| Trademark Class 17 | Rubber, gutta-percha, and plastics in extruded form. |
| Trademark Class 18 | Leather and imitation leather goods. |
| Trademark Class 19 | Non-metallic building materials. |
| Trademark Class 20 | Furniture and furnishings. |
| Trademark Class 21 | Household utensils and containers. |
| Trademark Class 22 | Ropes, string, nets, and tarpaulins. |
| Trademark Class 23 | Yarns and threads for textile use. |
| Trademark Class 24 | Textiles and textile goods. |
| Trademark Class 25 | Clothing, footwear, and headgear. |
| Trademark Class 26 | Lace, embroidery, and decorative textiles. |
| Trademark Class 27 | Carpets, rugs, mats, and floor coverings. |
| Trademark Class 28 | Toys, games, and sporting goods. |
| Trademark Class 29 | Meat, fish, poultry, and other food products. |
| Trademark Class 30 | Coffee, tea, spices, and other food products. |
| Trademark Class 31 | Agricultural, horticultural, and forestry products. |
| Trademark Class 32 | Beers, mineral waters, and soft drinks. |
| Trademark Class 33 | Alcoholic beverages (excluding beers). |
| Trademark Class 34 | Tobacco, smokers’ articles, and related products. |
List of Trademark Classes of Services in India (35-45 Classes)
| Trademark Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Trademark Class 35 | Business management, advertising, and consulting services. |
| Trademark Class 36 | Financial, banking, and insurance services. |
| Trademark Class 37 | Construction and repair services. |
| Trademark Class 38 | Telecommunications services. |
| Trademark Class 39 | Transport, packaging, and storage services. |
| Trademark Class 40 | Treatment of materials and manufacturing services. |
| Trademark Class 41 | Education, training, and entertainment services. |
| Trademark Class 42 | Scientific and technological services, including IT. |
| Trademark Class 43 | Food, drink, and temporary accommodation services. |
| Trademark Class 44 | Medical, beauty, and agricultural services. |
| Trademark Class 45 | Legal services, security services, and social services. |
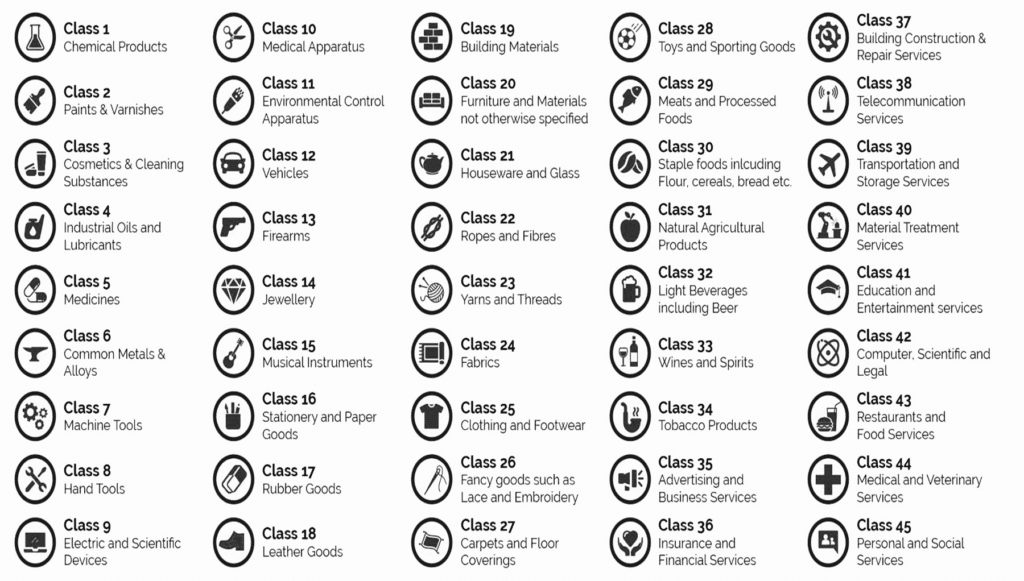

Online Tools available for Classifying Trademarks
Classifying products and services accurately is a crucial step in the trademark registration process in India. Several reliable online tools are available to simplify the trademark categories listing process:
- NICE Classification Tool: Developed by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), this tool provides a comprehensive guide to the classification of goods and services under the NICE system.
- TMclass Tool: Offered by the European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO), TMclass helps users determine the appropriate trademark class for their goods or services with ease.
Trademark classification is vital for the Trademark Registry to understand the scope of the trademark, its market segment, and the target audience it aims to address. It establishes the trademark’s value in the competitive market and serves as a unique identifier for the registrant.
Conclusion
Trademark classification is a foundational step in the trademark registration process, ensuring that a business’s intellectual property is accurately categorized and effectively protected. By adhering to the NICE classification system, businesses can prevent conflicts, enhance brand identity, and expand their market presence with confidence. Proper classification streamlines the registration process, minimizes legal risks, and safeguards brand equity. As trademarks play a pivotal role in defining a company’s market presence, leveraging expert guidance for classification is vital for long-term success.
FAQs on Trademark Classification in India
1. What is trademark classification, and why is it important?
Trademark classification is a system that organizes goods and services into 45 specific categories under the NICE classification. It is essential for ensuring accurate registration, avoiding conflicts, and securing protection for a business’s intellectual property in its relevant industry.
2. How are goods and services categorized under trademark classification?
Goods fall under the first 34 classes, and services fall under classes 35 to 45. The classification is based on the function, purpose, or material of the goods and the activity or purpose of the services.
3. Why is trademark classification essential during the registration process?
Proper classification:
- Helps prevent conflicts by identifying existing trademarks that may clash with the new mark.
- Ensures the trademark application is correctly filed, reducing the likelihood of rejection.
- Protects brand identity by categorizing trademarks accurately within their industry.
4. Can a trademark be registered under multiple classes?
Yes, businesses can register their trademark under multiple classes if their goods or services span across different categories. This ensures comprehensive protection.
5. What tools are available for trademark classification in India?
The following online tools are helpful:
- NICE Classification Tool by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).
- TMclass Tool by the European Union Intellectual Property Office.
6. How does trademark classification help prevent legal conflicts?
By conducting a trademark class search, businesses can identify existing trademarks in the same category and avoid conflicts, reducing the risk of legal disputes and costly lawsuits.
7. What is the significance of the NICE classification system?
The NICE classification, created by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), standardizes the categorization of goods and services worldwide. It streamlines trademark registration processes and ensures consistency.
8. What are the benefits of correct trademark classification?
- Prevention of Conflicts: Avoids disputes by identifying existing trademarks in the same class.
- Enhanced Brand Identity: Safeguards the brand within its industry.
- Streamlined Registration: Increases the likelihood of successful trademark registration.
- Market Expansion: Facilitates the introduction of new products and services under the same brand.
9. What happens if someone infringes my registered trademark?
- You can take legal action to stop the infringement and seek damages.
- Registration makes legal enforcement easier and more effective.
10. Where can I find more information and resources on trademark registration?
- The Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trademarks website: https://ipindia.gov.in/
- Start-up India resources: https://www.startupindia.gov.in/
- Consult a trademark attorney for personalized guidance.
References:
- [1] Nandhini Deluxe v Karnataka Co-operative Milk Producer Federation Ltd. 2018 (9) SCC 183
↩︎
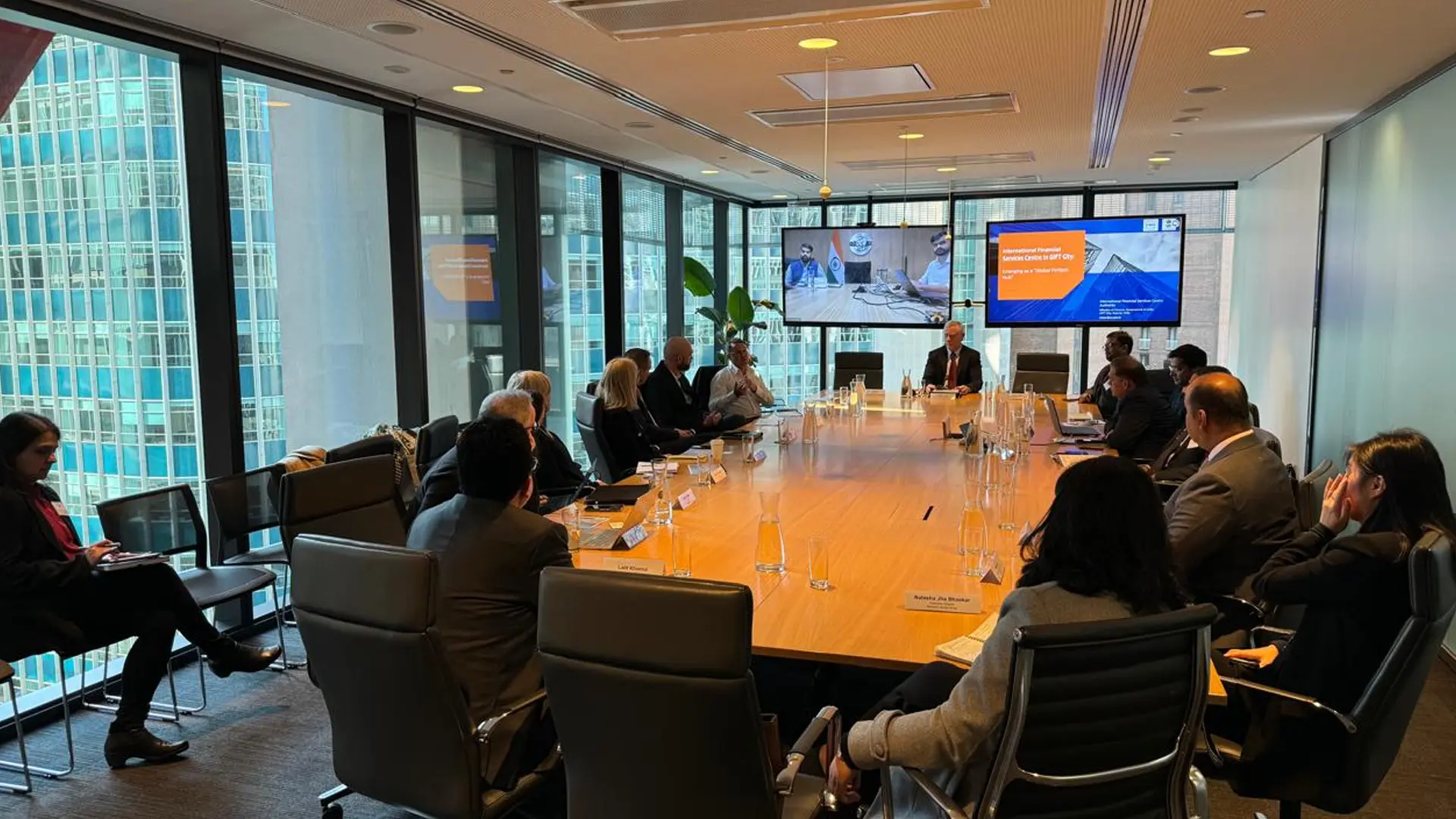


IFSCA releases consultation paper seeking comments on draft circular on “𝑷𝒓𝒊𝒏𝒄𝒊𝒑𝒍𝒆𝒔 𝒕𝒐 𝒎𝒊𝒕𝒊𝒈𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝑹𝒊𝒔𝒌 𝒐𝒇 𝑮𝒓𝒆𝒆𝒏𝒘𝒂𝒔𝒉𝒊𝒏𝒈 𝒊𝒏 𝑬𝑺𝑮 𝒍𝒂𝒃𝒆𝒍𝒍𝒆𝒅 𝒅𝒆𝒃𝒕 𝒔𝒆𝒄𝒖𝒓𝒊𝒕𝒊𝒆𝒔 𝒊𝒏 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝑰𝑭𝑺𝑪”
IFSCA listing regulations requires debt securities to adhere to international standards/principles to be labelled as “𝐠𝐫𝐞𝐞𝐧”, “𝐬𝐨𝐜𝐢𝐚𝐥”, “𝐬𝐮𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐚𝐛𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐭𝐲” 𝐚𝐧𝐝 “𝐬𝐮𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐚𝐛𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐭𝐲-𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐤𝐞𝐝” 𝐛𝐨𝐧𝐝.
As of September 30, 2024, the IFSC exchanges boasted a listing of approximately USD 14 billion in ESG-labelled debt securities, a significant chunk of the total USD 64 billion debt listings in a short period. This rapid growth highlights the growing appetite for sustainable investments among global investors.
Certain investors, particularly institutional ones like pension funds and socially responsible investment (SRI) funds, explicitly state in their investment mandates that they can only invest in ESG-labeled securities. To encourage and promote ESG funds, the IFSCA has waived fund filing fees for the first 10 ESG funds registered at GIFT-IFSC, to incentivise fund managers to launch ESG-focused funds.
However, this rapid growth also comes with a significant risk of “greenwashing” where companies or funds exaggerate or falsely claim their environmental and sustainability efforts.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 “𝐆𝐫𝐞𝐞𝐧𝐰𝐚𝐬𝐡𝐢𝐧𝐠”?
However, with this rapid growth comes a significant risk: greenwashing. Greenwashing occurs when companies or funds exaggerate or fabricate their environmental and sustainability efforts to project a greener image and attract investors. It’s essentially a deceptive marketing tactic that undermines the true purpose of sustainable investing.
IFSCA’s Consultation Paper: Mitigating Greenwashing
Recognizing the threat of greenwashing, the IFSCA has released a consultation paper seeking public comment on a draft circular titled “Principles to Mitigate the Risk of Greenwashing in ESG labelled debt securities in the IFSC.” This circular outlines principles that companies and funds issuing ESG-labelled debt securities on the IFSC platform must adhere to.
Refer link for consultation paper: https://ifsca.gov.in/ReportPublication?MId=8kS3KLrLjxk=
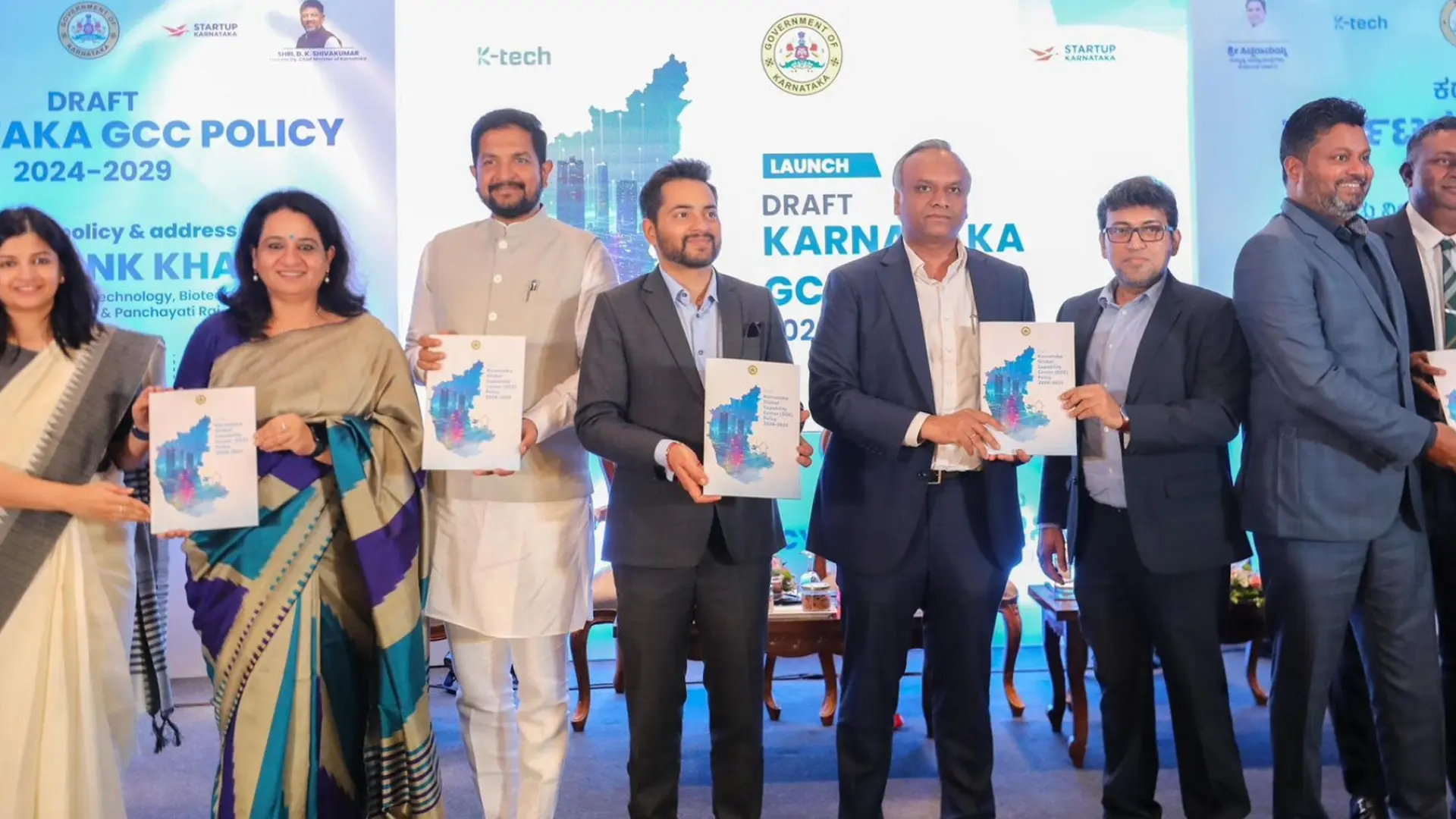


Karnataka’s Global Capability Centres Policy: A Game Changer for India’s Tech Landscape
Karnataka, a state in India known for its vibrant tech industry, has recently unveiled its Global Capability Centres (GCC) Policy 2024-2029. This ambitious policy aims to solidify Karnataka’s position as a leading hub for GCCs in India and propel the state’s tech ecosystem to even greater heights.
What are Global Capability Centres (GCCs)?
For those unfamiliar with the term, GCCs are specialized facilities established by companies to handle various strategic functions. These functions can encompass a wide range of areas, including:
- Information Technology (IT) services
- Customer support
- Research and development (R&D)
- Analytics
By setting up GCCs, companies can streamline operations, reduce costs, and tap into a pool of talented professionals. This allows them to achieve their global objectives more efficiently.
Why is Karnataka a Major Hub for GCCs?
India is a powerhouse for GCCs, boasting over 1,300 such centers. Karnataka takes the lead in this domain, housing nearly 30% of India’s GCCs and employing a staggering 35% of the workforce in this sector. Several factors contribute to Karnataka’s attractiveness for GCCs:
- Vast Talent Pool: Karnataka is home to some of India’s premier educational institutions, churning out a steady stream of highly skilled graduates in engineering, technology, and other relevant fields.
- Cost-Effectiveness:India offers a significant cost advantage for setting up and operating GCCs, compared to other global locations.
Key Highlights of Karnataka’s GCC Policy 2024-2029
The recently unveiled GCC Policy outlines a series of ambitious goals and initiatives aimed at propelling Karnataka to the forefront of the global GCC landscape. Here are some of the key highlights:
- Establishment of 500 New GCCs: The policy sets a target of establishing 500 new GCCs in Karnataka by 2029. This aggressive target signifies the government’s commitment to significantly expanding the state’s GCC footprint.
- Generating $50 Billion in Economic Output: The policy envisions generating a staggering $50 billion in economic output through GCCs by 2029. This substantial economic contribution will be a boon for Karnataka’s overall development.
- Creation of 3.5 Lakh Jobs: The policy aims to create 3.5 lakh (350,000) new jobs across Karnataka through the establishment and operation of new GCCs. This significant job creation will provide immense opportunities for the state’s workforce.
- Centre of Excellence for AI in Bengaluru: Recognizing the growing importance of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the policy proposes establishing a Centre of Excellence for AI in Bengaluru. This center will focus on driving research, development, and innovation in the field of AI, fostering a robust AI ecosystem in Karnataka.
- AI Skilling Council: The policy acknowledges the need to equip the workforce with the necessary skills to thrive in the AI-driven future. To address this, the policy proposes the creation of an AI Skilling Council. This council will be responsible for developing and delivering AI-related training programs, ensuring Karnataka’s workforce is well-prepared for the jobs of tomorrow.
- INR 100 Crore Innovation Fund: The policy establishes an INR 100 crore (approximately $12.3 million) Innovation Fund. This fund will support joint research initiatives between academia and GCCs, fostering a collaborative environment that fuels innovation and technological advancements.
The GCC Policy has a clear and ambitious goal: for Karnataka to capture 50% of India’s GCC market share by 2029. Read more about the policy here.


Major Boost for Reverse Flipping: Indian Startups Coming Home
In recent years, a significant number of Indian startups have chosen to incorporate their businesses outside India, primarily in locations like Delaware, Singapore and other global locations. This trend, known as “flipping,” offered advantages like easier access to foreign capital and tax benefits. However, the tide is starting to turn. We’re witnessing a growing phenomenon of “reverse flipping,” where these startups are now shifting their bases back to India.
This shift back home is driven by several factors, including a booming Indian market, attractive stock market valuations, and a desire to be closer to their target audience – Indian customers. To further incentivize this homecoming, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) has recently introduced a significant policy change.
MCA Streamlines Cross-border Mergers for Reverse Flipping
The MCA has amended the Companies (Compromises, Arrangements, and Amalgamations) Rules, 2016, to streamline the process of cross-border mergers. This move makes it easier for foreign holding companies to merge with their wholly-owned Indian subsidiaries, facilitating a smooth transition for startups seeking to return to their roots.
Key Takeaways of the Amended Rules
Here’s a breakdown of the key benefits for startups considering a reverse flip through this streamlined process:
- Fast-Track Mergers: The Indian subsidiary can file an application under Section 233 read with Rule 25 of the Act. This rule governs “fast-track mergers,” which receive deemed approval if the Central Government doesn’t provide a response within 60 days.
- RBI Approval: Both the foreign holding company and the Indian subsidiary need prior approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for the merger.
- Compliance with Section 233: The Indian subsidiary, acting as the transferee company, must comply with Section 233 of the Companies Act, which outlines the requirements for fast-track mergers.
- No NCLT Clearance Required: This streamlined process eliminates the need for clearance from the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT), further reducing time and complexity.
The Road Ahead
The MCA’s move represents a significant positive step for Indian startups looking to return home. This policy change, coupled with a thriving domestic market, is likely to accelerate the trend of reverse flipping. This not only benefits returning companies but also strengthens the overall Indian startup ecosystem, fostering innovation and entrepreneurial growth within the country.


IFSCA’s Single Window IT System (SWIT): A Game Changer for Businesses in GIFT City
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s recent launch of the IFSCA’s Single Window IT System (SWIT) marks a significant milestone for businesses looking to set up operations in India’s International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) at GIFT City. This unified digital platform promises to revolutionize the ease of doing business in this burgeoning financial hub.
What is the IFSC and Why is SWIT Important?
The International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) was established to develop a world-class financial center in India. Located in Gujarat’s GIFT City, the IFSC aims to attract international financial institutions and businesses by offering a global standard regulatory environment. However, setting up operations in the IFSC previously involved navigating a complex web of approvals from various regulatory bodies, including IFSCA itself, the SEZ authorities, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), and the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI). This process could be time-consuming and cumbersome for businesses.
SWIT: Streamlining the Application Process
The SWIT platform addresses this challenge by creating a one-stop solution for all approvals required for setting up a business in GIFT IFSC. Here’s how SWIT simplifies the process:
- Single Application Form: Businesses no longer need to submit separate applications to various authorities. SWIT provides a unified form that captures all the necessary information.
- Integrated Approvals: SWIT integrates with relevant regulatory bodies – RBI, SEBI, and IRDAI – for obtaining No Objection Certificates (NOCs) seamlessly.
- SEZ Approval Integration: The platform connects with the SEZ Online System for obtaining approvals from the SEZ authorities managing GIFT City.
- GST Registration: SWIT facilitates easy registration with the Goods and Services Tax (GST) authorities.
- Real-time Validation: The system verifies PAN, Director Identification Number (DIN), and Company Identification Number (CIN) in real-time, ensuring data accuracy.
- Integrated Payment Gateway: Applicants can make payments for various fees and charges directly through the platform.
- Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) Module: The platform enables users to obtain and manage DSCs, a crucial requirement for online submissions.
Benefits of SWIT for Businesses
The introduction of SWIT offers several advantages for businesses considering the IFSC:
- Reduced Time and Cost: By consolidating the application process into a single platform, SWIT significantly reduces the time and cost involved in obtaining approvals.
- Enhanced Transparency: SWIT provides a transparent and user-friendly interface that allows businesses to track the progress of their applications in real-time.
- Improved Ease of Doing Business: This makes GIFT City a more attractive proposition for global investors and businesses.
Looking Ahead: The Future of GIFT City
The launch of SWIT is a significant step forward in positioning GIFT City as a leading international financial center. By streamlining the application process and promoting ease of doing business, SWIT paves the way for increased investment and growth in the IFSC. This, in turn, will contribute to India’s ambition of becoming a global financial hub.


Sovereign Green Bonds in the IFSC
Blog Content Overview
In recent years, the global investment landscape has shifted dramatically, with sustainability becoming a central theme in financial markets. As nations and corporations commit to net-zero emissions, innovative financial instruments are emerging to facilitate this transition. One of the most promising of these instruments is Sovereign Green Bonds (SGrBs). Recently, the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) in India introduced a scheme for trading and settlement of SGrBs in the Gujarat International Finance Tec-City International Financial Services Centre (GIFT IFSC), marking a significant step towards attracting foreign investment into the country’s green infrastructure projects.
Understanding Sovereign Green Bonds
SGrBs are debt instruments issued by a government to raise funds specifically for projects that have positive environmental or climate benefits. The proceeds from these bonds are earmarked for green initiatives, such as renewable energy projects, energy efficiency improvements, and sustainable infrastructure development. As global awareness of climate change grows, SGrBs are gaining traction as a viable investment option for those seeking to align their portfolios with sustainable development goals.
The Role of IFSCA
The IFSCA’s initiative to facilitate SGrBs in the GIFT IFSC is a strategic move that aligns with India’s commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2070. The GIFT IFSC has been designed as a global financial hub, offering a regulatory environment that supports international business and financial services. By introducing SGrBs, the IFSCA aims to create a robust platform for sustainable finance in India.
Key Features of the IFSCA’s SGrB Scheme
1. Eligible Investors
The IFSCA’s scheme allows a diverse range of investors to participate in the SGrB market. Eligible investors include:
- Non-residents investors from jurisdictions deemed low-risk can invest in these bonds.
- Foreign Banks’ International Banking Units (IBUs): These entities, which do not have a physical presence or business operations in India, can also invest in SGrBs.
2. Trading and Settlement Platforms: The IFSCA has established electronic platforms through IFSC Exchanges for the trading of SGrBs in primary markets. Moreover, secondary market trading will be facilitated through Over-the-Counter (OTC) markets.
3. Enhancing Global Capital Inflows: One of the primary objectives of introducing SGrBs in the GIFT IFSC is to enhance global capital inflows into India. With the global community increasingly prioritizing sustainable investment opportunities, India stands to benefit significantly from the influx of foreign capital. The availability of SGrBs provides a unique opportunity for investors looking to contribute to environmental sustainability while achieving financial returns.
The IFSCA’s introduction of SGrBs in the GIFT IFSC is a forward-thinking initiative that aligns with global sustainability goals. By facilitating access for non-resident investors and creating robust trading platforms, India is positioning itself as a leader in sustainable finance. As the world moves toward a greener future, the role of SGrBs will become increasingly important. For investors, these bonds not only represent a chance to achieve financial returns but also to make a meaningful impact on the environment.














